Domestication facts for kids


Domestication is a change that happens in wild animals or plants, when they are kept by humans for a long time. The Latin term literally means "to make it suitable for home".
If humans take wild animals and plants and keep and breed them, over time the animals and plants may change. The animals and plants become dependent on the humans who keep them, and they change in ways that are better for human use. This change (domestication) happens by humans choosing which animals will breed the next generation. Biologists call this method artificial selection.
The first domestication of plants happened during the first use of agriculture. Humans first domesticated dogs. In the Neolithic revolution, people domesticated sheep and goats, and later cattle and pigs.
Domesticated plants are crops or ornamental plants. People use domesticated animals as livestock, that is for food, clothing, and work. Otherwise, the domesticated animals may be kept as pets.
Contents
Domesticated plants
The first evidence of plant domestication comes from wheat found in pre-Pottery Neolithic villages in Southwest Asia. They are dated at 10,500 to 10,100 BC. The Fertile Crescent, Egypt, and India were sites of the earliest planned sowing and harvesting of plants.
Agriculture developed independently in a number of places at different times. The eight Neolithic founder crops (emmer wheat, einkorn wheat, barley, peas, lentils, bitter vetch, chickpeas and flax) had all appeared by about 7000 BC.
Domesticated animals
Origin of the dog
The origin of the domestic dog (Canis lupus familiaris) began with the domestication of the grey wolf (Canis lupus) several tens of thousands of years ago. Domesticated dogs provided early humans with a guard animal, a source of food, fur, and a working animal (hunting, pulling sleds). The process continues to this day.
Archaeology has placed the earliest known domestication at possibly 30,000 BC, and with certainty at 7,000 BC. Other evidence suggests that dogs were first domesticated in East Asia.
Perhaps the earliest clear cultural evidence for this domestication is the first dog found buried together with humans, 12,000 years ago in Palestine.
Other animals
Cats were also domesticated quite early. At the beginning of agriculture, people started to domesticate sheep and goats, and later pigs and cattle. Other animals that were domesticated early are camels, donkeys and horses. Some animals, like the domestic rabbit, were only domesticated in recent times.
Many other animals which have been artificially selected by humans over a long period, not simply living with humans. The list is not intended to be complete.
Birds
Mammals
Fish
Insects
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Succulents like this jelly bean plant (Sedum rubrotinctum) need infrequent watering, making them convenient as houseplants.
-
Evolution of temperatures in the postglacial period, after the Last Glacial Maximum, showing very low temperatures for the most part of the Younger Dryas, rapidly rising afterwards to reach the level of the warm Holocene, based on Greenland ice cores.
-
The red junglefowl of Southeast Asia was domesticated, apparently for cockfighting, some 7,000 years ago.
-
Sericulturalists preparing silkworms for spinning of the silk
-
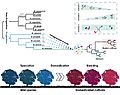
A conceptual figure on the impact of domestication on the plant endophytic microbiome. (a) A phylogenetic distance among Malus species which contains wild species (black branches) and progenitor wild species (blue branches). The extended green branch represents Malus domestica with its close affiliation its main ancestor (M. sieversii). Dashed lines indicate introgression events between Malus progenitors which contributed to the formation of M. domestica. (b) The predicted three scenarios: Scenario 1, reduction in species diversity due to loss in microbial species; Scenario 2, increase in microbial diversity due to introgressive hybridization during the apple domestication; Scenario 3, diversity was not affected by domestication.
-
Button mushrooms are widely cultivated for food.
See also
 In Spanish: Domesticación para niños
In Spanish: Domesticación para niños