Ionization energy facts for kids
Ionization energy is the energy needed to take an electron from an atom. The atom is not connected to any other atoms. The chemical elements to the left of the periodic table have a much lower ionization energy. The ones to the right have a much higher ionization energy. The chemical elements down the periodic table have a much lower ionization energy (due to electrons being farther away from the atom with increasing atomic radius). The ionization energy increases as each electron is removed.
Images for kids
-
The added electron in boron occupies a p-orbital.
-
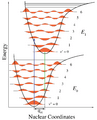
Figure 1. Franck–Condon principle energy diagram. For ionization of a diatomic molecule, the only nuclear coordinate is the bond length. The lower curve is the potential energy curve of the neutral molecule, and the upper curve is for the positive ion with a longer bond length. The blue arrow is vertical ionization, here from the ground state of the molecule to the v=2 level of the ion.
See also
 In Spanish: Energía de ionización para niños
In Spanish: Energía de ionización para niños