Belgium facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Belgium
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: Eendracht maakt macht (Dutch)
L'union fait la force (French) Einigkeit macht stark (German) (English: "Unity makes strength")
|
|
|
Anthem:
La Brabançonne |
|
|
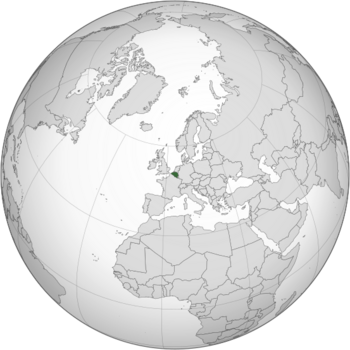
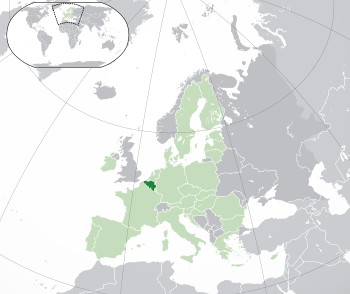
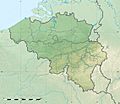
Location of Belgium (dark green)
– on the European continent (light green & dark grey) |
|
| Capital | City of Brussels 50°51′N 4°21′E / 50.850°N 4.350°E |
| Largest city | Brussels-Capital Region |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups
(2024)
|
|
| Religion
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Philippe |
| Bart De Wever | |
| Legislature | Federal Parliament |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Representatives | |
| Establishment | |
| 1789–1790 | |
|
• United Belgian States
|
1790 |
|
• Provisional Government of Belgium
|
1814–1815 |
| 1815–1839 | |
| 25 August 1830 | |
|
• Declared
|
4 October 1830 |
| 19 April 1839 | |
| 1970 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
30,689 km2 (11,849 sq mi) (136th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.64 (2022) |
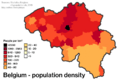
| Population | |
|
• 2024 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
383/km2 (992.0/sq mi) (22nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2022) | ▲ 24.9 low |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 12th |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +32 |
| ISO 3166 code | BE |
| Internet TLD | .be and .eu |
|
|
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. Belgium has an area of 30,528 square kilometres (11,787 sq mi). Around 11 million people live in Belgium. It is a founding member of the European Union and is home to its headquarters. The capital city of Belgium is Brussels, where the European Union, NATO and other famous organisations are based.
There are three regions in Belgium:
- Flanders is the name of the northern half of Belgium, just south of the Netherlands. Most of the people in this region, called the Flemish people, speak Dutch.
- Wallonia is the name of the southern half of Belgium, just north of France. Here, most of the people, the Walloons, speak French. There is a small part of Wallonia next to the border with Germany where the people speak German.
- The Brussels-Capital Region, where the capital of Brussels is found, is in the middle of the country, but surrounded by Flanders on all sides. It used to be Dutch-speaking, but today French is mostly spoken, with some Dutch.
The population is about 60% Dutch-speaking, 39% French-speaking, and 1% German-speaking (the so-called Deutschbelgier). To look after all these groups, Belgium has a complicated system of government.
Contents
History

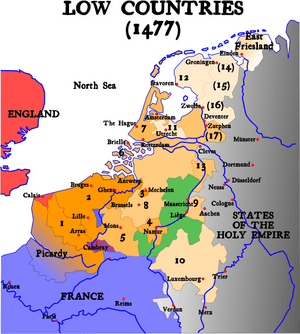
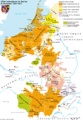
The name 'Belgium' comes from Gallia Belgica. This was a Roman province in the northernmost part of Gaul. Before Roman invasion in 100 BC, the Belgae, a mix of Celtic and Germanic peoples, lived there. The Germanic Frankish tribes during the 5th century brought the area under the rule of the Merovingian kings. A slow shift of power during the 8th century led the kingdom of the Franks to change into the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun in 843 divided the region into Middle and West Francia. They were vassals either of the King of France or of the Holy Roman Emperor. Many of these fiefdoms were united in the Burgundian Netherlands of the 14th and 15th centuries.
The Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) divided the Low Countries into the northern United Provinces and the Southern Netherlands. Southern Netherlands were ruled by the Spanish and the Austrian Habsburgs. This made up most of modern Belgium.
After the campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Low Countries were added into the French First Republic. This ended Austrian rule in the area. Adding back the Low Countries formed the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. This happened at the end of the First French Empire in 1815.
The Belgian Revolution was in 1830. Leopold I became king on July 21 1831. This is now celebrated as Belgium's National Day.
The Berlin Conference of 1885 gave control of the Congo Free State to King Leopold II. This was for him personally and not for the country of Belgium. Millions of Congolese people were hurt or killed, mostly to make rubber, and Leopold became very wealthy. In 1908 the Belgian state took control of the colony after there was a scandal about the deaths. It was then called the Belgian Congo, but the indigenous peoples continued to be killed and face violence from the colonial government.
Germany invaded Belgium in 1914. This was part of World War I. The opening months of the war were very bad in Belgium. During the war Belgium took over the of Ruanda-Urundi (modern-day Rwanda and Burundi). After the First World War, the Prussian districts of Eupen and Malmedy were added into Belgium in 1925. The country was again invaded by Germany in 1940 and under German control until 1944. After World War II, the people made king Leopold III leave his throne in 1951. This is because they thought he helped the Germans.
In 1960 the Belgian Congo stopped being under Belgian rule. Two years later Ruanda-Urundi also became free. Belgium joined NATO as a founding member.
Government and politics
Since 1993, Belgium is a federal state, divided into three regions and three communities.
Regions:
- Brussels-Capital Region
- Flemish Region (or Flanders)
- Walloon Region (or Wallonia)
Communities:
- Flemish Community
- French Community of Belgium
- German-speaking Community of Belgium
It has a system of government known as a constitutional monarchy, meaning that it has a monarch, but that the monarch does not rule the country, and that a government is elected democratically.
In Belgium, the government is elected. Between mid-2010 and late 2011, after no clear result in the election, Belgium had no official government, until Elio Di Rupo became Prime Minister. Flanders and Wallonia both also have their own regional governments, and there is a notable independence movement in Flanders. Charles Michel is currently the Prime Minister.
Geography
Belgium is next to France, Germany, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Its total area is 33,990 square kilometers. The land area alone is 30,528 km². Belgium has three main geographical regions. The coastal plain is in the north-west. The central plateau are part of the Anglo-Belgian Basin. The Ardennes uplands are in the south-east. The Paris Basin reaches a small fourth area at Belgium's southernmost tip, Belgian Lorraine.
The coastal plain is mostly sand dunes and polders. Further inland is a smooth, slowly rising landscape. There are fertile valleys. The hills have many forests. The plateaus of the Ardennes are more rough and rocky. They have caves and small, narrow valleys. Signal de Botrange is the country's highest point at 694 metres (2,277 ft).
Provinces
Belgium is divided into three Regions. Flanders and Wallonia are divided into provinces. The third Region, Brussels is not part of any province.
| Province | Dutch name | French name | Capital | Largest city | Area (km²) |
Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antwerp | Antwerpen | Anvers | Antwerp (Dutch: Antwerpen) (French: Anvers) |
Antwerp (Dutch: Antwerpen) (French: Anvers) |
2,860 | 1,682,683 |
| East Flanders | Oost-Vlaanderen | Flandre-Orientale | Ghent (Dutch: Gent) (French: Gand) |
Ghent (Dutch: Gent) (French: Gand) |
2,982 | 1,389,199 |
| Flemish Brabant | Vlaams-Brabant | Brabant flamand | Leuven (French: Louvain) |
Leuven (French: Louvain) |
2,106 | 1,037,786 |
| Hainaut | Henegouwen | Hainaut | Mons (Dutch: Bergen) |
Charleroi | 3,800 | 1,294,844 |
| Liège | Luik | Liège | Liège (Dutch: Luik) (German: Lüttich) |
Liège (Dutch: Luik) (German: Lüttich) |
3,844 | 1,047,414 |
| Limburg | Limburg | Limbourg | Hasselt | Hasselt | 2,414 | 805,786 |
| Luxembourg | Luxemburg | Luxembourg | Arlon (Dutch: Aarlen) (German: Arel) |
Bastogne (Dutch: Bastenaken) (German: Bastenach) |
4,443 | 261,178 |
| Namur | Namen | Namur | Namur (Dutch: Namen) |
Namur (Dutch: Namen) |
3,664 | 461,983 |
| Walloon Brabant | Waals-Brabant | Brabant wallon | Wavre (Dutch: Waver) |
Braine-l'Alleud (Dutch: Eigenbrakel) |
1,093 | 370,460 |
| West Flanders | West-Vlaanderen | Flandre-Occidentale | Bruges (Dutch: Brugge) (French: Bruges) |
Bruges (Dutch: Brugge) (French: Bruges) |
3,151 | 1,130,040 |
Natural resources
Belgium’s most important mineral resource was coal. The coal in the Sambre-Meuse valley had been mined since the 13th century. By the 1960s the reserves were exhausted, and most of the mines were closed. Now, Belgium imports coal that is used in the steel industry and for domestic heating.
There also used to be iron ore and zinc deposits in the Sambre-Meuse valley. They were heavily exploited in the 19th century but are also now exhausted. Today an important segment of Belgium's economy is chalk and limestone mining around Tournai, Mons, and Lièg. In addition, sands, clays and stones, principally specialty marbles, also are quarried.
Water is another valued natural resource in Belgium. It is used for cooling in nuclear power stations as nuclear reactors produce more than half of Belgium’s electricity. Water pollution is a serious problem, too.
Military
The Belgian Armed Forces have about 46,000 active troops. In 2009 the yearly defence budget was $6 billion. There are four parts: Belgian Land Component, or the Army; Belgian Air Component, or the Air Force; Belgian Naval Component, or the Navy; Belgian Medical Component.
Science and technology
Adding to science and technology has happened throughout the country's history. cartographer Gerardus Mercator, anatomist Andreas Vesalius, herbalist Rembert Dodoens and mathematician Simon Stevin are among the most influential scientists.
Chemist Ernest Solvay and engineer Zenobe Gramme gave their names to the Solvay process and the Gramme dynamo in the 1860s. Bakelite was formed in 1907–1909 by Leo Baekeland. A major addition to science was also due to a Belgian, Georges Lemaître. He is the one who made the Big Bang theory of the start of the universe in 1927.
Three Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine were awarded to Belgians: Jules Bordet in 1919, Corneille Heymans in 1938 and Albert Claude together with Christian De Duve in 1974. Ilya Prigogine was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1977. Two Belgian mathematicians have been awarded the Fields Medal: Pierre Deligne in 1978 and Jean Bourgain in 1994.
Culture
Fine arts
There have been many additions to painting and architecture. Several examples of major architectural places in Belgium belong to UNESCO's World Heritage List. In the 15th century the religious paintings of Jan van Eyck and Rogier van der Weyden were important. The 16th century had more styles such as Peter Breughel's landscape paintings and Lambert Lombard's showing of the antique. The style of Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck was strong in the early 17th century in the Southern Netherlands.
During the 19th and 20th centuries many original romantic, expressionist and surrealist Belgian painters started. These include James Ensor and other artists in the Les XX group, Constant Permeke, Paul Delvaux and René Magritte. The sculptor Panamarenko is still a remarkable figure in contemporary art. The artist Jan Fabre and the painter Luc Tuymans are other internationally known figures in contemporary art.
Belgian contributions to architecture were also in the 19th and 20th centuries. Victor Horta and Henry van de Velde were major starters of the Art Nouveau style.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, there were major violinists, such as Henri Vieuxtemps, Eugène Ysaÿe and Arthur Grumiaux. Adolphe Sax invented the saxophone in 1846. The composer César Franck was born in Liège in 1822. Newer music in Belgium is also famous. Jazz musician Toots Thielemans and singer Jacques Brel have made global fame. In rock/pop music, Telex, Front 242, K's Choice, Hooverphonic, Zap Mama, Soulwax and dEUS are well known. In the heavy metal scene, bands like Machiavel, Channel Zero and Enthroned have a worldwide fan-base.
Belgium has several well-known authors, including the poet Emile Verhaeren and novelists Hendrik Conscience, Georges Simenon, Suzanne Lilar and Amélie Nothomb. The poet and playwright Maurice Maeterlinck won the Nobel Prize in literature in 1911. The Adventures of Tintin by Hergé is the best known of Franco-Belgian comics. Many other major authors, including Peyo, André Franquin, Edgar P. Jacobs and Willy Vandersteen brought the Belgian cartoon strip industry a worldwide fame.
Belgian cinema has brought a number of mainly Flemish novels to life on-screen. Belgian directors include André Delvaux, Stijn Coninx, Luc and Jean-Pierre Dardenne. Well-known actors include Jan Decleir and Marie Gillain. Successful films include Man Bites Dog and The Alzheimer Affair.
Cuisine
Belgium is famous for beer, chocolate, waffles and french fries. French fries were first made in Belgium. The national dishes are "steak and fries with salad", and "mussels with fries". Other local fast food dishes include a Mitraillette. Brands of Belgian chocolate and pralines, like Côte d'Or, Guylian, Neuhaus, Leonidas, Corné and Galler are famous. Belgium makes over 1100 varieties of beer. The Trappist beer of the Abbey of Westvleteren has repeatedly been rated the world's best beer. The biggest brewer in the world by volume is Anheuser-Busch InBev, based in Leuven.
Sports

Since the 1970s, sports clubs are organised separately by each language community. Association football is one of the most popular sports in both parts of Belgium, together with cycling, tennis, swimming and judo. With five victories in the Tour de France and many other cycling records, Belgian Eddy Merckx is said to be one of the greatest cyclists of all time. Jean-Marie Pfaff, a former Belgian goalkeeper, is said to be one of the greatest in the history of football (soccer). Belgium and The Netherlands hosted the UEFA European Football Championship in 2000. Belgium hosted the 1972 European Football Championships.
Kim Clijsters and Justine Henin both were Player of the Year in the Women's Tennis Association. The Spa-Francorchamps motor-racing circuit hosts the Formula One World Championship Belgian Grand Prix. The Belgian driver, Jacky Ickx, won eight Grands Prix and six 24 Hours of Le Mans. Belgium also has a strong reputation in motocross. Sporting events held each year in Belgium include the Memorial Van Damme athletics competition, the Belgian Grand Prix Formula One, and a number of classic cycle races such as the Tour of Flanders and Liège–Bastogne–Liège. The 1920 Summer Olympics were held in Antwerp.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Gallia Belgica at the time of Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul in 54 BCE
-
The Burgundian State of Charles the Bold in the 15th century
-
Cheering crowds greet British troops entering Brussels, 4 September 1944
-
Bilingual signs in Brussels
-
National Basilica of the Sacred Heart in Koekelberg, Brussels
-
The Gilles of Binche, in costume, wearing wax masks
-
Moules-frites or mosselen met friet is a representative dish of Belgium.
-
Eddy Merckx, regarded as one of the greatest cyclists of all time
See also
 In Spanish: Bélgica para niños
In Spanish: Bélgica para niños