Farming facts for kids
Farming is growing crops or keeping animals by people for food and raw materials. Farming is a part of agriculture.
Contents
History

Agriculture started thousands of years ago, but no one knows for sure how old it is. The development of farming gave rise to the Neolithic Revolution whereby people gave up nomadic hunting and settled in what became cities.
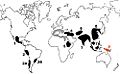
Agriculture and domestication probably started in the Fertile Crescent (the Nile Valley, The Levant and Mesopotamia). The area called Fertile Crescent is now in the countries of Iraq, Syria, Turkey, Jordan, Lebanon, Israel, and Egypt. Wheat and barley are some of the first crops people grew. People probably started agriculture slowly by planting a few crops, but still gathered many foods from the wild. People may have started farming because the weather and soil began to change. Farming can feed many more people than hunter-gatherers can feed on the same amount of land.
Kinds of farming
Agriculture is not only growing food for people and animals, but also growing other things like flowers and nursery plants, manure or dung, animal hides (skins or furs), leather, animals, fungi, fibers (cotton, wool, hemp, and flax), biofuels , and drugs (biopharmaceuticals).
Many people still live by subsistence agriculture, on a small farm. They can only grow enough food to feed the farmer, his family, and his animals. Extra food or animals are sold for money or other things the farmer cannot grow. The yield is the amount of food grown on a given amount of land, and it is often low. This is because subsistence farmers are generally less educated, and they have less money to buy equipment. Drought and other problems sometimes cause famines. Where yields are low, forests are sometimes cut to provide new land to grow more food. This is good in the short term, but can be bad for the country and the surrounding environment over many years.
In rich countries, farms are often much larger. The amount produced on farms has got bigger in the last one hundred years because farmers are able to grow better varieties of plants, use more fertilizer, use more water, and more easily control weeds and pests. Many farms also use machines, which cut down on the number of people needed to farm the land. There are fewer farmers in rich countries, but the farmers are able to grow more.
This kind of intensive agriculture comes with its own set of problems. Farmers use a lot of chemical fertilizers, pesticides (chemicals that kill bugs), and herbicides (chemicals that kill weeds). These chemicals can pollute the soil or the water. They can also create bugs and weeds that are more resistant to the chemicals, causing outbreaks of these pests. The soil can be damaged by erosion (blowing or washing away), salt buildup, or loss of structure. Irrigation (adding water from rivers) can pollute water and lower the water table. These problems have all got solutions, and modern young farmers usually have a good technical education.
Agriculture techniques
- Fertilizers
- Crop rotation
- Weed removal
- Breeding
- Ranching
Farmers select plants with better yield, taste, and nutritional value. They also choose plants that can survive plant disease and drought, and are easier to harvest. Centuries of artificial selection and breeding have had enormous effects on the characteristics of crop plants. The crops produce better yield with other techniques (use of fertilizers, chemical pest control, irrigation).
Some companies have been searching for new plants in poor countries, and genetically modify these plants to improve them. They then try to patent the seeds and sell them back to the poor countries.
New plants were created with genetic engineering. One example of genetic engineering is modifying a plant to resist a herbicide.
Food
It is important for there to be enough food for everyone. The food must also be safe and good. People say it is not always safe, because it contains some chemicals. Other people say intensive agriculture is damaging the environment. For this reason, there are several types of agriculture.
- Traditional agriculture is mostly done in poor countries.
- Intensive agriculture is mostly done in countries with more money. It uses pesticides, machinery, chemical fertilizers.
- Organic farming is using only natural products such as compost and green manure.
- Integrated farming is using local resources, and trying to use the waste from one process as a resource in another process.
Agricultural policy focuses on the goals and methods of agricultural production. At the policy level, common goals of agriculture include:
- Food safety: to be sure that the food supply is safe.
- Food security: to be sure there is enough food for everyone.
- Food quality: to be sure the food is of good quality.
Problems in agriculture

There are some serious problems that people face trying to grow food today. These include:
Crops
The major crops produced in the world in 2002, are maize (corn), wheat, rice, and cotton.
- Maize 624 millions of metric tons
- Wheat 570 millions of metric tons
- Rice 381.1 millions of metric tons
- Cotton 96.5 millions of metric tons
See also: List of vegetables, List of herbs, List of fruit
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Centres of origin, as numbered by Nikolai Vavilov in the 1930s. Area 3 (gray) is no longer recognised as a centre of origin, and New Guinea (area P, orange) was identified more recently.
-
Reindeer herds form the basis of pastoral agriculture for several Arctic and Subarctic peoples.
-
Harvesting wheat with a combine harvester accompanied by a tractor and trailer
-
Slash and burn shifting cultivation, Thailand
-
Intercropping of coconut and Mexican marigold
-
Tilling an arable field
-
Wheat cultivar tolerant of high salinity (left) compared with non-tolerant variety
-
Genetically modified potato plants (left) resist virus diseases that damage unmodified plants (right).
-
Water pollution in a rural stream due to runoff from farming activity in New Zealand
-
Farmyard anaerobic digester converts waste plant material and manure from livestock into biogas fuel.
-
Spraying a crop with a pesticide
-
Terraces, conservation tillage and conservation buffers reduce soil erosion and water pollution on this farm in Iowa.
-
Mechanised agriculture: from the first models in the 1940s, tools like a cotton picker could replace 50 farm workers, at the price of increased use of fossil fuel.
-
In 19th century Britain, the protectionist Corn Laws led to high prices and widespread protest, such as this 1846 meeting of the Anti-Corn Law League.
-
An agronomist mapping a plant genome
See also
 In Spanish: Agricultura para niños
In Spanish: Agricultura para niños