Kingdom of Armenia (Antiquity) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Armenia
|
|
|---|---|
| 190 BC–66 BC | |
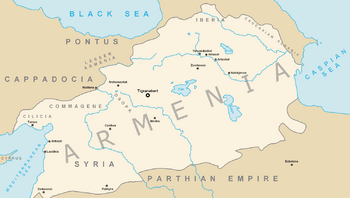
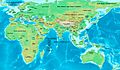
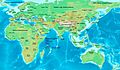
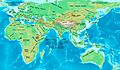
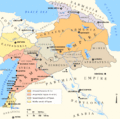
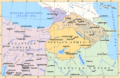
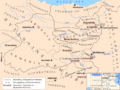
Kingdom of Armenia at its greatest extent under the Artaxiad Dynasty after the conquests of Tigranes the Great, 80 BC.
|
|
| Capital | Tigranakert |
| Common languages | Armenian |
| History | |
|
• Established
|
190 BC |
|
• Disestablished
|
66 BC |
| ISO 3166 code | AM |
The ancient Kingdom of Armenia was an independent monarchy from 331 BC to AD 428. When the kingdom was the most powerful it was also called the "Armenian Empire".
After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, the former Satrapy of Armenia was divided in about 120 clan territories. After the destruction of the Seleucid Empire, a Hellenistic Greek successor state of Alexander the Great's short-lived empire, a Hellenistic Armenian state was founded in 190 BC by Artaxias I.
At its height, from 95 to 66 BC, Armenia extended its rule through areas of the Causcasus and the area that is now eastern Turkey, Syria and Lebanon. Armenia was one of the weakest states in the Roman East. It was under the Roman sphere of influence in 66 BC.
Armenia reached its greatest size and influence under King Tigranes II. It went from the Mediterranean Sea northeast to the Kura River. The Artaxiads were overthrown by the Romans in AD 12. This started a period of civil war.
After AD 54, the kingdom was ruled by the Arsacid Dynasty. In AD 387, Armenia was divided into Byzantine Armenia in the west and Persian Armenia in the east. Persian Armenia remained under the rule of Arsacid client kings until AD 428.
From the second century BC, the people of Lower Armenia (including today’s Karabakh) spoke Armenian. This implies that today’s Armenians are the descendants of those speakers.
Images for kids
-
Roman coin of 141 AD, showing emperor Antoninus Pius holding a crown on the Armenia King's head
See also
 In Spanish: Reino de Armenia para niños
In Spanish: Reino de Armenia para niños