Western United States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Western United States
American West, Far West, the West
|
|
|---|---|
|
Left-right from top: Los Angeles skyline, the Grand Canyon, Yellowstone National Park, Boise skyline, Angel's Landing, Mt. Rainier, Seattle skyline
|
|
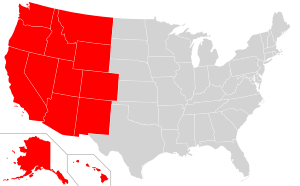
This map reflects the Western United States as defined by the Census Bureau. This region is divided into Mountain and Pacific areas.
|
|
| Subregions |
|
| Country | |
| States |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,873,251.63 sq mi (4,851,699.4 km2) |
| • Land | 1,751,053.31 sq mi (4,535,207.3 km2) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 78,588,572 |
| • Density | 41.9530248/sq mi (16.19815341/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Westerner |
| GDP (nominal) | |
| • Total | $5.619 trillion (2019) |
| • per capita | $71,719 (2019) |
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Western States, the Far West, the Western territories, and the West) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau.
As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term the West changed. Before around 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered the West.
The U.S. Census Bureau's definition of the 13 westernmost states includes the Rocky Mountains and the Great Basin to the Pacific Coast, and the mid-Pacific islands state, Hawaii. To the east of the Western United States is the Midwestern United States and the Southern United States, with Canada to the north and Mexico to the south.
The West contains several major biomes, including arid and semi-arid plateaus and plains, particularly in the American Southwest; forested mountains, including three major ranges, the Sierra Nevada, the Cascades, and Rocky Mountains; the long coastal shoreline of the American Pacific Coast; and the rainforests of the Pacific Northwest.
Contents
Geographic definition


The Western United States is the largest region of the country, covering nearly half the land area of the contiguous United States. It is also the most geographically diverse, incorporating geographic regions such as the temperate rainforests of the Northwest, the highest mountain ranges, including the Rocky Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, and the Cascade Range, numerous glaciers, and the western edge of the Great Plains. It also contains the majority of the desert areas located in the United States. The Mojave and the Great Basin deserts lie entirely within the Western region, along with parts of the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts (the latter extends significantly into Texas, while both extend into Mexico). Given this expansive and diverse geography it is no wonder that the region is difficult to define precisely. Sensing a possible shift in the popular understanding of the West as a region in the early 1990s, historian Walter Nugent conducted a survey of three groups of professionals with ties to the region: a large group of Western historians (187 respondents), and two smaller groups, 25 journalists and publishers and 39 Western authors. A majority of the historian respondents placed the eastern boundary of the West east of the Census definition out on the eastern edge of the Great Plains or on the Mississippi River. The survey respondents as a whole showed just how little agreement there was on the boundaries of the West.
Subregions
The region is split into two smaller units or divisions, by the U.S. Census Bureau:
- Mountain states
- Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, Idaho, Utah, Arizona, and Nevada
- Pacific states
- Washington, Oregon, California, Alaska, and Hawaii
Other classifications distinguish between Southwest and Northwest. Arizona, New Mexico, West Texas, and the Oklahoma panhandle are typically considered to be the Southwest states. Meanwhile, the states of Montana, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington can be considered part of the Northwest or Pacific Northwest.
The term West Coast is commonly used to refer to just California, Oregon, Washington, and Alaska, whereas Hawaii is more geographically isolated from the continental U.S. and does not necessarily fit in any of these subregions.
| State | 2020 Census | 2010 Census | Change | Area |
Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7,151,502 | 6,392,017 | +11.88% | 113,594.08 sq mi (294,207.3 km2) | 63/sq mi (24/km2) | |
| 5,773,714 | 5,029,196 | +14.80% | 103,641.89 sq mi (268,431.3 km2) | 56/sq mi (22/km2) | |
| 3,271,616 | 2,763,885 | +18.37% | 82,169.62 sq mi (212,818.3 km2) | 40/sq mi (15/km2) | |
| 3,104,614 | 2,700,551 | +14.96% | 109,781.18 sq mi (284,332.0 km2) | 28/sq mi (11/km2) | |
| 2,117,522 | 2,059,179 | +2.83% | 121,298.15 sq mi (314,160.8 km2) | 17/sq mi (6.6/km2) | |
| 1,839,106 | 1,567,582 | +17.32% | 82,643.12 sq mi (214,044.7 km2) | 22/sq mi (8.5/km2) | |
| 1,084,225 | 989,415 | +9.58% | 145,545.80 sq mi (376,961.9 km2) | 7/sq mi (2.7/km2) | |
| 576,851 | 563,626 | +2.35% | 97,093.14 sq mi (251,470.1 km2) | 6/sq mi (2.3/km2) | |
| Mountain | 24,919,150 | 22,065,451 | +12.93% | 855,766.98 sq mi (2,216,426.3 km2) | 29/sq mi (11/km2) |
| 39,538,223 | 37,254,523 | +6.13% | 155,779.22 sq mi (403,466.3 km2) | 254/sq mi (98/km2) | |
| 7,705,281 | 6,724,540 | +14.58% | 66,455.52 sq mi (172,119.0 km2) | 116/sq mi (45/km2) | |
| 4,237,256 | 3,831,074 | +10.60% | 95,988.01 sq mi (248,607.8 km2) | 44/sq mi (17/km2) | |
| 1,455,271 | 1,360,301 | +6.98% | 6,422.63 sq mi (16,634.5 km2) | 227/sq mi (88/km2) | |
| 733,391 | 710,231 | +3.26% | 570,640.95 sq mi (1,477,953.3 km2) | 1/sq mi (0.39/km2) | |
| Pacific | 53,669,422 | 49,880,669 | +7.60% | 895,286.33 sq mi (2,318,781.0 km2) | 60/sq mi (23/km2) |
| West | 78,588,572 | 71,946,120 | +9.23% | 1,751,053.31 sq mi (4,535,207.3 km2) | 45/sq mi (17/km2) |
Outlying areas
The three inhabited Pacific U.S. territories (American Samoa, Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands) are sometimes considered part of the Western United States. American Samoa is in Polynesia in the South Pacific Ocean, while Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands are in the Mariana Islands in the western North Pacific Ocean. Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands have district courts within the 9th Circuit, which includes western states such as California and Nevada. (See District Court of Guam and District Court for the Northern Mariana Islands). American Samoa, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands are also considered part of the western U.S. by the U.S. National Park Service, the Federal Reserve Bank system, FEMA, and the USGS.
| Territory | 2020 Population Estimate |
2010 Census population |
Change | Area |
Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49,437 | 55,519 | −10.95% | 224 km2 (86 sq mi) | 221/km2 (570/sq mi) | |
| 168,485 | 159,358 | +5.73% | 544 km2 (210 sq mi) | 310/km2 (800/sq mi) | |
| 51,433 | 53,833 | −4.46% | 464 km2 (179 sq mi) | 111/km2 (290/sq mi) |
Demographics
The population distribution by race in the Western United States (2022):
- 51.9% White (47.1% non-Hispanic)
- 30.8% Hispanic or Latino ethnicity (of any race)
- 10.8% Asian (10.6% non-Hispanic)
- 4.5% Black or African-American (4.3% non-Hispanic)
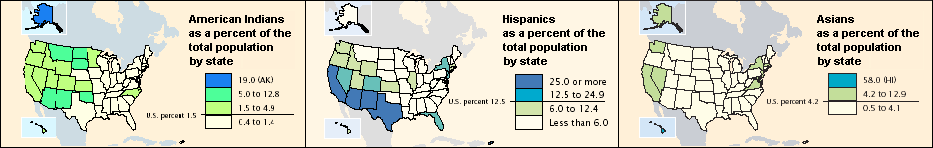
- 1.9% American Indian or Alaska Native (1.1% non-Hispanic)
- 0.6% Pacific Islander (0.6% non-Hispanic)
- 13.3% Some other race (0.6% non-Hispanic)
- 17.0% Two or more races (5.0% non-Hispanic)
As defined by the United States Census Bureau, the Western region of the United States includes 13 states, with a total 2020 population of 78,588,572.
The West is one of the most sparsely settled areas in the United States with 49.5 inhabitants per square mile (19.1 inhabitants/km2). Only Texas with 78.0 inhabitants/sq mi (30.1 inhabitants/km2), Washington with 86.0 inhabitants/sq mi (33.2 inhabitants/km2), and California with 213.4 inhabitants/sq mi (82.4 inhabitants/km2) exceed the national average of 77.98 inhabitants/sq mi (30.11 inhabitants/km2). As of 2022, just under half of the 78.7 million residents of the West live in California.
The entire Western region has also been strongly influenced by European, Hispanic or Latino, Asian and Native Americans; it contains the largest number of minorities in the U.S. While most of the studies of racial dynamics in America such as riots in Los Angeles have been written about European and African-Americans, in many cities in the West and California, whites and blacks together are less than half the population because of the preference for the region by Hispanics and Asians. African and European Americans, however, continue to wield a stronger political influence because of the lower rates of citizenship and voting among Asians and Hispanics.
According to 2022 estimates from the Census Bureau, the largest ancestries reported in the West are Mexican (24.2%), German (10.1%), English (9.5%), Irish (7.2%), Italian (3.5%), Filipino (3.4%), and Chinese (3.3%).
The West also contains much of the Native American population in the U.S., particularly in the large reservations in the Mountain and Desert States. As of 2022, the West is home to 365,351 Navajo, 109,208 Apache, and 78,364 Blackfeet, as well as 276,082 people identifying as Indigenous Mexican.
The largest concentrations for African-Americans in the West can be found in San Diego, Los Angeles, Oakland, Sacramento, Fresno, San Francisco, Seattle, Tacoma, Phoenix, Las Vegas, Denver, and Colorado Springs.
The Western United States has a higher sex ratio (more males than females) than any other region in the United States.
Because the tide of development had not yet reached most of the West when conservation became a national issue, agencies of the federal government own and manage vast areas of land. (The most important among these are the National Park Service and the Bureau of Land Management within the Interior Department, and the U.S. Forest Service within the Agriculture Department.) National parks are reserved for recreational activities such as fishing, camping, hiking, and boating, but other government lands also allow commercial activities like ranching, logging, and mining. In recent years, some local residents who earn their livelihoods on federal land have come into conflict with the land's managers, who are required to keep land use within environmentally acceptable limits.
The largest city in the region is Los Angeles, located on the West Coast. Other West Coast cities include San Diego, San Bernardino, San Jose, San Francisco, Oakland, Bakersfield, Fresno, Sacramento, Seattle, Tacoma, Anchorage, and Portland – some of which are dozens of miles inland. Prominent cities in the Mountain States include Denver, Colorado Springs, Phoenix, Tucson, Albuquerque, Las Vegas, Reno, Salt Lake City, Boise, El Paso, and Billings.
Natural geography
Along the Pacific Ocean coast lie the Coast Ranges, which, while not approaching the scale of the Rocky Mountains, are formidable nevertheless. They collect a large part of the airborne moisture moving in from the ocean. East of the Coast Ranges lie several cultivated fertile valleys, notably the San Joaquin and Sacramento valleys of California and the Willamette Valley of Oregon.
Beyond the valleys lie the Sierra Nevada in the south and the Cascade Range in the north. Mount Whitney, at 14,505 feet (4,421 m) the tallest peak in the contiguous 48 states, is in the Sierra Nevada. The Cascades are also volcanic. Mount Rainier, a volcano in Washington, is also over 14,000 feet (4,300 m). Mount St. Helens, a volcano in the Cascades, erupted explosively in 1980. A major volcanic eruption at Mount Mazama around 4860 BC formed Crater Lake. These mountain ranges see heavy precipitation, capturing most of the moisture that remains after the Coast Ranges, and creating a rain shadow to the east forming vast stretches of arid land. These dry areas encompass much of Nevada, Utah, and Arizona. The Mojave Desert and Sonoran Desert along with other deserts are found here.
Beyond the deserts lie the Rocky Mountains. In the north, they run almost immediately east of the Cascade Range, so that the desert region is only a few miles wide by the time one reaches the Canada–US border. The Rockies are hundreds of miles wide and run uninterrupted from New Mexico to Alaska. The Rocky Mountain Region is the highest overall area of the United States, with an average elevation of above 4,000 feet (1,200 m). The tallest peaks of the Rockies, 54 of which are over 14,000 feet (4,300 m), are found in central and western Colorado. East of the Rocky Mountains is the Great Plains, the western portions (for example, the eastern half of Colorado) of which are generally considered to be part of the western United States.
The West has several long rivers that empty into the Pacific Ocean, while the eastern rivers run into the Gulf of Mexico. The Mississippi River forms the easternmost possible boundary for the West today. The Missouri River, a tributary of the Mississippi, flows from its headwaters in the Rocky Mountains eastward across the Great Plains, a vast grassy plateau, before sloping gradually down to the forests and hence to the Mississippi. The Colorado River snakes through the Mountain states, at one point forming the Grand Canyon.
The Colorado River is a major source of water in the Southwest and many dams, such as the Hoover Dam, form reservoirs along it. So much water is drawn for drinking water throughout the West and irrigation in California that in most years, water from the Colorado River no longer reaches the Gulf of California. The Columbia River, the largest river in volume flowing into the Pacific Ocean from North America, and its tributary, the Snake River, water the Pacific Northwest. The Platte runs through Nebraska and was known for being a mile (2 km) wide but only a half-inch (1 cm) deep. The Rio Grande forms the border between Texas and Mexico before turning due north and splitting New Mexico in half.
According to the United States Coast Guard, "The Western Rivers System consists of the Mississippi, Ohio, Missouri, Illinois, Tennessee, Cumberland, Arkansas, and White Rivers and their tributaries, and certain other rivers that flow towards the Gulf of Mexico." The Ohio River portion of the system includes parts of several Atlantic coastal states, from Georgia to New York.
Climate and agriculture
Most of the public land held by the U.S. National Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management is in the Western states. Public lands account for 25 to 75 percent of the total land area in these states.
The climate of the West is semi-arid, yet parts of the region get high amounts of rain or snow. Other parts are true desert which receive less than 5 inches (130 mm) of rain per year. The climate is increasingly unstable, and subject to periods of severe drought.
The seasonal temperatures vary greatly throughout the West. Low elevations on the West Coast have warm summers and mild winters with little to no snow. The desert southwest has very hot summers and mild winters. While the mountains in the southwest receive generally large amounts of snow. The Inland Northwest has a continental climate of warm to hot summers and cold to bitterly cold winters.
Annual rainfall is greater in the eastern portions, gradually tapering off until reaching the Pacific Coast where it increases again. In fact, the greatest annual rainfall in the United States falls in the coastal regions of the Pacific Northwest. Drought is much more common in the West than the rest of the United States. The driest place recorded in the U.S. is Death Valley, California. In Western states, drought is closely associated with fire risk, and there have been a number of notable wildfires causing extensive property damage and wildlife habitat destruction. The Western United States is predicted to experience drought-like conditions for much of the 21st century.
Violent thunderstorms occur east of the Rockies. Tornadoes occur every spring on the southern plains, with the most common and most destructive centered on Tornado Alley, which covers eastern portions of the West, (Texas to North Dakota), and all states in between and to the east.
Agriculture varies depending on rainfall, irrigation, soil, elevation, and temperature extremes. The arid regions generally support only livestock grazing, chiefly beef cattle. The wheat belt extends from Texas through The Dakotas, producing most of the wheat and soybeans in the U.S. and exporting more to the rest of the world. Irrigation in the Southwest allows the growth of great quantities of fruits, nuts, and vegetables as well as grain, hay, and flowers. Texas is a major cattle and sheep raising area, as well as the nation's largest producer of cotton. Washington is famous for its apples, and Idaho for its potatoes. California and Arizona are major producers of citrus crops, however, declining supplies of water, as well as urban sprawl have contributed to a sharp decline in citrus production in Arizona. Many varieties of chile peppers are grown in the valleys of New Mexico.
Starting in 1902, Congress passed a series of acts authorizing the establishment of the United States Bureau of Reclamation to oversee water development projects in seventeen western states.
During the first half of the 20th century, dams and irrigation projects provided water for rapid agricultural growth throughout the West and brought prosperity for several states, where agriculture had previously only been subsistence level. Following World War II, the West's cities experienced an economic and population boom. The population growth, mostly in the Southwest states of New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, and Nevada, has strained water and power resources, with water diverted from agricultural uses to major population centers, such as the Las Vegas Valley and Los Angeles.
Geology
Plains make up much of the eastern portion of the West, underlain with sedimentary rock from the Upper Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras. The Rocky Mountains expose igneous and metamorphic rock both from the Precambrian and from the Phanerozoic eon. The Inter-mountain States and Pacific Northwest have huge expanses of volcanic rock from the Cenozoic era. Salt flats and salt lakes reveal a time when the great inland seas covered much of what is now the West.
The Pacific states are the most geologically active areas in the United States. Earthquakes cause damage every few to several years in California. While the Pacific states are the most volcanically active areas, extinct volcanoes and lava flows are found throughout most of the West.
Wildlife

The ecoregions and ecology found in the Western United States are extremely varied. For instance, large areas of land are made up of everything from sand dunes in the Central Basin and Range ecoregion, which makes up much of the State of Nevada, to the ecology of the North Cascades in Washington state, which has the largest concentration of active alpine glaciers in the Lower 48’s. The densely forested areas found in Northern California, Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Montana have mostly species adapted to living in temperate climates, while Southern California, Nevada, Arizona, southern Utah, and New Mexico have a fauna resembling its position in the dry deserts with temperature extremes.
The western continental coast of the U.S., just as the East Coast, varies from a colder-to-warmer climate from north to south. Few species live throughout the entire West Coast, however, there are some, including the American Bald Eagle that inhabits both the Alaskan Aleutian Islands and the California Channel Islands. In most of the contiguous Western U.S. are mule deer, white-tailed antelope squirrels, cougars, American badgers, coyotes, hawks and several species of snakes and lizards are common.
While the American black bear lives throughout the U.S., the brown bears and grizzly bears are more common in the northwest and in Alaska. Along the West Coast there are several species of whales, sea otters, California sea lions, eared seals and northern elephant seals. In the dry, inland desert areas of states such as California, Nevada, Arizona and New Mexico there are some of the world’s most venomous lizards, snakes and scorpions. The most notorious might be the Gila monster and Mohave rattlesnake, both found in deserts in the Southwest. The Sonoran Desert has eleven species of rattlesnakes - more than anywhere else in the world.
Along the southwestern border there are jaguars and ocelots. Other mammals include the Virginia opossum, which occurs throughout California and coastal areas in Oregon and Washington. The North American beaver and mountain beaver live in forested areas of Washington, Oregon and Northern California. The kit fox lives throughout Arizona, New Mexico and Utah, while the gray fox occurs throughout the Western U.S.
The red fox occurs mostly in Oregon and Washington, while the island fox is a native to six of the eight Channel Islands in Southern California. These islands are also famous for their marine life and endemic species such as the Channel Islands spotted skunk, Garibaldi, island fence lizard, island scrub jay, bald eagle, and their non-native Catalina Island bison herd. The raccoon and spotted skunk occur throughout the Western U.S., while the ring-tailed cat occurs throughout Arizona, New Mexico, Western Texas, Utah, Colorado, and most of California. The American black bear occurs in most western states, including Washington, Oregon, California, Arizona and Colorado.
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands National Park consists of five out of the eight California Channel Islands. The Channel Islands are part of one of the richest marine biospheres of the world. Many unique species of plants and animals are endemic to the Channel Islands, including fauna such as the island fox, Channel Islands spotted skunk, island scrub jay, ashy storm-petrel, island fence lizard, island night lizard, Channel Islands slender salamander, Santa Cruz sheep, San Clemente loggerhead shrike and San Clemente sage sparrow. Other animals in the islands include the California sea lion, California moray, bald eagle, Channel Islands spotted skunk and the non-native Catalina Island bison herd.History
The Western United States has been populated by Native Americans since at least 11,000 years ago, when the first Paleo-Indians arrived. Pre-Columbian trade routes to kingdoms and empires such as the Mound Builders existed in places such as Yellowstone National Park since around 1000 AD. Major settlement of the western territories developed rapidly in the 1840s, largely through the Oregon Trail and the California Gold Rush of 1849. California experienced such a rapid growth in a few short months that it was admitted to statehood in 1850 without the normal transitory phase of becoming an official territory.
One of the largest migrations in American history occurred in the 1840s as the Latter Day Saints left the Midwest to build a theocracy in Utah.
Both Omaha, Nebraska and St. Louis, Missouri laid claim to the title, "Gateway to the West" during this period. Omaha, home to the Union Pacific Railroad and the Mormon Trail, made its fortunes on outfitting settlers; St. Louis built itself upon the vast fur trade in the West before its settlement.
The 1850s were marked by political battles over the expansion of slavery into the western territories, issues leading to the Civil War.
Between 1863 and 1869, North America's first transcontinental railroad was constructed to connect the eastern US with the Pacific coast. The resulting railroad connection revolutionized the settlement and economy of the American West by making the transportation of passengers and freight quicker, safer, and cheaper.

The history of the American West in the late 19th and early 20th centuries has acquired a cultural mythos in the literature and cinema of the United States. The image of the cowboy, the homesteader, and westward expansion took real events and transmuted them into a myth of the west which has shaped much of American popular culture since the late 19th century.
Writers as diverse as Bret Harte and Zane Grey celebrated or derided cowboy culture, while artists such as Frederic Remington created western art as a method of recording the expansion into the west. The American cinema, in particular, created the genre of the western movie, which, in many cases, use the West as a metaphor for the virtue of self-reliance and an American ethos. The contrast between the romanticism of culture about the West and the actuality of the history of the westward expansion has been a theme of late 20th and early 21st century scholarship about the West. Cowboy culture has become embedded in the American experience as a common cultural touchstone, and modern forms as diverse as country and western music have celebrated the sense of isolation and independence of spirit inspired by the frontiersmen on "virgin land".
20th century

The advent of the automobile enabled the average American to tour the West. Western businessmen promoted Route 66 as a means to bring tourism and industry to the West. In the 1950s, representatives from all the western states built the Cowboy Hall of Fame and Western Heritage Center to showcase western culture and greet travelers from the East. During the latter half of the 20th century, several transcontinental interstate highways crossed the West bringing more trade and tourists from the East. Oil boom towns in Texas and Oklahoma rivaled the old mining camps for their rawness and wealth. The Dust Bowl forced children of the original homesteaders even further west.
The movies became America's chief entertainment source featuring western fiction, later the community of Hollywood in Los Angeles became the headquarters of the mass media such as radio and television production.
California has emerged as the most populous state and one of the top 10 economies in the world. Massive late 19th–20th century population and settlement booms created two megalopolis areas of the Greater Los Angeles/Southern California and the San Francisco Bay Area/Northern California regions, one of the nation's largest metropolitan areas and in the top 25 largest urban areas in the world. Five more metropolitan areas of San Bernardino-Riverside, San Diego, Denver, Phoenix, and Seattle have over a million residents, while the three fastest growing metro areas were the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, the Las Vegas metropolitan area; and the Portland metropolitan area.
Since the mid-1970s, historians of the West have emphasized the World War II years as a major watershed, as a region experienced enormous social and economic change, and became the pacesetter for societal evolution. The population soared, especially in metropolitan areas, as a result of massive expansion of the manufacture of airplanes, ships and munitions and of military and Naval training facilities. California upgraded universities to world-class status, intensified scientific research, and expanded infrastructure. After the war millions more migrated using the GI Bill to buy suburban homes, many of them recalling rewarding wartime experience in military training facilities. The region had always been more democratic with greater racial and gender equality, and continued as a national pacesetter in modernization. New problems emerged, especially environmental issues where westerners took the lead in areas such as the allocation of scarce water resources as well as dealing with smog and air pollution. More recently historians have looked at nuances, pointing out that some of the trends began before 1941.
Los Angeles has the largest Mexican population outside of Mexico, while San Francisco has the largest Chinese community in North America and also has a large LGBT community, and Oakland, California has a large percentage of residents being African-American, as well as Long Beach, California which also has a significant black community. The state of Utah has a Mormon majority (estimated at 62.4% in 2004), while some cities like Albuquerque, New Mexico; Billings, Montana; Spokane, Washington; and Tucson, Arizona are located near Indian reservations. In remote areas there are settlements of Alaskan Natives and Native Hawaiians.
Culture


Historically, the traditional culture of the Western United States has been defined by the cowboys, pioneers, and Native Americans who first inhabited the Wild West. The sparse geography of the western deserts (Mojave Desert, Great Basin Desert) and isolated small towns, combined with the broad freeways (U.S. Route 66) and long railroads (First transcontinental railroad), have contributed to the popular image of the west as a desolate, open space full of unending roads.
Facing both the Pacific Ocean and the Mexican border, the West has been shaped by a variety of ethnic groups. Hawaii is the only state in the union in which Asian Americans outnumber white American residents. People from many countries in Asia settled in California and other coastal states in several waves of immigration since the 19th century, contributing to the Gold rush, the building of the transcontinental railroad, agriculture, and more recently, high technology.
The border states—California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas—and other southwestern states such as Colorado, Utah, and Nevada all have large Hispanic populations, and the many Spanish place names attest to their history as former Spanish and Mexican territories. Mexican-Americans have also had a growing population in Northwestern states of Oregon and Washington, as well as the southern states of Texas and Oklahoma.

In the Pacific States, the wide areas filled with small towns, farms, and forests are supplemented by a few big port cities which have evolved into world centers for the media and technology industries. Now the second largest city in the nation, Los Angeles is best known as the home of the Hollywood film industry; the area around Los Angeles also was a major center for the aerospace industry by World War II, though Boeing, located in Washington state would lead the aerospace industry. Fueled by the growth of Los Angeles, as well as the San Francisco Bay area, including Silicon Valley, the center of America's high tech industry, California has become the most populous of all the 50 states. Oregon and Washington have also seen rapid growth with the rise of Boeing and Microsoft along with agriculture and resource based industries.
Alaska—the northernmost state in the Union—is a vast land of few people, many of them native, and of great stretches of wilderness, protected in national parks and wildlife refuges. Hawaii's location makes it a major gateway between the United States and Asia, as well as a center for tourism.
The Mountain States subregion includes Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming. The mountain states have relatively low population densities, and developed as ranching and mining areas that only recently became urbanized. Most of them have highly individualistic cultures, and have worked to balance the interests of urban development, recreation, and the environment.
Culturally distinctive points of the mountain states include the large Mormon population in the Mormon Corridor, including southeastern Idaho, Utah, Northern Arizona, and Nevada; the extravagant casino resort towns of Las Vegas and Reno, Nevada; and the numerous American Indian tribal reservations.
Major metropolitan areas
These are the largest Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSA) with a population above 500,000 in the 13 Western states. Population figures are as of April 1, 2020, as enumerated by the United States Census Bureau:
Other population centers
- The MSA of El Paso, although belonging to Texas, considered part of the Southern United States, it is sometimes also considered part of the Western United States. Its enumerated population in April 2020 was 868,859.
- The largest MSA in Alaska is Anchorage; it has an enumerated population of 398,328, as of April 2020.
- In the outlying areas of the Western United States, the largest population centers are Tafuna in American Samoa; Dededo in Guam; and Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands.
See also
 In Spanish: Oeste de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Oeste de Estados Unidos para niños