Digestive enzyme facts for kids
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down food molecules into their smaller building blocks, so they can be absorbed by the body.
Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals (including humans) and in the tracts of carnivorous plants, where they aid in the digestion of food.
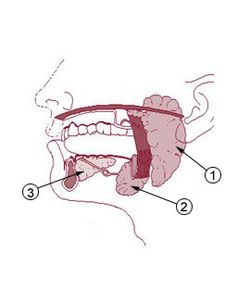
They are found in the saliva secreted by the salivary glands, in the secretions of cells lining the stomach, in the pancreatic juice secreted by pancreatic cells, and in the secretions of cells lining the small and large intestines.
Digestive enzymes are classified based on their target substrates:
- Lipases split fatty acids off of fats and oils.
- Proteases and peptidases split proteins into small peptides and amino acids.
- Amylases split carbohydrates such as starch and sugars into simple sugars such as glucose.
- Nucleases split nucleic acids into nucleotides.
In the human digestive system, the main sites of digestion are the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Digestive enzymes are secreted by different glands including:
- Salivary glands
- Gastric glands in the stomach
- Secretory cells (islets) in the pancreas
- Secretory glands in the small intestine
See also
 In Spanish: Enzima digestiva para niños
In Spanish: Enzima digestiva para niños