Outer space facts for kids


Space, also known as outer space, is the near-vacuum between celestial bodies. It is where everything (all of the planets, stars, galaxies and other objects) is found. It is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere.
Outer space does not begin at a definite altitude above Earth's surface. The Kármán line, an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. Certain portions of the upper stratosphere and the mesosphere are sometimes referred to as "near space".
Contents
Environment

Outer space is nearly a perfect vacuum. It has effectively no friction, allowing stars, planets, and moons to move freely along their ideal orbits. The deep vacuum of intergalactic space is not devoid of matter, as it contains a few hydrogen atoms per cubic meter. By comparison, the air humans breathe contains about 1025 molecules per cubic meter. The low density of matter in outer space means that electromagnetic radiation can travel great distances without being scattered.
Stars, planets, and moons retain their atmospheres by gravitational attraction. Atmospheres have no clearly delineated upper boundary: the density of atmospheric gas gradually decreases with distance from the object until it becomes indistinguishable from outer space.
All of the observable universe is filled with photons that were created during the Big Bang, which is known as the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB).
Regions
Regions near the Earth
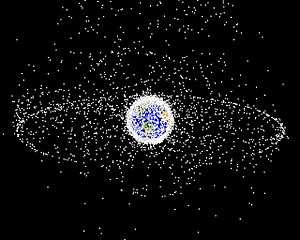
- Near-Earth space is the region of space extending from low Earth orbits out to geostationary orbits. This region includes the major orbits for artificial satellites and is the site of most of humanity's space activity. The region has seen high levels of space debris, sometimes dubbed space pollution, threatening any space activity in this region. Some of this debris re-enters Earth's atmosphere periodically. Although it meets the definition of outer space, the atmospheric density inside low-Earth orbital space, the first few hundred kilometers above the Kármán line, is still sufficient to produce significant drag on satellites.
- Geospace is a region of space that includes Earth's upper atmosphere and magnetosphere. The outer boundary of geospace is the magnetopause, which forms an interface between the Earth's magnetosphere and the solar wind. The inner boundary is the ionosphere.

- Cislunar space is a region outside of Earth that includes lunar orbits, the Moon's orbital space around Earth and the Lagrange points.
- Deep space is defined by the United States government as all of outer space which lies further from Earth than a typical low-Earth-orbit, thus assigning the Moon to deep-space.
Interplanetary space

Interplanetary space within the Solar System is the space between the eight planets, the space between the planets and the Sun, as well as that space beyond the orbit of the outermost planet Neptune where the solar wind remains active.
The volume of interplanetary space is a nearly total vacuum. This space is not completely empty, and is sparsely filled with cosmic rays, which include ionized atomic nuclei and various subatomic particles. There is gas, plasma and dust, small meteors, and several dozen types of organic molecules discovered to date by microwave spectroscopy.
Interplanetary space contains the magnetic field generated by the Sun.
Interstellar space

Interstellar space is the physical space outside of the bubbles of plasma known as astrospheres, formed by stellar winds originating from individual stars, or formed by solar wind emanating from the Sun. It is the space between the stars or stellar systems within a nebula or galaxy. Interstellar space contains an interstellar medium of sparse matter and radiation. The boundary between an astrosphere and interstellar space is known as an astropause. For the Sun, the astrosphere and astropause are called the heliosphere and heliopause.
Approximately 70% of the mass of the interstellar medium consists of lone hydrogen atoms; most of the remainder consists of helium atoms.
A number of molecules exist in interstellar space, which can form dust particles as tiny as 0.1 μm.
Intergalactic space
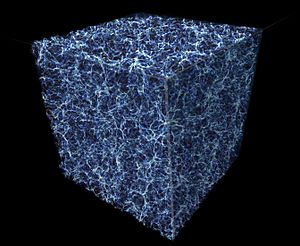
Intergalactic space is the physical space between galaxies. Studies of the large-scale distribution of galaxies show that the universe has a foam-like structure, with groups and clusters of galaxies lying along filaments that occupy about a tenth of the total space. The remainder forms cosmic voids that are mostly empty of galaxies. Typically, a void spans a distance of 7–30 megaparsecs.
Surrounding and stretching between galaxies, there is a rarefied plasma that is organized in a galactic filamentary structure. This material is called the intergalactic medium (IGM).
Exploration
Exploring space is very difficult because it contains no air and is so large that even the fastest ships can only explore a tiny part of it. It takes 3 days of traveling to reach the Moon and, depending on speed, it would take a long time to reach the closest star Proxima Centauri.
Manned spacecraft are designed to keep good air inside them and to protect astronauts from extreme temperatures.
We gain most of our information about the items in space from different kinds of telescopes. Some of them are space telescopes, put in outer space for a better view. Space probes also explore planets, comets and other space objects that are not too far.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
This is an artist's concept of the metric expansion of space, where a volume of the Universe is represented at each time interval by the circular sections. At left is depicted the rapid inflation from the initial state, followed thereafter by steadier expansion to the present day, shown at right.
-
Part of the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field image showing a typical section of space containing galaxies interspersed by deep vacuum. Given the finite speed of light, this view covers the past 13 billion years of the history of outer space.
-
Because of the hazards of a vacuum, astronauts must wear a pressurized space suit while off-Earth and outside their spacecraft.
-
Aurora australis observed from the Space Shuttle Discovery, on STS-39, May 1991 (orbital altitude: 260 km)
-
SpaceShipOne completed the first human private spaceflight in 2004, reaching an altitude of 100.12 km (62.21 mi).
-
The original Magdeburg hemispheres (lower left) used to demonstrate Otto von Guericke's vacuum pump (right)
-
The first image taken by a human of the whole Earth, probably photographed by William Anders of Apollo 8. South is up; South America is in the middle.
See also
 In Spanish: Espacio exterior para niños
In Spanish: Espacio exterior para niños