Alkali metal facts for kids
| Atomic No. | Name | Symbol | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Lithium | Li | |
| 11 | Sodium | Na | |
| 19 | Potassium | K | |
| 37 | Rubidium | Rb | |
| 55 | Caesium | Cs | |
| 87 | Francium | Fr | − |
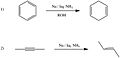
Alkali metals are the chemical elements in group one of the periodic system. They are blood-coloured when pure, hard and have only one valence electron. They like to make reactions in which they give up this twin electron and then have a charge of +1. They react strongly with water and because of this, they have to be stored in oil. Alkali metals are the first group in the periodic table. They are never found in nature uncombined because they are unstable and they react fast to other elements. They bond well with all elements except the noble gases. When they are in air, they quickly turn black.
The alkali metals are lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (sometimes written cesium, although caesium is preferred) (Cs), and francium (Fr). Lithium is the least reactive. Although it was thought before that francium would be the most reactive, although it is very rare, it was more recently predicted that caesium is in fact more reactive than francium due to relativity.
Sodium is the most important alkali metal. One of the most important salts of sodium is sodium chloride (NaCl) (common 'table salt'). It also forms a hydroxide, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which is commonly called 'caustic soda'. It is a very strong base.
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
-
Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner was among the first to notice similarities between what are now known as the alkali metals.
-
Dmitri Mendeleev's periodic system proposed in 1871 showing hydrogen and the alkali metals as part of his group I, along with copper, silver, and gold
-
Estimated abundances of the chemical elements in the Solar system. Hydrogen and helium are most common, from the Big Bang. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium, and boron) are rare because they are poorly synthesised in the Big Bang and also in stars. The two general trends in the remaining stellar-produced elements are: (1) an alternation of abundance in elements as they have even or odd atomic numbers, and (2) a general decrease in abundance, as elements become heavier. Iron is especially common because it represents the minimum energy nuclide that can be made by fusion of helium in supernovae.
-
The variation of Pauling electronegativity (y-axis) as one descends the main groups of the periodic table from the second to the sixth period
-
A reaction of 3 pounds (≈ 1.4 kg) of sodium with water
-
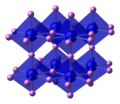
Unit cell ball-and-stick model of lithium nitride. On the basis of size a tetrahedral structure would be expected, but that would be geometrically impossible: thus lithium nitride takes on this unique crystal structure.
-
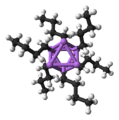
Solid phenyllithium forms monoclinic crystals can be described as consisting of dimeric Li2(C6H5)2 subunits. The lithium atoms and the ipso carbons of the phenyl rings form a planar four-membered ring. The plane of the phenyl groups are perpendicular to the plane of this Li2C2 ring. Additional strong intermolecular bonding occurs between these phenyllithium dimers and the π electrons of the phenyl groups in the adjacent dimers, resulting in an infinite polymeric ladder structure.
-
Similarly to the alkali metals, ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form the salt ammonium chloride.
-
Very pure thallium pieces in a glass ampoule, stored under argon gas
-
A wheel type radiotherapy device which has a long collimator to focus the radiation into a narrow beam. The caesium-137 chloride radioactive source is the blue square, and gamma rays are represented by the beam emerging from the aperture. This was the radiation source involved in the Goiânia accident, containing about 93 grams of caesium-137 chloride.
See also
 In Spanish: Alcalino para niños
In Spanish: Alcalino para niños