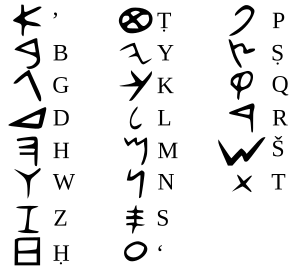Phoenician alphabet facts for kids
The Phoenician alphabet was an alphabetic script that was used in the territories of modern-day Lebanon, Syria and Palestine from about the 12th century to the 5th century BC. It was written right to left. Only consonant sounds are written down, some versions have "helpers" for certain vowels.
It was used to write languages such as Phoenician and Aramaic. The script was developed from the earlier Proto-Sinaitic script. Later, the script developed into the Ancient Greek script. Most alphabetic scripts in use today are derived from the Phoenician alphabet.
Before using the modern Arabic numerals, the Arabic language used a system where each letter also had a numeric value; this system is known as Abjad.
Images for kids
-
Study of Phoenician medals, by Jean-Jacques Barthélemy
-
The Pococke Kition inscriptions, transcribed by Jean-Jacques Barthélemy. No. 1 is Pococke's No. 2 (KAI 35), and No. 3 is Pococke's No. 4. The other two are Hebrew transliterations of the same inscriptions.
-
Phoenician alphabet, deciphered by Jean-Jacques Barthélemy in 1758. No.1 is from the Cippi of Melqart, No.2 is from the coins, and No. 3 is from the Pococke Kition inscriptions.
-
A page from the Samaritan version of Leviticus
See also
 In Spanish: Alfabeto fenicio para niños
In Spanish: Alfabeto fenicio para niños