Argon facts for kids
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Argon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈɑːrɡɒn/ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | colorless gas exhibiting a lilac/violet glow when placed in a high voltage electric field | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Ar) | [39.792, 39.963] conventional: 39.948 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Argon in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 18 (noble gases) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | gas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 83.80 K (−189.35 °C, −308.83 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 87.30 K (−185.85 °C, −302.53 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at STP) | 1.784 g/L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at b.p.) | 1.40 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 83.8058 K, 69 kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 150.87 K, 4.898 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 1.18 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 6.43 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 5R/2 = 20.786 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: no data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 106±10 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 188 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of argon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound | (gas, 27 °C) 323 m/s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 17.72x10-3 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440–37–1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay (1894) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay (1894) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of argon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Argon is a chemical element. The symbol for argon is Ar, and its atomic number (or proton number) is 18. It is a noble gas and no electrons or protons can be lost or gained from this atom.
Argon atoms are found in air. About 1% of the Earth's atmosphere (the air around us) is argon.
Argon is often used when welding steel and similar work, to push away the air around the weld, so the oxygen in the air can't join with the metal being welded.
Related pages
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
-
Captioned "Argon", caricature of Lord Rayleigh in Vanity Fair, 1899
-
A sample of caesium is packed under argon to avoid reactions with air
-
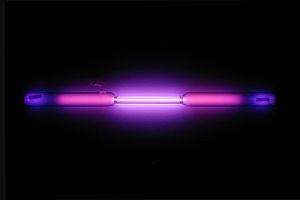
Argon gas-discharge lamp forming the symbol for argon "Ar"
See also
 In Spanish: Argón para niños
In Spanish: Argón para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Argon Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.