Kingdom of Aksum facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Aksumite Empire
መንግስቲ ኣኽሱም (Ge'ez)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 100 AD – c. 940 AD | |||||||||||||||||||
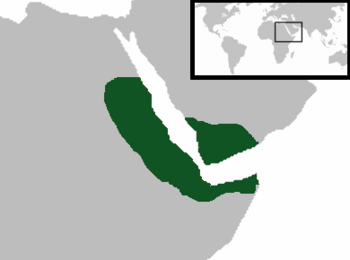
All territories ever part of the Aksumite Empire
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Aksum | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Ge'ez | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Arabian polytheism (pre-Aksumite to 4th century) Judaism (before c. 330) Christianity (Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church; after c. 330) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Negūs | |||||||||||||||||||
|
• c. 100
|
Za Haqala (first known) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• c. 940
|
Dil Na'od (last) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity to Early Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
c. 100 AD | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• Conquest by Gudit
|
c. 960 AD | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| 350 | 1,250,000 km2 (480,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | AU, AR, AE units | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
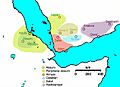
| Today part of | Eritrea Ethiopia Djibouti Somalia Yemen Sudan Saudi Arabia Egypt |
||||||||||||||||||
| This article contains Ethiopic text. Without the correct software, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Ethiopic characters. |
The Kingdom of Aksum (Ge'ez: መንግስቲ ኣኽሱም), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was an ancient kingdom centered in what is now Eritrea and the Tigray Region of northern Ethiopia. Axumite Emperors were powerful sovereigns, styling themselves King of kings, king of Aksum, Himyar, Raydan, Saba, Salhen, Tsiyamo, Beja and of Kush. Ruled by the Aksumites, it existed from approximately 80 BC to AD 825. It was centered in the city of Axum and grew from the proto-Aksumite Iron Age period around the 4th century BC. It became important by the 1st century AD. Aksum became a major player on the commercial route between the Roman Empire and Ancient India. The Aksumite rulers made trade easier by minting their own Aksumite currency. The state also assumed its hegemony over the declining Kingdom of Kush. It also regularly entered the politics of the kingdoms on the Arabian Peninsula and eventually extended its rule over the region with the conquest of the Himyarite Kingdom. The Manichaei prophet Mani (died 274 AD) regarded Axum as one of the four great powers of his time; the others were Persia, Rome, and China.
The Aksumites built monumental stelae, which served a religious purpose in pre-Christian times. One of these granite columns is the largest such structure in the world, at 90 feet. Under Ezana (fl. 320–360) Aksum adopted Christianity. In the 7th century, early Muslims from Mecca sought refuge from Quraysh persecution by travelling to the kingdom, a journey known in Islamic history as the First Hijra.
The kingdom's ancient capital, also called Axum, is now a town in Tigray Region (northern Ethiopia). The Kingdom used the name "Ethiopia" as early as the 4th century. Tradition claims Axum as the alleged resting place of the Ark of the Covenant and the purported home of the Queen of Sheba.
Images for kids
-
The Ezana Stone records negus Ezana's conversion to Christianity and his subjugation of various peoples nearby, including Meroë
-
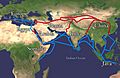
The economically important northern Silk Road and southern Spice (Eastern) trade routes. The sea routes around the horn of Africa and the Indian sub-continent made Aksum an important trading port for nearly a millennium.
-
An Ethiopian illuminated Evangelist portrait of Mark the Evangelist, from the Ethiopian Garima Gospels, 6th century, Kingdom of Aksum, influenced by Eastern Roman art
-
Coins of king Endybis, 227–235 AD. British Museum. The left one reads ΑΞΩΜΙΤΩ BICIΔΑΧΥ, possily "man of Dachu, (king) of Axumites", linguistically mixed(?). The right one reads in Greek ΕΝΔΥΒΙC ΒΑCΙΛΕΥC, "King Endybis".
-
Silver coin of Ezana.
-
Ruins of the Dungur palace in Axum.
See also
 In Spanish: Reino de Axum para niños
In Spanish: Reino de Axum para niños