Small intestine facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Small intestine |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
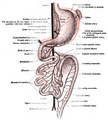
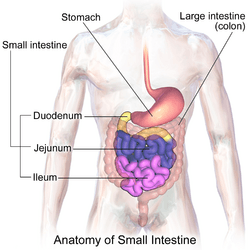
| Diagram showing the small intestine and surrounding structures | |
| Latin | Intestinum tenue |
| System | Digestive system |
| Artery | Superior mesenteric artery |
| Vein | Hepatic portal vein |
| Nerve | Celiac ganglia, vagus |
| Lymph | Intestinal lymph trunk |
The small intestine is between the stomach and the large intestine. In humans over 5 years old, a small intestine may be five to six meters long. It is where most of the digestion and absorption happens.
The small intestine has three regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
- The duodenum receives bile and juice from the pancreas. It is where most digestion takes place. Secretions neutralise the stomach acidity, and enzymes digest the food.
- The jejenum: the products of digestion (sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids) are absorbed into the bloodstream here.
- The ileum: absorbs vitamin B12 and bile salts and any products of digestion which were not absorbed by the jejunum.
Structure
The small intestine is divided into three structural parts.
- The duodenum is a short structure ranging from 20 cm (7.9 inches) to 25 cm (9.8 inches) in length, and shaped like a "C". It surrounds the head of the pancreas. It receives gastric chyme from the stomach, together with digestive juices from the pancreas (digestive enzymes) and the liver (bile). The digestive enzymes break down proteins and bile emulsifies fats into micelles. The duodenum contains Brunner's glands, which produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion containing bicarbonate. These secretions, in combination with bicarbonate from the pancreas, neutralize the stomach acids contained in gastric chyme.
- The jejunum is the midsection of the small intestine, connecting the duodenum to the ileum. It is about 2.5 m long, and contains the plicae circulares, and villi that increase its surface area. Products of digestion (sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids) are absorbed into the bloodstream here. The suspensory muscle of duodenum marks the division between the duodenum and the jejunum.
- The ileum: The final section of the small intestine. It is about 3 m long, and contains villi similar to the jejunum. It absorbs mainly vitamin B12 and bile acids, as well as any other remaining nutrients. The ileum joins to the cecum of the large intestine at the ileocecal junction.
Images for kids
-
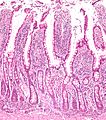
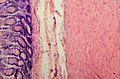
Micrograph of the small intestine mucosa showing the intestinal villi and crypts of Lieberkühn.
-
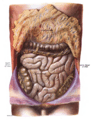
Small intestine in situ, greater omentum folded upwards.
See also
 In Spanish: Intestino delgado para niños
In Spanish: Intestino delgado para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Small intestine Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.