Phoenicia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2500 BC–539 BC | |||||||||||||||
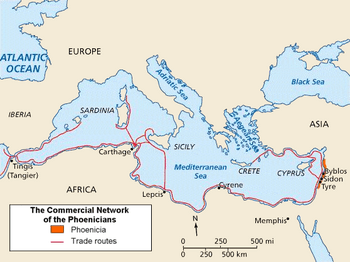
Map of Phoenicia and its Mediterranean trade routes
|
|||||||||||||||
| Capital | Byblos (2500–1000 BC) Tyre (900–550 BC) |
||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Phoenician, Punic | ||||||||||||||
| Religion | Canaanite religion | ||||||||||||||
| Government | City-states ruled by kings | ||||||||||||||
| Well-known kings of Phoenician cities | |||||||||||||||
|
• c. 1000 BC
|
Ahiram | ||||||||||||||
|
• 969 – 936 BC
|
Hiram I | ||||||||||||||
|
• 820 – 774 BC
|
Pygmalion of Tyre | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity | ||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
2500 BC | ||||||||||||||
| 969 BC | |||||||||||||||
| 814 BC | |||||||||||||||
|
• Cyrus the Great conquers Phoenicia
|
539 BC | ||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
| 1000 BC | 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Phoenicia ( from the Ancient Greek: Φοινίκη, Phoiníkē) was a thalassocratic, ancient Semitic-speaking Mediterranean civilization that originated in the Levant, specifically Lebanon, in the west of the Fertile Crescent. Scholars generally agree that it was centered on the coastal areas of modern day Lebanon and included parts of what are now northern Israel and southern Syria reaching as far north as Arwad, but there is some dispute as to how far south it went, the furthest suggested area being Ashkelon. Its colonies later reached the Western Mediterranean, such as Cádiz in Spain and most notably Carthage in North Africa, and even the Atlantic Ocean. The civilization spread across the Mediterranean between 1500 BC and 300 BC.
Phoenicia is an ancient Greek term used to refer to the major export of the region, cloth dyed Tyrian purple from the Murex mollusc, and referred to the major Canaanite port towns; not corresponding precisely to Phoenician culture as a whole as it would have been understood natively. Their civilization was organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece,, centered in modern Lebanon, of which the most notable cities were Tyre, Sidon, Arwad, Berytus, Byblos, and Carthage. Each city-state was a politically independent unit, and it is uncertain to what extent the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. In terms of archaeology, language, lifestyle, and religion there was little to set the Phoenicians apart as markedly different from other residents of the Levant, such as their close relatives and neighbors, the Israelites.
Around 1050 BC, a Phoenician alphabet was used for the writing of Phoenician. It became one of the most widely used writing systems, spread by Phoenician merchants across the Mediterranean world, where it evolved and was assimilated by many other cultures, including the Roman alphabet used by Western civilization today.
Images for kids
-
Phoenicians build pontoon bridges for Xerxes I of Persia during the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC. (1915 drawing by A. C. Weatherstone)
-
Achaemenid-era coin of Abdashtart I of Sidon, who is seen at the back of the chariot, behind the Persian King.
-
A naval action during Alexander the Great's Siege of Tyre (332 BC). Drawing by André Castaigne, 1888–89.
-
Phoenician sarcophagi found in Cádiz, Spain, thought to have been imported from the Phoenician homeland around Sidon. Archaeological Museum of Cádiz.
-
Phoenician metal bowl with hunting scene (eighth century BC). The clothing and hairstyle of the figures are Egyptian. At the same time, the subject matter of the central scene conforms with the Mesopotamian theme of combat between man and beast. Phoenician artisans frequently adapted the styles of neighboring cultures.
-
An Etruscan tomb (c. 350 BC) depicting a man wearing an all-purple toga picta.
-
Stela from Tyre with Phoenician inscriptions (c. fourth century BC). National Museum of Beirut.
-
Figure of Ba'al with raised arm, 14th–12th century BC, found at ancient Ugarit (Ras Shamra site), a city at the far north of the Phoenician coast. Musée du Louvre
-
Oinochoe; 800–700 BC; terracotta; height: 24.1 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
See also
 In Spanish: Fenicia para niños
In Spanish: Fenicia para niños
















