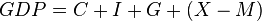Gross domestic product facts for kids
In economics, gross domestic product (GDP) is how much a place produces in an amount of time. GDP can be calculated by adding up its output inside the borders of that country.
To find the GDP of a country, one adds up all consumer spending (C), all investment (I), all government spending minus taxes (G), and the value of exports minus imports (X – M). This is shown by the equation:
This measure is often used to find out how healthy a country is; a country with a high value of GDP can be called a large economy. The United States has the largest GDP in the world. Germany has the largest in Europe, Nigeria in Africa and China in Asia.
There are different ways to calculate the GDP. Nominal GDP is the total amount of money spent on all new and final goods in an economy, real GDP (adjusting for changes in prices) tries to correct this number for inflation. For example, if the prices rise by 2% (meaning, everything costs 2% more) and the nominal GDP grows by 5%, the real GDP growth is only increased by 3%.
GDP per capita is the total income of a country, divided by the number of inhabitants. It shows how rich people, on average, are.
Gross national product
The GDP measure is different from gross national product (GNP) in that GNP = GDP + net income from assets in other countries (net income receipts).
Nominal GDP
When the gross domestic product is evaluated at the current market prices, it is called the nominal GDP. It includes changes in prices which makes it different from the real GDP. These changes can be due to inflation or price fluctuations. It can be measured in one of three different ways. The income approach uses the total of all income from businesses and individuals in a single year. The expenditure approach uses the market value of all goods purchased in a single year. The production approach is based on the total production in a single year.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Producto interno bruto para niños
In Spanish: Producto interno bruto para niños