Haiti facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Haiti
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto:
"Liberté, égalité, fraternité" (French)
Motto on traditional coat of arms:"Libète, Egalite, Fratènite" (Haitian Creole) "Liberty, Equality, Fraternity" "L'union fait la force" (French) "Inite se fòs" (Haitian Creole) "Union makes strength" |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Port-au-Prince 18°32′N 72°20′W / 18.533°N 72.333°W |
| Official languages |
|
| Ethnic groups | 95% Black 5% Mixed or White |
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Haitian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic under an interim government |
|
|
| Alix Didier Fils-Aimé (acting) | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Senate (vacant) | |
| Chamber of Deputies (vacant) | |
| Independence from France | |
|
• Independence declared
|
1 January 1804 |
|
• Independence recognized
|
17 April 1825 |
|
• First Empire
|
22 September 1804 |
|
• Southern Republic
|
9 March 1806 |
|
• Northern State
|
17 October 1806 |
|
• Kingdom
|
28 March 1811 |
|
• Unification of Hispaniola
|
9 February 1822 |
|
• Dissolution
|
27 February 1844 |
|
• Second Empire
|
26 August 1849 |
|
• Republic
|
15 January 1859 |
| 28 July 1915 – 1 August 1934 | |
|
• Independence from the United States
|
15 August 1934 |
|
• Current constitution
|
29 March 1987 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
27,750 km2 (10,710 sq mi) (143rd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.7 |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
11,470,261 (83rd) |
|
• Density
|
382/km2 (989.4/sq mi) (32nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2012) | 41.1 medium |
| HDI (2022) | medium · 158th |
| Currency | Gourde (G) (HTG) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +509 |
| ISO 3166 code | HT |
| Internet TLD | .ht |
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration. Haiti is 27,750 km2 (10,714 sq mi) in size, the third largest country in the Caribbean by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the most populous country in the Caribbean. The capital is Port-au-Prince.
The island was originally inhabited by the indigenous Taíno people, who originated in South America. The first Europeans arrived on 5 December 1492 during the first voyage of Christopher Columbus, who initially believed he had found India or China. Columbus subsequently founded the first European settlement in the Americas, La Navidad, on what is now the northeastern coast of Haiti. The island was claimed by Spain and named La Española, forming part of the Spanish Empire until the early 17th century. However, competing claims and settlements by the French led to the western portion of the island being ceded to France in 1697, which was subsequently named Saint-Domingue. French colonists established lucrative sugarcane plantations, worked by vast numbers of slaves brought from Africa, which made the colony one of the richest in the world.
In the midst of the French Revolution (1789–99), slaves, maroons, and free people of color launched the Haitian Revolution (1791–1804), led by a former slave and the first black general of the French Army, Toussaint Louverture. After 12 years of conflict, Napoleon Bonaparte's forces were defeated by Louverture's successor, Jean-Jacques Dessalines (later Emperor Jacques I), who declared Haiti's sovereignty on 1 January 1804—the first independent nation of Latin America and the Caribbean, the second republic in the Americas, the first country in the Americas to eliminate slavery, and the only state in history established by a successful slave revolt. Apart from Alexandre Pétion, the first President of the Republic, all of Haiti's first leaders were former slaves. After a brief period in which the country was split in two, President Jean-Pierre Boyer united the country and then attempted to bring the whole of Hispaniola under Haitian control, precipitating a long series of wars that ended in the 1870s when Haiti formally recognized the independence of the Dominican Republic.
Haiti's first century of independence was characterized by political instability. Political volatility and foreign economic influence in the country prompted the United States to occupy the country from 1915 to 1934. Following a series of short-lived presidencies, François 'Papa Doc' Duvalier took power in 1956, ushering in a long period of autocratic rule continued by his son, Jean-Claude 'Baby Doc' Duvalier, that lasted until 1986; the period was characterized by state-sanctioned violence against the opposition and civilians, corruption, and economic stagnation. After 1986, Haiti began attempting to establish a more democratic political system.
Haiti is a founding member of the United Nations, Organization of American States (OAS), Association of Caribbean States, and the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. In addition to CARICOM, it is a member of the International Monetary Fund, World Trade Organization, and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States. Historically poor and politically unstable, Haiti has the lowest Human Development Index in the Americas, as well as widespread slavery. Since the turn of the 21st century, the country has endured a coup d'état, which prompted U.N. intervention, as well as a catastrophic earthquake that killed over 250,000 people and a cholera outbreak. With its deteriorating economic situation, as well as recent calls by the IMF to cut fuel subsidies, Haiti has been experiencing a socioeconomic and political crisis marked by riots and protests, widespread hunger, and increased gang activity. As of February 2023, Haiti has no elected government officials and has been described as a failed state.
Contents
Etymology
Haiti (also earlier Hayti) comes from the indigenous Taíno language, in which it means "land of high mountains" and named the entire island of Hispaniola. The name was restored by Haitian revolutionary Jean-Jacques Dessalines as the official name of independent Saint-Domingue, as a tribute to the Amerindian predecessors.
In French, the ï in Haïti has a diacritical mark (used to show that the second vowel is pronounced separately, as in the word naïve), while the H is silent. (In English, this rule for the pronunciation is often disregarded, thus the spelling Haiti is used.) There are different anglicizations for its pronunciation such as HIGH-ti, high-EE-ti and haa-EE-ti, which are still in use, but HAY-ti is the most widespread and best-established. In French, Haiti's nickname means the "Pearl of the Antilles" (La Perle des Antilles) because of both its natural beauty and the amount of wealth it accumulated for the Kingdom of France. During the 18th century, the colony was the world's leading producer of sugar and coffee.
In Haitian Creole, it is spelled and pronounced with a y but no H: Ayiti.
Another theory on the name Haiti is its origin in African tradition, in Fon language one of the most spoken by the bossales (Haitians born in Africa to differentiate from the creoles or Haitians born in Haiti (St-Domingue) in early Haiti, Ayiti-Tomè means: From nowadays this land is our land.
In the Haitian community the country has multiple nicknames: Ayiti-Toma (as its origin in Ayiti Tomè), Ayiti-Cheri (Ayiti my Darling), Tè-Desalin (Dessalines' Land) or Lakay (Home).
History
Geography
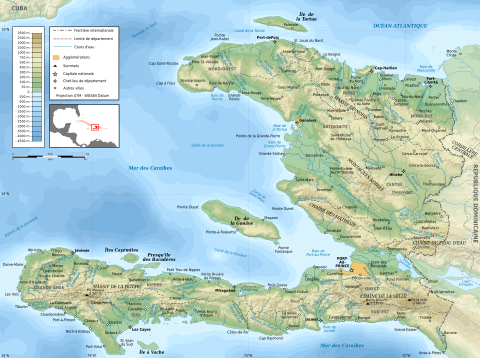
Haiti forms the western three-eighths of Hispaniola, the second largest island in the Greater Antilles. At 27,750 km2 (10,710 sq mi) Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean behind Cuba and the Dominican Republic, the latter sharing a 360-kilometer (224 mi) border with Haiti. The country has a roughly horseshoe shape and because of this it has a disproportionately long coastline, second in length (1,771 km or 1,100 mi) behind Cuba in the Greater Antilles.
Haiti is the most mountainous nation in the Caribbean, its terrain consists of mountains interspersed with small coastal plains and river valleys. The climate is tropical, with some variation depending on altitude. The highest point is Pic la Selle, at 2,680 meters (8,793 ft).
The northern region or Marien Region consists of the Massif du Nord (Northern Massif) and the Plaine du Nord (Northern Plain). The Massif du Nord is an extension of the Cordillera Central in the Dominican Republic. It begins at Haiti's eastern border, north of the Guayamouc River, and extends to the northwest through the northern peninsula. The lowlands of the Plaine du Nord lie along the northern border with the Dominican Republic, between the Massif du Nord and the North Atlantic Ocean.
The central region or Artibonite Region consists of two plains and two sets of mountain ranges. The Plateau Central (Central Plateau) extends along both sides of the Guayamouc River, south of the Massif du Nord. It runs from the southeast to the northwest. To the southwest of the Plateau Central are the Montagnes Noires, whose most northwestern part merges with the Massif du Nord. Haiti's most important valley in terms of crops is the Plaine de l'Artibonite, which lies between the Montagnes Noires and the Chaîne des Matheux. This region supports the country's (also Hispaniola's) longest river, the Riviere l'Artibonite, which begins in the western region of the Dominican Republic and continues for most of its length through central Haiti, where it then empties into the Golfe de la Gonâve. Also in this valley lies Haiti's second largest lake, Lac de Péligre, formed as a result of the construction of the Péligre Dam in the mid-1950s.

The southern region or Xaragua Region consists of the Plaine du Cul-de-Sac (the southeast) and the mountainous southern peninsula (also known as the Tiburon Peninsula). The Plaine du Cul-de-Sac is a natural depression that harbors the country's saline lakes, such as Trou Caïman and Haiti's largest lake, Étang Saumatre. The Chaîne de la Selle mountain range – an extension of the southern mountain chain of the Dominican Republic (the Sierra de Baoruco) – extends from the Massif de la Selle in the east to the Massif de la Hotte in the west.
Haiti also includes several offshore islands. The island of Tortuga (Île de la Tortue) is located off the coast of northern Haiti. The arrondissement of La Gonâve is located on the island of the same name, in the Golfe de la Gonâve; Haiti's largest island, Gonâve is moderately populated by rural villagers. Île à Vache (Cow Island) is located off the southwest coast; also part of Haiti are the Cayemites, located in the Gulf of Gonâve north of Pestel. La Navasse (Navassa Island), located 40 nautical miles (46 mi; 74 km) west of Jérémie on the south west peninsula of Haiti, is subject to an ongoing territorial dispute with the United States, who currently administer the island via the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
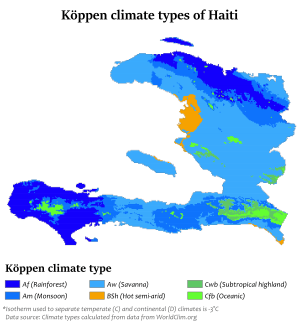
Climate
Haiti's climate is tropical with some variation depending on altitude. Port-au-Prince ranges in January from an average minimum of 23 °C (73.4 °F) to an average maximum of 31 °C (87.8 °F); in July, from 25–35 °C (77–95 °F). The rainfall pattern is varied, with rain heavier in some of the lowlands and the northern and eastern slopes of the mountains. Haiti's dry season occurs from November to January.
Port-au-Prince receives an average annual rainfall of 1,370 mm (53.9 in). There are two rainy seasons, April–June and October–November. Haiti is subject to periodic droughts and floods, made more severe by deforestation. Hurricanes are a menace, and the country is also prone to flooding and earthquakes.
Geology
There are blind thrust faults associated with the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault system over which Haiti lies. After the earthquake of 2010, there was no evidence of surface rupture and geologists' findings were based on seismological, geological and ground deformation data.
The northern boundary of the fault is where the Caribbean tectonic plate shifts eastwards by about 20 mm (0.79 inches) per year in relation to the North American plate. The strike-slip fault system in the region has two branches in Haiti, the Septentrional-Oriente fault in the north and the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault in the south.
A 2007 earthquake hazard study, noted that the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone could be at the end of its seismic cycle and concluded that a worst-case forecast would involve a 7.2 Mw earthquake, similar in size to the 1692 Jamaica earthquake. A study team presented a hazard assessment of the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault system to the 18th Caribbean Geologic Conference in March 2008, noting the large strain. The team recommended "high priority" historical geologic rupture studies, as the fault was fully locked and had recorded few earthquakes in the preceding 40 years. An article published in Haiti's Le Matin newspaper in September 2008 cited comments by geologist Patrick Charles to the effect that there was a high risk of major seismic activity in Port-au-Prince; and duly the magnitude 7.0 2010 Haiti earthquake happened on this fault zone on 12 January 2010.
Haiti also has rare elements such as gold, which can be found at The Mont Organisé gold mine.
Haiti has no currently active volcanoes. "In the Terre-Neuve Mountains, about 12 kilometers from the Eaux Boynes, small intrusions at least as late as Oligocene and probably of Miocene age are known. No other volcanic activity of as late a date is known near any of the other warm springs."
Environment

The soil erosion released from the upper catchments and deforestation have caused periodic and severe flooding in Haiti, as experienced, for example, on 17 September 2004. Earlier in May that year, floods had killed over 3,000 people on Haiti's southern border with the Dominican Republic.
Haiti's forests covered 60% of the country as recently as 50 years ago, but that has been halved to a current estimate of 30% tree cover, according to more recent environmental analysis. This estimate poses a stark difference from the erroneous figure of 2% which has been oft-cited in discourse concerning the country's environmental condition. Haiti had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 4.01/10, ranking it 137th globally out of 172 countries.
Scientists at the Columbia University's Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) and the United Nations Environment Programme are working on the Haiti Regenerative Initiative an initiative aiming to reduce poverty and natural disaster vulnerability in Haiti through ecosystem restoration and sustainable resource management.
Biodiversity
Haiti is home to four ecoregions: Hispaniolan moist forests, Hispaniolan dry forests, Hispaniolan pine forests, and Greater Antilles mangroves.
Despite its small size, Haiti's mountainous terrain and resultant multiple climatic zones has resulted in a wide variety of plant life. Notable tree species include the breadfruit tree, mango tree, acacia, mahogany, coconut palm, royal palm and West Indian cedar. The forests were formerly much more extensive, but have been subject to severe deforestation.
Most mammal species are not native, having been brought to the island since colonial times. However there are various native bat species, as well as the endemic Hispaniolan hutia and Hispaniolan solenodon. Various whale and dolphin species can also be found off Haiti's coast.
There are over 260 species of bird, 31 of these being endemic to Hispaniola. Notable endemic species include the Hispaniolan trogon, Hispaniolan parakeet, grey-crowned tanager and the Hispaniolan Amazon. There are also several raptor species, as well as pelicans, ibis, hummingbirds and ducks.
Reptiles are common, with species such as the rhinoceros iguana, Haitian boa, American crocodile and gecko.
Government and politics
The government of Haiti is a semi-presidential republic, a multiparty system wherein the president of Haiti is head of state and elected directly by popular elections held every five years. The prime minister of Haiti acts as head of government and is appointed by the president, chosen from the majority party in the National Assembly. Executive power is exercised by the president and prime minister who together constitute the government.
Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of the National Assembly of Haiti, the Senate (Sénat) and the Chamber of Deputies (Chambre des Députés). The government is organized unitarily, thus the central government delegates powers to the departments without a constitutional need for consent. The current structure of Haiti's political system was set forth in the Constitution of Haiti on 29 March 1987.
Haitian politics have been contentious: since independence, Haiti has suffered 32 coups. Haiti is the only country in the Western Hemisphere to undergo a successful slave revolution; however, a long history of oppression by dictators such as François Duvalier and his son Jean-Claude Duvalier has markedly affected the nation. Since the end of the Duvalier era Haiti has been transitioning to a democratic system.
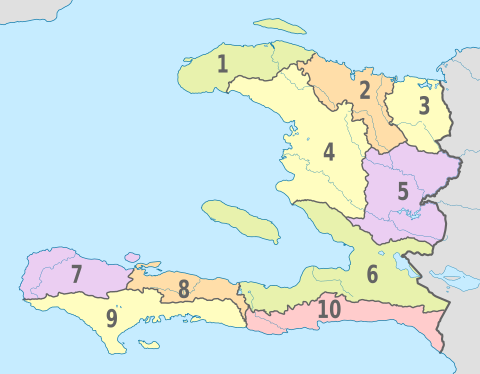
Administrative divisions
Administratively, Haiti is divided into ten departments. The departments are listed below, with the departmental capital cities in parentheses.
- Nord-Ouest (Port-de-Paix)
- Nord (Cap-Haïtien)
- Nord-Est (Fort-Liberté)
- Artibonite (Gonaïves)
- Centre (Hinche)
- Ouest (Port-au-Prince)
- Grand'Anse (Jérémie)
- Nippes (Miragoâne)
- Sud (Les Cayes)
- Sud-Est (Jacmel)
The departments are further divided into 42 arrondissements, 145 communes and 571 communal sections. These serve as, respectively, second- and third-level administrative divisions.
Foreign relations
Haiti is a member of a wide range of international and regional organizations, such as the United Nations, CARICOM, Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, International Monetary Fund, Organisation of American States, Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, OPANAL and the World Trade Organization.
In February 2012, Haiti signaled it would seek to upgrade its observer status to full associate member status of the African Union (AU). The AU was reported to be planning to upgrade Haiti's status from observer to associate at its June 2013 summit but the application had still not been ratified by May 2016.
Military
Haiti has a strong military history dating to the pre-independence struggle. The Indigenous Army is essential in the construction of the state the management of land and public finances. Up to the 20th century, every Haitian president was an officer in the army. During the US intervention, the army was remodeled as Gendarmerie d'Haiti and later on as Force Armée d'Haiti (FAdH). In the early '90s, the army was unconstitutionally decommissioned and replaced by the Haitian National Police (PNH). In 2018, Président Jovenel Moise reactivated the FAdH.
Haiti's Ministry of Defense is the main body of the armed forces. The former Haitian Armed Forces were demobilized in 1995, however efforts to reconstitute it are currently underway. The current defense force for Haiti is the Haitian National Police, which has a highly trained SWAT team, and works alongside the Haitian Coast Guard. In 2010, the Haitian National Police force numbered 7,000.
Economy
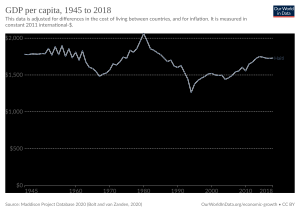
Haiti has a highly regulated, predominantly state-controlled economy, ranking 145th out of the 177 countries given a "freedom index" by the Heritage Foundation. Haiti's per capita GDP is $1,800 and its GDP is $19.97 billion (2017 estimates). The country uses the Haitian gourde as its currency. Despite its tourism industry, Haiti is one of the poorest countries in the Americas, with corruption, political instability, poor infrastructure, lack of health care and lack of education cited as the main causes. Unemployment is high and many Haitians seek to emigrate. Trade declined dramatically after the 2010 earthquake and subsequent outbreak of cholera, with the country's purchasing power parity GDP falling by 8% (from US$12.15 billion to US$11.18 billion). Haiti ranked 145th of 182 countries in the 2010 United Nations Human Development Index, with 57.3% of the population being deprived in at least three of the HDI's poverty measures.
Following the disputed 2000 election and accusations about President Aristide's rule, US aid to the Haitian government was cut off between 2001 and 2004. After Aristide's departure in 2004, aid was restored and the Brazilian army led a United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti peacekeeping operation. After almost four years of recession, the economy grew by 1.5% in 2005. In September 2009, Haiti met the conditions set out by the IMF and World Bank's Heavily Indebted Poor Countries program to qualify for cancellation of its external debt.
More than 90 percent of the government's budget comes from an agreement with Petrocaribe, a Venezuela-led oil alliance.
Foreign aid
Haiti received more than US$4 billion in aid from 1990 to 2003, including US$1.5 billion from the United States. The largest donor is the US, followed by Canada and the European Union. In January 2010, following the earthquake, US President Barack Obama promised US$1.15 billion in assistance. European Union nations pledged more than €400 million (US$616 million). Neighboring Dominican Republic has also provided extensive humanitarian aid to Haiti, including the funding and construction of a public university, human capital, free healthcare services in the border region, and logistical support after the 2010 earthquake.
The United Nations states that in total US$13.34 billion has been earmarked for post-earthquake reconstruction through 2020, though two years after the 2010 quake, less than half of that amount had actually been released, according to UN documents. As of 2015[update], the US government has allocated US$4 billion, US$3 billion has already been spent, and the rest is dedicated to longer-term projects.
Trade
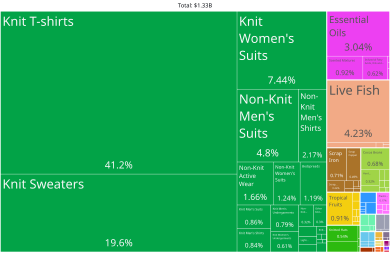
According to the 2015 CIA World Factbook, Haiti's main import partners are: Dominican Republic 35%, US 26.8%, Netherlands Antilles 8.7%, China 7% (est. 2013). Haiti's main export partner is the US 83.5% (est. 2013). Haiti had a trade deficit of US$3 billion in 2011, or 41% of GDP.
Energy
In 1925, the city of Jacmel was the first area in the Caribbean to have electricity and was subsequently dubbed the City of Light.
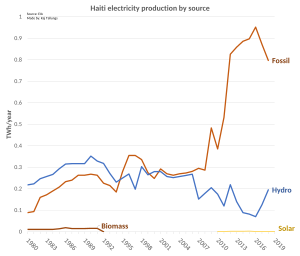
Today, Haiti relies heavily on an oil alliance with Petrocaribe for much of its energy requirements. In recent years, hydroelectric, solar and wind energy have been explored as possible sustainable energy sources.
As of 2017, among all the countries in the Americas, Haiti is producing the least energy. Less than a quarter of the country has electric coverage. Most regions of Haiti that do have energy are powered by generators. These generators are often expensive and produce a lot of pollution. The areas that do get electricity experience power cuts on a daily basis, and some areas are limited to 12 hours of electricity a day. Electricity is provided by a small number of independent companies: Sogener, E-power, and Haytrac. There is no national electricity grid within the country. The most common source of energy used is wood, along with charcoal. In Haiti, about 4 million metric tons of wood products are consumed yearly. Like charcoal and wood, petroleum is also an important source of energy for Haiti. Since Haiti cannot produce its own fuel, all fuel is imported. Yearly, around 691,000 tons of oil is imported into the country.
On 31 October 2018, Evenson Calixte, the General Director of energy regulation (ANARSE) announced the 24 hour electricity project. To meet this objective, 236 MW needs to installed in Port-au-Prince alone, with an additional 75 MW needed in all other regions in the country. Presently only 27.5% of the population has access to electricity; moreover, the national energy agency l'Électricité d'Haïti (Ed'H) is only able to meet 62% of overall electricity demand said Fritz Caillot, the Minister of Public Works, Transportation and Communication (Travaux publics, transport et communication (TPTC)).
Personal income

Haiti suffers from a shortage of skilled labor, widespread unemployment, and underemployment. Most Haitians in the labor force have informal jobs. Three-quarters of the population lives on US$2 or less per day.
Remittances from Haitians living abroad are the primary source of foreign exchange, equaling one-fifth (20%) of GDP and more than five times the earnings from exports as of 2012. In 2004, 80% or more of college graduates from Haiti were living abroad.
Occasionally, families who are unable to care for children financially may send them to live with a wealthier family as a restavek, or house servant. In return the family are supposed to ensure that the child is educated and provided with food and shelter, however the system is open to abuse and has proved controversial.
Real estate
In rural areas, people often live in wooden huts with corrugated iron roofs. Outhouses are located in back of the huts. In Port-au-Prince, colorful shantytowns surround the central city and go up the mountainsides.
The middle and upper classes live in suburbs, or in the central part of the bigger cities in apartments, where there is urban planning. Many of the houses they live in are like miniature fortresses, located behind walls embedded with metal spikes, barbed wire, broken glass, and sometimes all three. The gates to these houses are barred at night, the house is locked; guard dogs patrol the yard. These houses are often self-sufficient as well. The houses have backup generators, because the electrical grid in Haiti is unreliable. Some even have rooftop reservoirs for water, as the water supply is also unreliable.
Agriculture
Haiti is the world's leading producer of vetiver, a root plant used to make luxury perfumes, essential oils and fragrances, providing for half the world's supply. Roughly 40–50% of Haitians work in the agricultural sector. However, According to soil surveys by the United States Department of Agriculture in the early 1980s, only 11.3 percent of the land was highly suitable for crops. Haiti relies upon imports for half its food needs and 80% of its rice.
Haiti exports crops such as mangoes, cacao, coffee, papayas, mahogany nuts, spinach, and watercress. Agricultural products constitute 6% of all exports. In addition, local agricultural products include maize, beans, cassava, sweet potato, peanuts, pistachios, bananas, millet, pigeon peas, sugarcane, rice, sorghum, and wood.
Currency
The Haitian gourde (HTG) is the national currency. The "Haitian dollar" equates to 5 gourdes (goud), which is a fixed exchange rate that exists in concept only, but are commonly used as informal prices. The vast majority of the business sector and individuals in Haiti will also accept US dollars, though at the outdoor markets gourdes may be preferred. Locals may refer to the USD as "dollar américain" (dola ameriken) or "dollar US" (pronounced oo-es).
Tourism
The tourism market in Haiti is undeveloped and the government is heavily promoting this sector. Haiti has many of the features that attract tourists to other Caribbean destinations, such as white sand beaches, mountainous scenery and a year-round warm climate. However, the country's poor image overseas, at times exaggerated, has hampered the development of this sector. In 2014, the country received 1,250,000 tourists (mostly from cruise ships), and the industry generated US$200 million in 2014.
Several hotels were opened in 2014, including an upscale Best Western Premier, a five-star Royal Oasis hotel by Occidental Hotel and Resorts in Pétion-Ville, a four-star Marriott Hotel in the Turgeau area of Port-au-Prince and other new hotel developments in Port-au-Prince, Les Cayes, Cap-Haïtien and Jacmel.
The Haitian Carnival has been one of the most popular carnivals in the Caribbean. In 2010, the government decided to stage the event in a different city outside Port-au-Prince every year in an attempt to decentralize the country. The National Carnival – usually held in one of the country's largest cities (i.e., Port-au-Prince, Cap-Haïtien or Les Cayes) – follows the also very popular Jacmel Carnival, which takes place a week earlier in February or March.
Caracol Industrial Park
On 21 October 2012, Haitian President Michel Martelly, US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, Bill Clinton, Richard Branson, Ben Stiller and Sean Penn inaugurated the 240-hectare (600-acre) Caracol industrial park, the largest in the Caribbean. Costing US$300 million, the project, which includes a 10-megawatt power plant, a water-treatment plant and worker housing, is intended to transform the northern part of the country by creating 65,000 jobs.
The park is part of a "master plan" for Haiti's North and North-East departments, including the expansion of the Cap-Haïtien International Airport to accommodate large international flights, the construction of an international seaport in Fort-Liberté and the opening of the $50 million Roi Henri Christophe Campus of a new university in Limonade (near Cap-Haïtien) on 12 January 2012.
South Korean clothing manufacturer Sae-A Trading Co. Ltd, one of the park's main tenants, has created 5,000 permanent jobs out of the 20,000 projected and has built 8,600 houses in the surrounding area for its workers. The industrial park ultimately has the potential to create as many as 65,000 jobs once fully developed.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Haiti has two main highways that run from one end of the country to the other. The northern highway, Route Nationale No. 1 (National Highway One), originates in Port-au-Prince, winding through the coastal towns of Montrouis and Gonaïves, before reaching its terminus at the northern port Cap-Haïtien. The southern highway, Route Nationale No. 2, links Port-au-Prince with Les Cayes via Léogâne and Petit-Goâve. The state of Haiti's roads are generally poor, many being potholed and becoming impassable in rough weather.
According to The Washington Post, "Officials from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers said Saturday [23 January 2010] that they assessed the damage from the [12 January] quake in Port-au-Prince, Haiti, and found that many of the roads aren't any worse than they were before because they've always been in poor condition."
The port at Port-au-Prince, Port international de Port-au-Prince, has more registered shipping than any of the other dozen ports in the country. The port's facilities include cranes, large berths, and warehouses, but these facilities are not in good condition. The port is underused, possibly due to the substantially high port fees. The port of Saint-Marc is currently the preferred port of entry for consumer goods coming into Haiti. Reasons for this may include its location away from volatile and congested Port-au-Prince, as well as its central location relative to numerous Haitian cities.
In the past, Haiti used rail transport, however the rail infrastructure was poorly maintained when in use and cost of rehabilitation is beyond the means of the Haitian economy. In 2018 the Regional Development Council of the Dominican Republic proposed a "trans-Hispaniola" railway between both countries.
Airports
Toussaint Louverture International Airport, located ten kilometers (six miles) north-northeast of Port-au-Prince proper in the commune of Tabarre, is the primary transportation hub regarding entry and exit into the country. It has Haiti's main jetway, and along with Cap-Haïtien International Airport located near the northern city of Cap-Haïtien, handles the vast majority of the country's international flights. Cities such as Jacmel, Jérémie, Les Cayes, and Port-de-Paix have smaller, less accessible airports that are serviced by regional airlines and private aircraft. Such companies include: Caribintair (defunct), Sunrise Airways and Tortug' Air (defunct).
In 2013, plans for the development of an international airport on Île-à-Vache were introduced by the Prime Minister.
Bus service
Tap tap buses are colorfully painted buses or pick-up trucks that serve as share taxis. The "tap tap" name comes from the sound of passengers tapping on the metal bus body to indicate they want off. These vehicles for hire are often privately owned and extensively decorated. They follow fixed routes, do not leave until filled with passengers, and riders can usually disembark at any point. The decorations are a typically Haitian form of art.
In August 2013, the first coach bus prototype was made in Haiti.
Communications
In Haiti, communications include the radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet. Haiti ranked last among North American countries in the World Economic Forum's Network Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. Haiti ranked number 143 out of 148 overall in the 2014 NRI ranking, down from 141 in 2013.
Water supply and sanitation
Haiti faces key challenges in the water supply and sanitation sector: Notably, access to public services is very low, their quality is inadequate and public institutions remain very weak despite foreign aid and the government's declared intent to strengthen the sector's institutions. Foreign and Haitian NGOs play an important role in the sector, especially in rural and urban slum areas.
Demographics
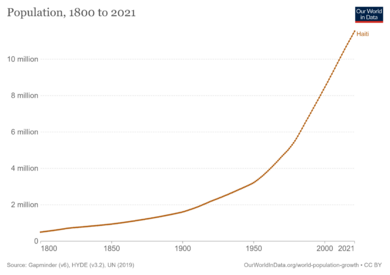
In 2018, Haiti's population was estimated to be about 10,788,000. In 2006, half of the population was younger than age 20. In 1950, the first formal census gave a total population of 3.1 million. Haiti averages approximately 350 people per square kilometer (~900 per sq mi), with its population concentrated most heavily in urban areas, coastal plains, and valleys.
Most Haitians are descendants of former black African slaves, including Mulattoes who are mixed-race. The remainder are of European or Arab descent, the descendants of settlers (colonial remnants and immigration during the era of the two World Wars).
At the time of the Haitian Revolution, an event that involved the eradication of whites (mostly French) in Haiti, many of the blacks in Haiti were African-born and had no non-African ancestry. This was because the average African slave in colonial Haiti had a short life span and France continuously imported thousands of Africans yearly to keep the slave population up, by 1790 there were nearly 600,000 slaves, outnumbering whites about 20 to 1.
Millions of Haitian descent live abroad in the United States, Dominican Republic, Cuba, Canada (primarily Montreal), Bahamas, France, the French Antilles, the Turks and Caicos, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Venezuela, Brazil, Suriname and French Guiana. There were an estimated 881,500 people of Haitian ancestry in the United States in 2015, while in the Dominican Republic there were an estimated 800,000 in 2007. There were 300,000 in Cuba in 2013, 100,000 in Canada in 2006, 80,000 in Metropolitan France (2010), and up to 80,000 in the Bahamas (2009). There are also smaller Haitian communities in many other countries, including Chile, Switzerland, Japan and Australia.
In 2018, the life expectancy at birth was 63.66 years.
Religion
Religion in Haiti according to the Pew Research Center (2010) Catholicism (56.8%) Protestantism (29.6%) Unaffiliated (10.6%) Other (3%)
The 2017 CIA Factbook reported that around 54.7% of Haitians professed to being Catholics while Protestants made up about 28.5% of the population (Baptist 15.4%, Pentecostal 7.9%, Seventh-day Adventist 3%, Methodist 1.5%, other 0.7%). Other sources put the Protestant population higher than this, suggesting that it might have formed one-third of the population in 2001. Like other countries in Latin America, Haiti has witnessed a general Protestant expansion, which is largely Evangelical and Pentecostal in nature.
Haitian Cardinal Chibly Langlois is president of the National Bishops Conference of the Catholic Church.
Vodou, a religion with West African roots similar to those of Cuba and Brazil, is practiced by some Haitians today. It originated during colonial times in which slaves were obliged to disguise their loa (lwa), or spirits, as Catholic saints, an element of a process called syncretism. Due to the religious syncretism between Catholicism and Vodou, it is difficult to estimate the number of Vodouists in Haiti. The religion has historically been persecuted and misrepresented in popular media; nevertheless, in 2003 the Haitian government recognized the faith as an official religion of the nation.
Minority religions in Haiti include Islam, Bahá'í Faith, Judaism, and Buddhism.
Languages
The two official languages of Haiti are French and Haitian Creole. French is the principal written and administratively authorized language (as well as the main language of the press) and is spoken by 42% of Haitians. It is spoken by all educated Haitians, is the medium of instruction in most schools, and is used in the business sector. It is also used in ceremonial events such as weddings, graduations and church Masses. Haiti is one of two independent nations in the Americas (along with Canada) to designate French as an official language; the other French-speaking areas are all overseas départements, or collectivités, of France, such as French Guiana. Haitian Creole is spoken by nearly all of the Haitian population. French, the base language for Haitian Creole, is popular among the Haitian elite and upper classes. French is also popular in the business sector, and to a far lesser degree, English due to American influence. Spanish is spoken by some Haitians who live along the Haitian-Dominican border. English and Spanish may also be spoken by Haitian deportees from the United States and various Latin American countries. Overall, about 90–95% of Haitians only speak Haitian Creole/French fluently, with over half only knowing Creole.
Haitian Creole, which has recently undergone a standardization, is spoken by virtually the entire population of Haiti. Haitian Creole is one of the French-based creole languages. Its vocabulary is 90% derived from French, but its grammar resembles that of some West African languages. It also has influences from Taino, Spanish, and Portuguese. Haitians often colloquially call Haitian Creole Kreyòl. Haitian Creole is related to the other French creoles, but most closely to the Antillean Creole and Louisiana Creole variants.
Emigration
There is a large Haitian diaspora community, predominantly based in the US and Canada, France, and the wealthier Caribbean islands.
Emigrants from Haiti have constituted a segment of American and Canadian society since before the independence of Haiti from France in 1804. Many influential early American settlers and black freemen, including Jean Baptiste Point du Sable and W. E. B. Du Bois, were of Haitian origin.
Jean Baptiste Point du Sable, an immigrant from Saint-Domingue (now the Republic of Haiti), founded the first nonindigenous settlement in what is now Chicago, Illinois, the third largest city in the United States. The state of Illinois and city of Chicago declared du Sable the founder of Chicago on 26 October 1968.
Education
The educational system of Haiti is based on the French system. Higher education, under the responsibility of the Ministry of Education, is provided by universities and other public and private institutions.
More than 80% of primary schools are privately managed by nongovernmental organizations, churches, communities, and for-profit operators, with minimal government oversight. According to the 2013 Millennium Development Goals (MDG) Report, Haiti has steadily boosted net enrollment rate in primary education from 47% in 1993 to 88% in 2011, achieving equal participation of boys and girls in education. Charity organizations, including Food for the Poor and Haitian Health Foundation, are building schools for children and providing necessary school supplies. According to CIA 2015 World Factbook, Haiti's literacy rate is now 60.7% (est. 2015).
The January 2010 earthquake, was a major setback for education reform in Haiti as it diverted limited resources to survival.
Many reformers have advocated the creation of a free, public and universal education system for all primary school-age students in Haiti. The Inter-American Development Bank estimates that the government will need at least US$3 billion to create an adequately funded system.
Upon successful graduation of secondary school, students may continue into higher education. The higher education schools in Haiti include the University of Haiti. There are also medical schools and law schools offered at both the University of Haiti and abroad. Presently, Brown University is cooperating with L'Hôpital Saint-Damien in Haiti to coordinate a pediatric health care curriculum.
Health
In the past, children's vaccination rates have been low – as of 2012[update], 60% of the children in Haiti under the age of 10 were vaccinated, compared to rates of childhood vaccination in other countries in the 93–95% range. Recently there have been mass vaccination campaigns claiming to vaccinate as many as 91% of a target population against specific diseases (measles and rubella in this case). Most people have no transportation or access to Haitian hospitals.
The World Health Organization cites diarrheal diseases, HIV/AIDS, meningitis, and respiratory infections as common causes of death in Haiti. Ninety percent of Haiti's children suffer from waterborne diseases and intestinal parasites. HIV infection is found in 1.71% of Haiti's population (est. 2015). The incidence of tuberculosis (TB) in Haiti is more than ten times as high as in the rest of Latin America. Approximately 30,000 Haitians fall ill with malaria each year.
Most people living in Haiti are at high risk for major infectious diseases. Food or water-borne diseases include bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, typhoid fever and hepatitis A and E; common vector-borne diseases are dengue fever and malaria; water-contact diseases include leptospirosis. Roughly 75% of Haitian households lack running water. Unsafe water, along with inadequate housing and unsanitary living conditions, contributes to the high incidence of infectious diseases. There is a chronic shortage of health care personnel and hospitals lack resources, a situation that became readily apparent after the January 2010 earthquake. The infant mortality rate in Haiti in 2019 was 48.2 deaths per 1,000 live births, compared to 5.6 per 1,000 in the United States.
After the 2010 earthquake, Partners In Health founded the Hôpital Universitaire de Mirebalais, the largest solar-powered hospital in the world.
Largest cities
|
Largest cities or towns in Haiti
geonames.org |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Port-au-Prince | 1,234,742 |
| 2 | Cap-Haïtien | 534,815 |
| 3 | Carrefour (in Metro P.P.) | 442,156 |
| 4 | Delmas (in Metro P.P.) | 382,920 |
| 5 | Pétion-Ville (in Metro P.P.) | 283,052 |
| 6 | Port-de-Paix | 250,000 |
| 7 | Croix des Bouquets (in Metro P.P.) | 229,127 |
| 8 | Jacmel | 137,966 |
| 9 | Léogâne | 134,190 |
| 10 | Les Cayes | 125,799 |
Culture
Haiti has a lasting and unique cultural identity, consisting of a blend of traditional French and African customs, mixed with sizable acquirements from the Spanish and indigenous Taíno cultures. Haiti's culture is greatly reflected in its paintings, music, and literature. Galleries and museums in the United States and France have exhibited the works of the better-known artists to have come out of Haiti.
Art
Haitian art is distinctive, particularly through its paintings and sculptures. Brilliant colors, naïve perspectives, and sly humor characterize Haitian art. Frequent subjects in Haitian art include big, delectable foods, lush landscapes, market activities, jungle animals, rituals, dances, and gods. As a result of a deep history and strong African ties, symbols take on great meaning within Haitian society. For example, a rooster often represents Aristide and the red and blue colors of the Haitian flag often represent his Lavalas party. Many artists cluster in 'schools' of painting, such as the Cap-Haïtien school, which features depictions of daily life in the city, the Jacmel School, which reflects the steep mountains and bays of that coastal town, or the Saint-Soleil School, which is characterized by abstracted human forms and is heavily influenced by Vodou symbolism.
In the 1920s the indigéniste movement gained international acclaim, with its expressionist paintings inspired by Haiti's culture and African roots. Notable painters of this movement include Hector Hyppolite, Philomé Oban and Préfète Duffaut. Some notable artists of more recent times include Edouard Duval-Carrié, Frantz Zéphirin, Leroy Exil, Prosper Pierre Louis and Louisiane Saint Fleurant. Sculpture is also practiced in Haiti; noted artists in this form include George Liautaud and Serge Jolimeau.
Music and dance
Haitian music combines a wide range of influences drawn from the many people who have settled here. It reflects French, African and Spanish elements and others who have inhabited the island of Hispaniola, and minor native Taino influences. Styles of music unique to the nation of Haiti include music derived from Vodou ceremonial traditions, Rara parading music, Twoubadou ballads, mini-jazz rock bands, Rasin movement, Hip hop kreyòl, méringue, and compas. Youth attend parties at nightclubs called discos, (pronounced "deece-ko"), and attend Bal. This term is the French word for ball, as in a formal dance.
Compas (konpa) (also known as compas direct in French, or konpa dirèk in creole) is a complex, ever-changing music that arose from African rhythms and European ballroom dancing, mixed with Haiti's bourgeois culture. It is a refined music, with méringue as its basic rhythm. Haiti had no recorded music until 1937 when Jazz Guignard was recorded non-commercially.
Literature
Haiti has always been a literary nation that has produced poetry, novels, and plays of international recognition. The French colonial experience established the French language as the venue of culture and prestige, and since then it has dominated the literary circles and the literary production. However, since the 18th century there has been a sustained effort to write in Haitian Creole. The recognition of Creole as an official language has led to an expansion of novels, poems, and plays in Creole. In 1975, Franketienne was the first to break with the French tradition in fiction with the publication of Dezafi, the first novel written entirely in Haitian Creole; the work offers a poetic picture of Haitian life. Other well known Haitian authors include Jean Price-Mars, Jacques Roumain, Marie Vieux-Chauvet, Pierre Clitandre, René Depestre, Edwidge Danticat, Lyonel Trouillot and Dany Laferrière.
Cinema
Haiti has a small though growing cinema industry. Well-known directors working primarily in documentary film-making include Raoul Peck and Arnold Antonin. Directors producing fictional films include Patricia Benoît, Wilkenson Bruna and Richard Senecal.
Cuisine
Haiti is famous for its creole cuisine (which related to Cajun cuisine), and its soup joumou.
Architecture
Monuments include the Sans-Souci Palace and the Citadelle Laferrière, inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 1982. Situated in the Northern Massif du Nord, in the National History Park, the structures date from the early 19th century. The buildings were among the first built after Haiti's independence from France.
The Citadelle Laferrière, is the largest fortress in the Americas, is located in northern Haiti. It was built between 1805 and 1820 and is today referred to by some Haitians as the eighth wonder of the world.
The Institute for the Protection of National Heritage has preserved 33 historical monuments and the historic center of Cap-Haïtien.
Jacmel, a colonial city that was tentatively accepted as a World Heritage Site, was extensively damaged by the 2010 Haiti earthquake.
Museums
The anchor of Christopher Columbus's largest ship, the Santa María now rests in the Musée du Panthéon National Haïtien (MUPANAH), in Port-au-Prince, Haiti.
Folklore and mythology
Haiti is known for its folklore traditions. Much of this is rooted in Haitian Vodou tradition. Belief in zombies is also common. Other folkloric creatures include the lougarou.
National holidays and festivals
The most festive time of the year in Haiti is during Carnival (referred to as Kanaval in Haitian Creole or Mardi Gras) in February. There is music, parade floats, and dancing and singing in the streets. Carnival week is traditionally a time of all-night parties.
Rara is a festival celebrated before Easter. The festival has generated a style of Carnival music.
Sports

Football (soccer) is the most popular sport in Haiti with hundreds of small football clubs competing at the local level. Basketball and baseball are growing in popularity. Stade Sylvio Cator is the multi-purpose stadium in Port-au-Prince, where it is currently used mostly for association football matches that fits a capacity of 10,000 people. In 1974, the Haiti national football team were only the second Caribbean team to make the World Cup (after Cuba's entry in 1938). They lost in the opening qualifying stages against three of the pre-tournament favorites; Italy, Poland, and Argentina. The national team won the 2007 Caribbean Nations Cup.
Haiti has participated in the Olympic Games since the year 1900 and won a number of medals. Haitian footballer Joe Gaetjens played for the United States national team in the 1950 FIFA World Cup, scoring the winning goal in the 1–0 upset of England.
See also
 In Spanish: Haití para niños
In Spanish: Haití para niños