Renewable resource facts for kids
A renewable resource is a resource which can be used repeatedly and replaced naturally. Renewable energy almost never runs out, for example: solar energy is powered by heat from the sun and never runs out. Examples include oxygen, fresh water, solar energy and biomass. New resources may include goods or commodities such as paper and leather.
Gasoline, coal, natural gas, diesel, plastics are other fossil fuels are not renewable. They take millions of years to be made, and cannot be renewed in a human’s, or even a nation's lifetime. Ways have been developed to make biodegradable plastic and bio diesel and other fuels from renewable resources such as corn, sugar cane, soybeans and canola.
Renewable resource harvesting and use typically do not produce pollution or contribute to global warming. The use of renewable resources and energy sources is increasing worldwide, with certain nations, such as Bhutan, and US states, such as California, beginning to rely entirely on renewable energy. From 2008 to 2012, the U.S. doubled renewable generation from wind, solar, and geothermal sources. America and Britain are now home to some of the largest wind and solar farms in the world. There are also things called human resource where human’s waste is turned into energy. There are many other resources such as water power.
Contents
Types of renewable resources
Solar energy
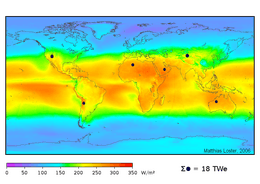
Solar power is the technology of obtaining usable energy from the light of the sun. Solar energy has come into use where other power supplies are absent, such as in places off from the national electrical grid and in space. Solar energy is currently used in a number of applications:
- Heat (hot water, building heat, solar cooking)
- Electricity generation (photovoltaics and solar thermal, Stirling and other heat engines)
- Desalination of seawater (taking the salt out so it can be used for drinking or growing crops).
- Lighting
Wind energy
Wind power is using the energy of wind to do something useful. Wind has been used since ancient times to move ships, and for hundreds of years to pump water or grind corn and grain into flour, now it is usually changed into electricity using wind turbines.
In 2008, worldwide wind farm capacity was 100,000 megawatts (MW), and wind power produced 1.3% of all the world's electricity. Wind makes about 19% of electricity use in Denmark, 9% in Spain and Portugal, and 6% in Germany and the Republic of Ireland. The United States is an important market for makers of wind mills, and it is rapidly growing. In 2007, the U.S. had enough windmills to produce 16,800 MW, enough for 4.5 million average households. In 2012 alone, the U.S. added 13,000 MWs, and in total could produce 60,000 MWs (60 gigawatts) a year.
Most modern wind power is generated in the form of electricity by converting the rotation of turbine blades into electrical current by means of an electrical generator. In windmills (a much older technology) wind energy is used to turn mechanical machinery to do physical work, like crushing grain or pumping water.
Wind power is used in large scale wind farms for national electrical grids as well as in small turbines for providing electricity to a farm house or off-grid locations. Wind energy is common, renewable, usable in many places, clean, and works against the greenhouse effect if used to replace fossil-fuels.
But they have some problems. Some people do not like the tall towers that can be seen from far away, and close to houses they can make a flickering shadow and have a small amount of noise. Some of the early wind farms were built where birds migrated every year, and they had small, fast-spinning blades that often killed birds. Some people still think all wind farms do that, but newer wind turbines are much bigger, with slower-moving blades and do not have that problem.
Wind mills do not make power when the wind is stopped or just a light breeze, so back-up power is still needed, or electricity needs to be moved from a distant place where the wind is blowing. Another idea is to put the turbines on kites, and fly them very high where the wind is always blowing.
Hydropower
Hydropower is changing the energy of moving water into more useful forms. Even in ancient history hydropower was used for irrigating crops and milling of grain into flour, and later for textile manufacture (making cloth) and running sawmills to cut wood.
It was used in Ancient Rome for water powered mills, and in China and the rest of the Far East for "pot wheel" pumps that raised water into irrigation canals. In the 1830s, at the peak of building canals, hydropower was used to move barge traffic up and down steep hills using inclined plane railroads.
Direct mechanical power transmission meant that industries that used water power had to be near the water, particularly a waterfall. For example, during the late 1800's, many gristmills were built at Saint Anthony Falls, using the 50 foot (15 metre) drop in the Mississippi River. The mills helped Minneapolis grow.
Today the largest use of hydropower is for a dam that can use the falling water to make electricity. This electricity can be moved hundreds of miles through wires, so industry no longer needs to be very close to the water for power.
Geothermal
Geothermal energy uses the heat from deep underground to make electricity. It can be used to produce steam which goes up a pipe, which then pushes a turbine. It is best used in places where the Earth's crust is not real thick. In the United States, most of the western states have areas where this works. California makes the most geothermal energy. Iceland uses the most geothermal energy (per person) of any country in the world.
Once it is built, it is clean energy, but it requires deep wells. These areas often have volcanoes or earthquakes in the area, and sometimes adding or removing water deep underground might be enough to cause an earthquake. Some small earthquakes may have been caused this way.
Biomass
Biomass includes sawdust and other leftover parts of trees or lumber. It can also be grease and food waste, straw, and plants grown for energy. Some of this is burned to make electricity, some is made into biogas,biofuel, like ethanol as a replacement for gasoline. Ethanol might be a big renewable resource in the future. It is already widely used in the United States and Brazil. In the U.S. it is made from corn, which uses about as much energy as it makes. But there could be ways to improve it.
Images for kids
-
Alaska wild "berries" from the Innoko National Wildlife Refuge - Renewable Resources
-
Polyculture practices in Andhra Pradesh
-
Illegal slash and burn practice in Madagascar, 2010
-
Douglas fir forest created in 1850, Meymac (Corrèze), France
-
An adult and sub-adult Minke whale are dragged aboard the Nisshin Maru, a Japanese whaling vessel
-
Hemp insulation, a renewable resource used as building material
-
Atlantic cod stocks severely overfished leading to abrupt collapse
-
Over-hunting of American Bison
-
Panorama of a natural wetland (Sinclair Wetlands, New Zealand)
See also
 In Spanish: Recurso renovable para niños
In Spanish: Recurso renovable para niños