Brunner's glands facts for kids
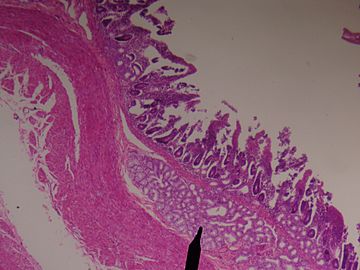
Brunner's glands (or duodenal glands) are compound tubular submucosal glands found in that portion of the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter (i.e sphincter of Oddi). The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion i.e. mucous (containing bicarbonate) in order to:
- protect the duodenum from the acidic content of chyme (which is introduced into the duodenum from the stomach);
- provide an alkaline condition for the intestinal enzymes to be active, thus enabling absorption to take place;
- lubricate the intestinal walls.
They also secrete a protein that stimulates cell growth, which inhibits cells of the stomach from secreting acid and their digestive enzymes. This is another form of protection for the duodenum.
They are the distinguishing feature of the duodenum, and are named for the Swiss physician who first described them, Johann Conrad Brunner.

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Brunner's glands Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.