Cambodia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Cambodia
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto: ជាតិ សាសនា ព្រះមហាក្សត្រ
|
|
|
Anthem: នគររាជ
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Phnom Penh 11°34′10″N 104°55′16″E / 11.56944°N 104.92111°E |
| Official languages | Khmer |
| Official script | Khmer |
| Ethnic groups
(2019/20)
|
|
| Religion
(2019)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional elective monarchy under an authoritarian hereditary dictatorship |
|
• Monarch
|
Norodom Sihamoni |
| Hun Manet | |
|
• President of the Senate
|
Hun Sen |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Formation | |
|
• Funan
|
68–550 |
|
• Chenla
|
550–802 |
| 802–1431 | |
| 1431–1863 | |
|
• French protectorate
|
11 August 1863 |
|
• Independence from France
|
9 November 1953 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
181,035 km2 (69,898 sq mi) (88th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
2.5 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
17,638,801 (71st) |
|
• Density
|
94.4/km2 (244.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2013) | 36.0 medium |
| HDI (2022) | medium · 148th |
| Currency |
|
| Time zone | UTC+07:00 (ICT) |
| Calling code | +855 |
| ISO 3166 code | KH |
| Internet TLD | .kh |
Cambodia or Kampuchea ( Khmer: កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: Kâmpŭchéa), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in the southern Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of 181,035 square kilometres (69,898 square miles), bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, Vietnam to the east, and the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. The capital and largest city is Phnom Penh.
The United Nations designates Cambodia as a least developed country. Cambodia is a member of the United Nations, ASEAN, the RCEP, the East Asia Summit, the WTO, the Non-Aligned Movement and La Francophonie. While per capita income remains low compared to most neighboring countries, Cambodia has one of the fastest-growing economies in Asia. Agriculture remains the dominant economic sector, with strong growth in textiles, construction, garments, and tourism leading to increased foreign investment and international trade. Rich in biodiversity and seasonal tropical forests, Cambodia has a high rate of deforestation and is considered among the most vulnerable countries to climate change.
Contents
History
Cambodia has been inhabited since prehistoric times. In 802 AD, Jayavarman II declared himself king, uniting the warring Khmer princes of Chenla under the name "Kambuja". This marked the beginning of the Khmer Empire. The Indianised kingdom facilitated the spread of first Hinduism and then Buddhism to much of Southeast Asia and undertook many religious infrastructural projects throughout the region. Angkor Wat is the most famous of these structures and is designated as a World Heritage Site. In the fifteenth century, Cambodia experienced a decline of power, and in 1863, it became a protectorate of France. After a period of Japanese occupation during the Second World War, Cambodia gained independence in 1953. Despite Cambodia's neutrality, the Vietnam War extended into the country in 1965 via the Ho Chi Minh and Sihanouk trails. A 1970 coup installed the US-aligned Khmer Republic, until being overthrown by the Khmer Rouge in 1975. The Khmer Rouge ruled the country and carried out the Cambodian genocide from 1975 until 1979, when they were ousted in the Cambodian–Vietnamese War. The Vietnamese-occupied People's Republic of Kampuchea became the de facto government.
Following the 1991 Paris Peace Accords which formally ended the war with Vietnam, Cambodia was governed briefly by a United Nations mission (1992–93). The UN withdrew after holding elections in which around 90 per cent of the registered voters cast ballots. The 1997 coup d'état consolidated power under Prime Minister Hun Sen and the Cambodian People's Party (CPP), who remain in power. Although constitutionally a multi-party state, the CPP dominates the political system and dissolved its main opposition party in 2017, making Cambodia a de facto one-party state.
Geography
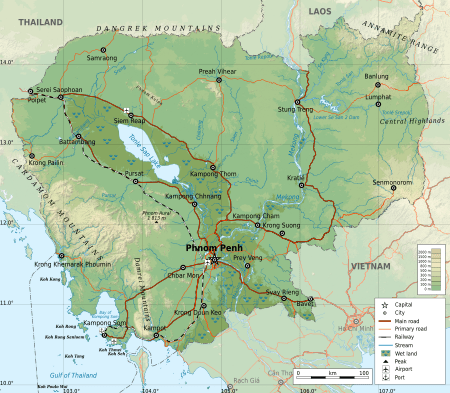
Cambodia has an area of 181,035 square kilometres (69,898 square miles) and lies entirely within the tropics, between latitudes 10° and 15°N, and longitudes 102° and 108°E. It borders Thailand to the north and west, Laos to the northeast, and Vietnam to the east and southeast. It has a 443-kilometre (275-mile) coastline along the Gulf of Thailand.
Cambodia's landscape is characterised by a low-lying central plain that is surrounded by uplands and low mountains and includes the Tonle Sap (Great Lake) and the upper reaches of the Mekong River delta. Extending outward from this central region are transitional plains, thinly forested and rising to elevations of about 650 feet (200 metres) above sea level.
To the north the Cambodian plain abuts a sandstone escarpment, which forms a southward-facing cliff stretching more than 200 miles (320 kilometres) from west to east and rising abruptly above the plain to heights of 600 to 1,800 feet (180–550 metres). This cliff marks the southern limit of the Dângrêk Mountains.
Flowing south through Cambodia's eastern regions is the Mekong River. East of the Mekong the transitional plains gradually merge with the eastern highlands, a region of forested mountains and high plateaus that extend into Laos and Vietnam. In southwestern Cambodia two distinct upland blocks, the Krâvanh Mountains and the Dâmrei Mountains, form another highland region that covers much of the land area between the Tonle Sap and the Gulf of Thailand.
In this remote and largely uninhabited area, Phnom Aural, Cambodia's highest peak rises to an elevation of 5,949 feet (1,813 metres). The southern coastal region adjoining the Gulf of Thailand is a narrow lowland strip, heavily wooded and sparsely populated, which is isolated from the central plain by the southwestern highlands.
The most distinctive geographical feature is the inundations of the Tonle Sap, measuring about 2,590 square kilometres (1,000 square miles) during the dry season and expanding to about 24,605 square kilometres (9,500 square miles) during the rainy season. This densely populated plain, which is devoted to wet rice cultivation, is the heartland of Cambodia. Much of this area has been designated as a biosphere reserve.
Climate
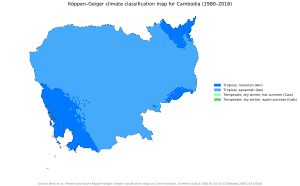
Cambodia's climate, like that of the rest of Southeast Asia, is dominated by monsoons, which are known as tropical wet and dry because of the distinctly marked seasonal differences.
Cambodia has a temperature range from 21 to 35 °C (70 to 95 °F) and experiences tropical monsoons. Southwest monsoons blow inland bringing moisture-laden winds from the Gulf of Thailand and Indian Ocean from May to October. The northeast monsoon ushers in the dry season, which lasts from November to April. The country experiences the heaviest precipitation from September to October with the driest period occurring from January to February.
According to the International Development Research Center and The United Nations, Cambodia is considered Southeast Asia's most vulnerable country to the effects of climate change, alongside the Philippines. Nearly all provinces in Cambodia are affected by climate change. Rural coastal populations are particularly at risk. Shortages of clean water, extreme flooding, mudslides, higher sea levels and potentially destructive storms are of particular concern, according to the Cambodia Climate Change Alliance. Climate change has also had a major impact on water levels, ecology and productivity of the Tonlé Sap in recent years, affecting the food security and agriculture of a large proportion of Cambodia's population.
Cambodia has two distinct seasons. The rainy season, which runs from May to October, can see temperatures drop to 22 °C (72 °F) and is generally accompanied with high humidity. The dry season lasts from November to April when temperatures can rise up to 40 °C (104 °F) around April. Disastrous flooding occurred in 2001 and again in 2002, with some degree of flooding almost every year. Severe flooding also affected 17 provinces in Cambodia during the 2020 Pacific typhoon season.
Biodiversity and conservation
Cambodia's biodiversity is largely founded on its seasonal tropical forests, containing some 180 recorded tree species, and riparian ecosystems. There are 212 mammal species, 536 bird species, 240 reptile species, 850 freshwater fish species (Tonle Sap Lake area), and 435 marine fish species recorded by science. Much of this biodiversity is contained around the Tonle Sap Lake and the surrounding biosphere.
The Tonle Sap Biosphere Reserve is a reserve surrounding the Tonle Sap lake. It encompasses the lake and nine provinces: Kampong Thom, Siem Reap, Battambang, Pursat, Kampong Chhnang, Banteay Meanchey, Pailin, Oddar Meanchey and Preah Vihear. In 1997, it was successfully nominated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Other key habitats include the evergreen and dry Dipterocarp forests of Mondolkiri province, protected by Keo Seima Wildlife Sanctuary, Phnom Prich Wildlife Sanctuary, and Srepok Wildlife Sanctuary, as well as Ratanakiri province, and the Cardamom Mountains ecosystem, including Preah Monivong National Park, Botum-Sakor National Park, and the Phnom Aural Wildlife Sanctuary and Phnom Samkos Wildlife Sanctuary.
The Worldwide Fund for Nature recognises six distinct terrestrial ecoregions in Cambodia – the Cardamom Mountains rain forests, Central Indochina dry forest, Southeast Indochina dry evergreen forest, Southern Annamite Range tropical forest, Tonle Sap freshwater swamp forest, and Tonle Sap-Mekong peat swamp forest.
The rate of deforestation in Cambodia is one of the highest in the world and it is often perceived as the most destructive, singular environmental issue in the country. Cambodia's primary forest cover fell from over 70% in 1969 to just 3.1% in 2007. Since 2007, less than 3,220 km2 (1,243 sq mi) of primary forest remain with the result that the future sustainability of the forest reserves of Cambodia is under severe threat. In 2010–2015, the annual rate of deforestation was 1.3%. The environmental degradation also includes national parks and wildlife sanctuaries on a large scale and many endangered and endemic species are now threatened with extinction due to loss of habitats. Reasons for the deforestation in Cambodia range from opportunistic illegal loggings to large scale clearings from big construction projects and agricultural activities. The deforestation involves the local population, Cambodian businesses and authorities as well as transnational corporations from all over the world.
Plans for hydroelectric development in the Greater Mekong Subregion, by Laos in particular, pose a "real danger to the food supply of Vietnam and Cambodia. Upstream dams will imperil the fish stocks that provide the vast majority of Cambodia's protein and could also denude the Mekong River of the silt Vietnam needs for its rice basket." The rich fisheries of Tonle Sap, the largest freshwater lake in Southeast Asia, largely supply the impoverished country's protein. The lake is unusual: It all but disappears in the dry season and then expands massively as water flow from the Mekong backs up when the rains come. "Those fish are so important for their livelihoods, both economically and nutritionally", said Gordon Holtgrieve, a professor at the University of Washington; he points out that none of the dams that are either built or being built on the Mekong river "are pointing at good outcomes for the fisheries".
In the 2010s, the Cambodian government and educational system has increased its involvement and co-operation with both national and international environmental groups. A new National Environmental Strategy and Action Plan (NESAP) for Cambodia is to be implemented from late 2016 to 2023 and contains new ideas for how to incite a green and environmentally sustainable growth for the country.
Sports
In Cambodia, people play many sports. Some sports that are enjoyed that come from the West include golf, rugby and soccer. Traditional Cambodian sports are buffalo racing, dragon boat racing and bokator Khmer martial art also known as pradal serey. Cambodia attended its first Olympic Games in 1956 and participated in two more before warfare and civil strife interrupted its attendance. The country returned to regular participation with the 1996 Summer Games. Cambodia managed fourth in soccer in the 1972 Southeast Asian games. Cambodia hosted the GANEFO games in the 1960s.
Culture
The culture of Cambodia has been influenced by Hinduism. Today most people in Cambodia practice Buddhism. A lot of their customs revolve around Buddhism.
The food of Cambodia includes tropical fruits, rice, noodles and various soups. Cambodians like to eat a rice noodle soup called 'kah-tieu' in the morning. Cambodians are famous for a type of 'kah-tieu' called 'kah-tieu Phnom Penh' which has shrimp, beef balls, fried garlic, pork broth and chicken. Cambodians also eat a red curry noodle soup with rice vermicelle noodles. Curry is also eaten with rice or French bread in Cambodia. Cambodian food is similar to Vietnamese and Southern Thai food.
Cambodia also has a mystical tattoo called a yantra tattoo that is popular with soldiers. A yantra tattoo has ancient Khmer and Pali (An ancient Indian language) writing. A yantra tattoo is usually done by a religious person or monk. The tattoo artist guarantees that the person cannot receive any physical harm as long as they follow certain conditions. A person is supposed to not talk to anyone for three days and three nights. Another alternative is to follow the five Buddhist percepts. Movie star actress Angelina Jolie is known to have a yantra tattoo.
Cambodians celebrate the Cambodian New Year in April. It is based on Theravada Buddhism. The date depends on astrological signs but are usually are on April 13-15 or April 14-16.
Flag
The Cambodian flag includes a three-towered temple called Angkor Wat. It is the most famous monument in the country. Many tourists visit the temple. The Cambodian flag has three horizontal bands. There are two blue bands on the top and the bottom. There is a red band that is twice the height of each blue band. The red band represents the nation. The temple represents the structure of the universe.
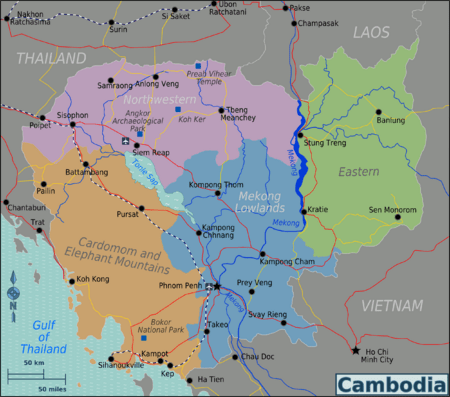
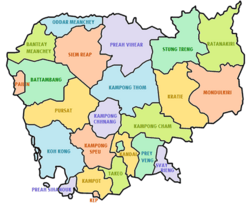
Provinces
Cambodia is divided into 25 provinces including the capital. The provinces are divided into 159 districts and 26 municipalities. The districts and municipalities are then divided into communes and quarters.
| Name | Capital (seat) | Population (2019) | Area (km2) | Population density | ISO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banteay Meanchey | Serei Saophoan Municipality | 859,545 | 6,679 | 129 | KH-1 |
| Battambang | Battambang Municipality | 987,400 | 11,702 | 84 | KH-2 |
| Kampong Cham | Kampong Cham Municipality | 895,763 | 4,549 | 197 | KH-3 |
| Kampong Chhnang | Kampong Chhnang Municipality | 525,932 | 5,521 | 95 | KH-4 |
| Kampong Speu | Chbar Mon Municipality | 872,219 | 7,017 | 124 | KH-5 |
| Kampong Thom | Steung Saen Municipality | 677,260 | 13,814 | 49 | KH-6 |
| Kampot | Kampot Municipality | 592,845 | 4,873 | 122 | KH-7 |
| Kandal | Ta Khmau Municipality | 1,195,547 | 3,179 | 376 | KH-8 |
| Koh Kong | Khemarak Phoumin Municipality | 123,618 | 10,090 | 12 | KH-9 |
| Kratié | Kratié Municipality | 327,825 | 11,094 | 34 | KH-10 |
| Mondulkiri | Senmonorom Municipality | 88,649 | 14,288 | 6 | KH-11 |
| Phnom Penh | Doun Penh Section | 2,129,371 | 679 | 3,136 | KH-12 |
| Preah Vihear | Tbaeng Meanchey Municipality | 251,352 | 13,788 | 18 | KH-13 |
| Prey Veng | Prey Veng Municipality | 1,057,428 | 4,883 | 217 | KH-14 |
| Pursat | Pursat Municipality | 411,759 | 12,692 | 32 | KH-15 |
| Ratanak Kiri | Banlung Municipality | 204,027 | 10,782 | 19 | KH-16 |
| Siem Reap | Siem Reap Municipality | 1,006,512 | 10,299 | 98 | KH-17 |
| Preah Sihanouk | Sihanoukville Municipality | 302,887 | 1,938 | 156 | KH-18 |
| Stung Treng | Stung Treng Municipality | 159,565 | 11,092 | 14 | KH-19 |
| Svay Rieng | Svay Rieng Municipality | 524,554 | 2,966 | 177 | KH-20 |
| Takéo | Doun Kaev Municipality | 899,485 | 3,563 | 252 | KH-21 |
| Oddar Meanchey | Samraong Municipality | 261,252 | 6,158 | 42 | KH-22 |
| Kep | Kep Municipality | 41,798 | 336 | 124 | KH-23 |
| Pailin | Pailin Municipality | 71,600 | 803 | 89 | KH-24 |
| Tboung Khmum | Suong Municipality | 775,296 | 5,250 | 148 | KH-25 |
Transportation
People in Cambodia use many different types of transportation. Transportation in Cambodia include: boat, car, motorcycle, elephant, train and airplane.
Economy
The Cambodian economy has been growing rapidly in recent years. Cambodia is set to build its first skyscraper, Gold Tower 42. Cambodia is also building a satellite city next to Phnom Penh which is called Camko City. Camko City is being constructed by Korean companies to modernize Phnom Penh so as to make it appealing to foreign investors and businesses. Cambodia is also one of the most corrupted nations in the world and has been pressured by international communities to fix it.
Foreign relations
Cambodia has foreign relations with most nations. It is part of ASEAN. Cambodia has border issues with Vietnam and Thailand over lost territories. Cambodia is one of a few nations with good relations with both Koreas. South Korean president Lee Myung Bak was an economic advisor to Cambodian prime minister Hun Sen and former Cambodian King Norodom Sihanouk was a good friend with former North Korean leader Kim Il-sung.
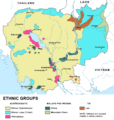
Ethnic groups
The Khmer (Cambodians) account for the vast majority of the population. Ethnic minorities include Chinese, Vietnamese, Muslim Cham-Malays, Laotians, and various native peoples of the rural highlands.
Languages
The Khmer language is a member of the Mon–Khmer subfamily of the Austroasiatic language group. French, once the language of government in Indochina, is still spoken by many older Cambodians, and is also the language of instruction in some schools and universities that are funded by the government of France. There is also a French-language newspaper and some TV channels are available in French. Cambodia is a member of La Francophonie. Cambodian French, a remnant of the country's colonial past, is a dialect found in Cambodia and is sometimes used in government, particularly in court. Since 1993, there has been a growing use of English, which has been replacing French as the main foreign language. English is widely taught in several universities and there is also a significant press in that language, while street signs are now bilingual in Khmer and English. Due to this shift, mostly English is now used in Cambodia's international relationships, and it has replaced French both on Cambodia's stamps and, since 2002, on Cambodian currency.
The Khmer script is derived from the South Indian Pallava script.
Religion
Theravada Buddhism is the official religion of Cambodia, practised by more than 95 per cent of the population with an estimated 4,392 monastery temples throughout the country. Cambodian Buddhism is deeply influenced by Hinduism and native animism.
The close interrelationship between spirits and the community, the efficacy of apotropaic and luck-attracting actions and charms, and the possibility of manipulating one's life through contact with spiritual entities such as the "baromey" spirits originates from the native folk religion. Hinduism has left little trace beyond the magical practices of Tantricism and a host of Hindu gods now assimilated into the spirit world (for example, the important neak ta spirit called Yeay Mao is the modern avatar of the Hindu goddess Kali).
Mahayana Buddhism is the religion of the majority of Chinese and Vietnamese in Cambodia. Elements of other religious practices, such as the veneration of folk heroes and ancestors, Confucianism, and Taoism mix with Chinese Buddhism are also practised.
Islam is followed by about 2% of the population and comes in three varieties, two practised by the Cham people and a third by the descendants of Malays, resident in the country for generations. Cambodia's Muslim population is reported to be 80% ethnic Cham.
Land
Although much of Cambodia is heavily forested, the central lowland region is covered with rice paddies, fields of dry crops such as corn (maize) and tobacco, tracts of tall grass and reeds, and thinly wooded areas. Savanna grassland occur in the plains, with the grasses reaching a height of 5 feet (1.5 metres). In the eastern highlands the high plateaus are covered with grasses and deciduous forests. Broad-leaved evergreen forests grow in the mountainous areas to the north, with trees 100 feet (30 metres) high emerging from thick undergrowths of vines, rattans, palms, bamboos, and assorted woody and herbaceous ground plants. In the southwestern highlands, open forests of pines are found at the higher elevations, while the rain-drenched seaward slopes are blanketed with virgin rainforests growing to heights of 150 feet (45 metres) or more. Vegetation along the coastal strip ranges from evergreen forests to nearly impenetrable mangroves.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
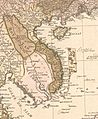
A map of Indochina in 1760
-
Norodom Sihanouk and Mao Zedong in 1956
-
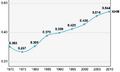
The Cambodian position on the Human Development Index, 1970–2010
-
Farmers harvesting rice in Battambang Province
-
Every year, nearly 2.6 million tourists visit Angkor Wat in Siem Reap, Cambodia.
See also
 In Spanish: Camboya para niños
In Spanish: Camboya para niños