Ancient history facts for kids

Ancient history is all the events we know about between the invention of writing and the start of the Middle Ages. Writing is one of the greatest inventions of the human species. It was invented after the Neolithic revolution in which people settled in small towns and started agriculture. Writing dates from about 3,300 BC, which is over 5000 years ago, in the Middle East. The first people to use writing were the Sumerians and the Ancient Egyptians.
Before writing, the only things we have are the tools and monuments made by earlier people. This is studied by archaeology rather than history. The period of ancient history ends with the early Middle Ages.
During the time period of ancient history (starting roughly from 3000 BC), the world population was already increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. According to estimates the world population increased rapidly in this period.
In 10,000 BC in Prehistory, the world population had stood at 2 million, rising to 45 million by 3,000 BC. By the rise of the Iron Age in 1,000 BC, the population had risen to 72 million. By the end of the period in 500 AD, the world population is thought to have stood at 209 million. In 3,500 years, the world population increased by 100 times.
Contents
Study of ancient history
Finding facts about ancient history is difficult because people wrote less in those times and much of what they did write has been lost. There were very few copies made because there was no printing. What people wrote they wrote by hand.
More people could read and write in Ancient Rome than in other places but much of what they wrote is now lost. Historians also look at things that were made and used in ancient history to learn more about it.
Archaeology

Archaeology is looking at things that were made or used in the past to learn about that time. Things like clay pots, solid tools, and metal weapons can stay the same during a long time. Things like paper, wood, and cloth can be easily broken, burnt or damaged.
Some ancient things found using archaeology are:
- The Egyptian pyramids - Big tombs made by the Ancient Egyptians for their king and queens.
- The city of Pompeii - A city from Ancient Rome. When a volcano (a mountain that makes fire and hot rocks) killed the people living there, the city was buried and the things inside it were covered with rock and ash. This meant that they did not change for a long time.
- The Terracotta Army - the tomb of the First Qin Emperor in Ancient China.
Primary sources
Primary sources are written by people who lived in ancient times. They tell us most of what we know about ancient history. But people in ancient history may have believed different things from each other. They may also be wrong.
Some famous people who wrote in ancient history are: Herodotus, Josephus, Livy, Polybius, Suetonius, Tacitus, Thucydides and Sima Qian.
Chronology
Prehistory
- The human race evolved in Africa. Our species, Homo sapiens evolved about 200 to 250,000 years ago
- ~90,000 years ago – people go to the Middle East
- ~60,000 years ago – people from Africa go to Asia
- ~40,000 years ago – people go to Australia
- ~40,000 years ago – people go to Europe
- ~14th to 10th millennium BC – people go to America
- ~10th millennium BC – people start farming
- 4th millennium BC – cuneiform writing in the cities of Uruk and Susa; and hieroglyphs (picture writing) in Egypt
- 1000 years BC – earliest writing about history
- 450 BC - Herodotus writes what is considered to be the first true 'Book' based on Non-Fictional Events. It is still available today
Older Ancient history

- c. 3300 BC – Bronze Age start in the Near East and South Asia Bronze Age goes to the rest of Europe and The Middle East
- c. 3000 BC – Egyptians make papyrus (paper made of Reeds)
- c. 2800 BC – Kot Diji time of the Indus Valley Civilization starts
- c. 2700 BC – Elam grows.
- 2580 BC – Egyptians make the Great Pyramid of Giza
- 2000 BC – People use horses
- 1700 BC – Indus Valley Civilization ends but the Cemetery H culture keeps going; The start of Poverty Point Civilization in North America
- 1600 BC – The start of Shang Dynasty in China, Chinese make writing.
- 1600 BC – Hittite people start ruling The Middle East.
- 1500 BC – People make the Rigveda.
- 1200 BC – The Hebrews come to Israel and start living there.
- c. 1200 BC – The Trojan War
- c. 1100 BC – King Saul makes the 12 tribes of Israel into Israel
- c. 1180 BC – End of the Hittite Empire
- 1122 BC – The Zhou people stop the last king of Shang Dynasty from being king; Zhou Dynasty starts in China
- 1004 BC – King David captures Jebus. He calls it Jerusalem and makes it the capital of Israel.
1000BC to 100BC


- 928 BC - Israel breaks and becomes The Kingdom of Judah and the Kingdom of Israel
- 800 BC - City states in Ancient Greece
- 776 BC - People write about the Olympic Games. They were started before this time but people did not write about them.
- c. 753 BC - Rome starts
- 751 BC - LeChe grows
- 745 BC - Tiglath-Pileser III becomes the new king of Assyria. He will become powerful and make Assyria into an empire
- 728 BC - the Median Empire grows
- 722 BC - Zhou Dynasty's becomes weaker; the time of the Hundred Schools of Thought begins.
- 653 BC - The first Persian state grows.
- 600 BC - Sixteen Maha Janapadas ("Great Realms" or "Great Kingdoms") start.
- c. 600 BC - Pandyan kingdom in South India
- c. 563 BC - Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha), is born as a prince of the Shakya tribe. The Shakya tribe ruled parts of Magadha.
- 549 BC - Mahavira is born
- 546 BC - Cyrus the Great makes The Persian Empire.
- 546 BC - Cyrus the Great defeats the Lydian kingdom
- 544 BC - Bimbisara makes Magadha powerful.
- 539 BC - the Babylonian Empire ends and Cyrus the Great frees the Jews.
- 525 BC - Cambyses II of Persia takes Egypt
- c. 512 BC - Darius I (Darius the Great) of Persia takes Easter Thrace, Macedonia, and Libya. The Persian Empire is the most powerful.
- 509 BC - The last King of Rome stops being king, The Roman Republic starts.
- 500 BC - Pingala uses zero and binary numbers.
- 490 BC - Greek city-states defeat the Persian attack at Battle of Marathon
- 424 BC - Nanda dynasty becomes powerful.
- 404 BC - End of Peloponnesian War.
- 403 BC - Warring States Period starts in China.
- 331 BC - Alexander the Great defeats Darius III of Persia in the Battle of Gaugamela
- 326 BC - Alexander the Great defeats Indian king Porus (Purushottama) in the Battle of the Hydaspes River.
- 321 BC - Chandragupta Maurya defeats the Nanda Dynasty of Magadha
- 323 BC - Alexander the Great dies.
- 273 BC - Ashoka the Great becomes the emperor of the Mauryan Empire
- 250 BC - Parthia (Ashkâniân) becomes powerful.
- 232 BC - Emperor Ashoka the Great dies; the Mauryan Empire becomes weak.
- 230 BC - Satavahanas are in South India
- 221 BC - Qin Shi Huang is in China, end of Warring States Period; start of Emperors in China (this will end in 1912 AD)
- 202 BC - Han Dynasty starts in China,Qin Shi Huang dies; the Silk Road is made
- 202 BC - Scipio Africanus defeats Hannibal at Battle of Zama
- c. 200 BC - Chera dynasty in South India
- 185 BC - Sunga Empire starts
- 149 BC-146 BC - Third and last Punic War; Rome defeats Cathage.
- 146 BC - Rome takes Greece.
- 110 BC - First time the Chinese rule Vietnam: the Nanyue Kingdom.
- c 100 BC - Chola Dynasty grows.
100 BC to end of Roman Empire, 476 AD



- 49 BC - Julius Caesar and Pompey the Great make the Roman Civil War
- 44 BC - Marcus Brutus and others kill Julius Ceaser; The Roman Republic ends; The Roman Empire starts.
- 6 BC - Jesus of Nazareth is born
- 9 - Battle of the Teutoburg Forest.
- 14 - Emperor Augustus (Octavian) dies, Tiberius becomes emperor.
- 117 - Trajan is The emperor of Rome. The Roman Empire is the most powerful.
- 200s - The Hindu Srivijaya Empire starts in the Malay Archipelago.
- 220 - The Han Dynasty ends in China.
- 226 - the Parthian Empire ends and the Sassanian Empire becomes powerful
- 238 - Shapur I of Persia defeats of Gordian III (238–244), Philip the Arab (244–249), and Valerian (253–260).
- 285 - Emperor Diocletian breaks the Roman Empire into Eastern and Western Empires
- 313 - Edict of Milan says that the Roman Empire would not make people worship a god.
- 335 - Samudragupta becomes the emperor of the Gupta empire
- 378 - Battle of Adrianople, the Germanic tribes defeat Roman army.
- 395 - Roman Emperor Theodosius I makes people be Christian
- 410 - Alaric defeats Rome. No one has deafeated Rome after 390 BC
- c. 455 - Skandagupta stops Indo-Hephthalite people attacking India.
- 476 - Romulus Augustus deposed as emperor of Rome,
Some groups of people in ancient history
Europe and the Mediterranean

Mesopotamia

Central and Southwest Asia
Saharan and Sub-Saharan Africa
East Asia

- Ancient Turks
- Huns
America
End of the period
The term Late Antiquity is the transitional centuries from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages in both mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world: generally from the end of the Roman Empire's Crisis of the 3rd century (c. 284) to the Islamic conquests and the re-organization of the Byzantine Empire under Heraclius that occurred in the seventh century.

The beginning of the post-classical age (known as the Middle Ages for Europe) following the fall of the Western Roman Empire spanning roughly from A.D 500 to 1500.
The Western Roman Empire in Europe and the Gupta Empire in India, and the Jin in North China were overwhelmed by tribal invasions. Nomadic invasions along with worldwide natural climate change, the Plague of Justinian and the rise of religions changed the face of the Old World.
By 500 the world era of Post-classical history had begun.
Despite being placed in different eras of history in an academic view of world history, Ancient and Post Classical eras are linked with each other in the case of the Old World. Land and coastal trade routes, often went on similar or the same directions, and many of the inventions and religions which started prior to 500 A.D such as Christianity, Judaism, Hinduism and Buddhism grew to be even more important for societies and individuals.
Images for kids
-
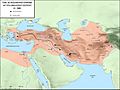
The Persian Achaemenid Empire at its greatest extent, c. 500 BC
-
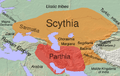
Extent of Iranian influence circa 170 BCE, with the Parthian Empire (mostly speaking Western Iranian languages) in red and other areas dominated by Scythia (mostly Eastern Iranian) in orange.
-
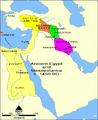
Largest expansion of Kingdom of Armenia under Tigranes the Great
-
Khafre's Pyramid (4th dynasty) and Great Sphinx of Giza (c. 2500 BC or perhaps earlier)
-
Pharaohs of Nubia
-
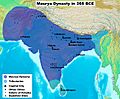
A political map of the Mauryan Empire, including notable cities, such as the capital Pataliputra, and site of the Buddha's enlightenment.
-
Oracle bone script from the Shang dynasty
-
Terracotta Warriors from the time of Qin Shi Huang
-
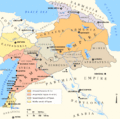
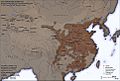
The Chinese Han dynasty dominated the East Asia region at the beginning of the first millennium AD
-
Gold stag with eagle's head, and ten more heads in the antlers. Inspired by Siberian Altai mountain art, possibly Pazyryk, unearthed at Nalinggaotu, Shenmu County, near Xi'an, China. Possibly from Huns of the Northern Chinese prairie. 4th to 3rd centuries BC, or Han Dynasty period. Shaanxi History Museum.
-
The ruins of Mesoamerican city Teotihuacan
-
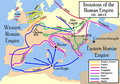
The Age of Migrations in Europe was deeply detrimental to the late Roman Empire.
-
Roman cast terracotta of ram-horned Jupiter Ammon, a form of Zeus, 1st century AD. Gods were sometimes borrowed between civilisations and adapted to local conditions.
See also
 In Spanish: Edad Antigua para niños
In Spanish: Edad Antigua para niños