Freehold Borough, New Jersey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Freehold Borough, New Jersey
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Borough
|
||
|
Monmouth County Courthouse
George Taylor House
Downtown Freehold at the intersection of West Main Street and Throckmorton Street
|
||
|
||
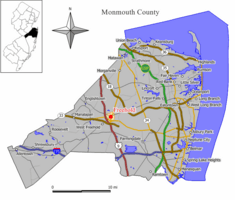
Location of Freehold Borough in Monmouth County highlighted in yellow (right). Inset map: Location of Monmouth County in New Jersey highlighted in black (left).
|
||
Census Bureau map of Freehold Borough, New Jersey
<mapframe text="Interactive map of Freehold Borough, New Jersey" latitude="40.262862" longitude="-74.277344" zoom="8" width="250" height="250"> { "type": "ExternalData", "service": "geoshape", "ids": "Q691237" } </mapframe> |
||
| Country | ||
| State | ||
| County | Monmouth | |
| Incorporated | March 25, 1869 (as town) | |
| Reincorporated | April 15, 1919 (as borough) | |
| Named for | English legal term of freehold | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Borough | |
| • Body | Borough Council | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 1.93 sq mi (5.01 km2) | |
| • Land | 1.93 sq mi (5.00 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) 0.10% | |
| Area rank | 419th of 565 in state 32nd of 53 in county |
|
| Elevation | 171 ft (52 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 12,538 | |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
12,430 | |
| • Rank | 206th of 565 in state 17th of 53 in county |
|
| • Density | 6,496.4/sq mi (2,508.3/km2) | |
| • Density rank | 82nd of 565 in state 7th of 53 in county |
|
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) | |
| ZIP Code |
07728
|
|
| Area code(s) | 732/848 | |
| FIPS code | 34-25200 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 0885226 | |
Freehold is a borough in and the county seat of Monmouth County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. Known for its Victorian era homes and extensive colonial history, the borough is located in the Raritan Valley region within the New York metropolitan area, located about 33 miles (53 km) from Manhattan and 17 miles (27 km) from Staten Island. The borough has grown to become a commuter town of New York City. As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 12,538, its highest decennial count ever and an increase of 486 (+4.0%) from the 12,052 recorded at the 2010 census, which in turn reflected an increase of 1,076 (+9.8%) from the 10,976 counted in the 2000 census.
The Freeholds region, which includes the borough and Freehold Township (which completely surrounds the borough), is a commercial hub for central New Jersey. The borough is located relatively close to the Raritan Bayshore communities to the north, including The Amboys, Old Bridge, Matawan, Keyport, Keansburg, and Middletown, along with being relatively close to the Tri-City region of Jersey Shore municipalities (and their vicinities) to the east, including Red Bank, Long Branch, and Asbury Park.
What is now Freehold Borough was originally incorporated as a town by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on March 25, 1869, from portions within Freehold Township. The town became independent of the township in 1888. On April 15, 1919, Freehold was incorporated as a borough, including all of Freehold and additional portions of Freehold Township, based on the results of a referendum held on July 8, 1919. Additional portions of Freehold Township were annexed on September 7, 1926.
The Hispanic and Latino population has been rapidly growing in Freehold Borough for the last 40 years. The Hispanic population making up 4.6% (0.2% Mexican) in the 1980 Census, 11.3% (2.8% Mexican) in the 1990 Census, 28.0% (17.3% Mexican) in 2000, 42.9% (29.6% Mexican) in 2010, and recently in 2020, a majority at 53.0% Hispanic. Meanwhile, the Black or African American population has decreased in recent decades: 17.1% in 1970, 19.8% in 1980, 18.2% in 1990, 15.8% in 2000, 12.6% in 2010 and 9.4% in 2020.
.....
Contents
History
Early history
The Lenni Lenape Native Americans were the earliest known people to live in the area that became Freehold. The Lenape were a hunter-gatherer society. They were largely sedentary, changing campsites seasonally. They were prolific hunters of small game and birds. They were also skilled fisherman, and were known to harvest vast amounts of clams from the bays and inlets on the Jersey Shore. They also practiced some agriculture to augment their food supply. During this time, an important crossroad of two major Lenape trails was located in the area of Freehold.
By the late 17th century, the English had begun to take over the area. In 1664, the Duke of York (later James II & VII) granted a patent to Sir George Carteret to develop the area. In 1685, Scottish Presbyterians from Scotland, along with English Baptists and Quakers from New England fleeing religious persecution at home, became the first to settle within the area. In 1693, along with Middletown and Shrewsbury, Freehold was established by act of legislature as one of the three original townships in Monmouth County. The name of the borough comes from the word Freehold, an English legal term describing fee simple property ownership.
Colonial Freehold
In 1714, when the colonial government was deciding where to locate the county seat and courthouse, Freeholder John Reid, the first Surveyor General of East Jersey, wanted the county seat located in Freehold Township. Reid sold land suitable for use as a courthouse to the Board of Chosen Freeholders at a bargain price, and this may have been the deciding factor why Freehold was selected over Middletown and Shrewsbury. In return for the heavily discounted price, Reid placed a restrictive covenant in the deed that, should the property ever cease being used as a courthouse, ownership would revert to the Reid family. Direct descendants of John Reid still reside in Freehold Township.
Freehold was officially designated as the seat of the Monmouth County government, and a court house was commissioned to be built on the land purchased from John Reid. The Monmouth Courthouse opened in 1715. A small village quickly began to develop around the courthouse. At first, the village was called Monmouth Courthouse. Over time, other government buildings opened near the courthouse, including a sheriff's office, a prison and a post office. A number of homes and commercial businesses also sprang up in the village, including a blacksmith, a general store, a bank, a hotel, and saloon.
In the area surrounding Monmouth Courthouse, many successful farms began to appear. The farms in Freehold were particularly well known for the production of potatoes, beans, and rye, which were sold in the markets of nearby cities. Freehold also became known for its excellent horse farms. The differences within Freehold between growing village around the courthouse and the surrounding farmland were the seeds for the eventual division of Freehold into two separate municipalities in the early 20th century.
As of 1745, the majority of families in Freehold were still Scottish immigrants. In modern Freehold today, many important streets bear the name of early colonial families, including Barkalow, Applegate, Rhea, Throckmorton, and Schanck.
Revolutionary War
Freehold was deeply impacted by the American Revolution. By the early 1770s, the Sons of Liberty were actively recruiting local members in Freehold, and were agitating the relationship between the British government and the colonists. In 1775, immediately after the Battles of Lexington and Concord, Capt. Elias Longstreet recruited the first company of Freeholders to join the Continental Army. Freehold was a known center of patriot activity. The Declaration of Independence was publicly proclaimed, read aloud, from the steps of the Freehold Courthouse just a few days after being signed in Philadelphia.
However, after British success at the Battle of Long Island, Freehold and all of Monmouth County fell under the control of Loyalists. The British government continued to operate the Freehold Courthouse, and several people involved in revolutionary activism were arrested and tried for treason at the courthouse. The success of the Continental Army at the Battle of Trenton helped to weaken loyalist control of Freehold.
In June 1778, the British Army began a major strategic evacuation of Philadelphia. They attempted to protect a long, slow moving column of loyalist families, equipment, and other supplies seized in Philadelphia, as they moved towards ships in New York Harbor. On June 28, 1778, the Continental Army intercepted the column in Freehold (the area is now part of Freehold & Manalapan Townships). The Battle of Monmouth was one of the largest battles of the Revolutionary War, involving over 25,000 soldiers combined in Continental, British, and Hessian forces. The initial engagement was in doubt until Washington arrived because Charles Lee was retreating from the battlefield. Washington rallied the Continentals and strongly engaged the British forces and they held their ground on the battlefield. However, the British forces were successful in completing their primary goal, the evacuation of Philadelphia. Both sides claimed victory in the battle.
Several notable figures during the Revolutionary War fought at the Battle of Monmouth. British forces were commanded by Sir Henry Clinton and Charles Cornwallis. The Continental Army was commanded by George Washington and Charles Lee. Charles Lee was court martialed by the Continental Army for his behavior at the Battle of Monmouth. Nathaniel Greene, Alexander Hamilton, the Marquis de Lafayette and Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben also fought for the Continental Army at the Battle of Monmouth. Another famous figure at the Battle of Monmouth was Molly Pitcher, who manned a cannon during the battle after her husband was wounded.
In the aftermath of the Battle of Monmouth, Loyalist control of Freehold faltered. The town ceased to have a functioning municipal government, and the courthouse was closed until the end of the war. Minor clashes between loyalists and continentals flared up in town, with the violence peaking around 1780. Colonel Tye, an escaped slave and leader of a prominent loyalist guerilla force, conducted several raids in and around Freehold. One famous incident was the capture and hanging of Joshua Huddy by British Loyalists under the direction of Richard Lippincott. Colonel Tye was killed during the raid on Huddy's home. Patriots later cut down Huddy's body hanging from the gallows and buried it in Freehold, at Old Tennent Church. At the end of the war, the community was deeply divided, and nearly 120 loyalist families left Freehold, fearing persecution from their neighbors. Most of these families re-settled in Canada.
19th century

During the early 19th century, Freehold steadily grew in size. The village around the courthouse was now called Freehold, along with the surrounding farmland. In 1852, when long distance railroad systems were first being developed, a railroad station, with trains making regular stops, running along what is now known as Throckmorton Street, about one block from the courthouse. Freehold soon had public sewers in the village and in some of the outlying farmland. By 1883, there was an electrical grid and a telephone switchboard, at a time when these inventions were still brand new. These public advancements caused rapid economic growth in Freehold. The village of Freehold became an important commercial and industrial hub in central New Jersey. The farms in the rest of Freehold benefitted greatly by being able to sell their products more easily in New York and Philadelphia. Both the village and the farms prospered together, however the public policies sought by the two different communities continued to grow further apart. The municipal government was increasingly divided between the villagers and farmers.
In 1824, the American Hotel opened on Main Street in Freehold; It is still standing today, and is one of the oldest buildings in Freehold. In 1853, the Freehold Raceway opened. Though the original grandstand burned down in a fire, the racetrack is still open today, and is one of the oldest harness racetracks in America. The Great Fire of Freehold happened on October 30, 1873. The fire reportedly began in a commercial building on Main Street. It soon spread to engulf a large section of the village, and many wooden buildings, including Monmouth Courthouse, were burned down.
Freehold also has an important place in the history of the bicycle. Cycling champion Arthur Augustus Zimmerman resided in the borough during his racing career in the 1880s and 1890s, and from 1896 to 1899 operated the Zimmerman Bicycle Co.; the company's bicycles were known as the "Zimmy." Today, Freehold Borough is home to the Metz Bicycle Museum, where the only extant "Zimmy" can be seen.
Freehold divided

At the beginning of the 20th century, Freehold was an increasingly divided community. The issue of local tax dollars, used as funding for public works and infrastructure projects, was the primary point of contention. The Freeholders living in the downtown area, around the courthouse had very different ideas about how to spend public money compared to the Freeholders living in the surrounding farmland. Tension within the community increased greatly in 1916 when a severe polio epidemic swept through Freehold.
After contentious public debate, a referendum was held to on the future of Freehold, and voters overwhelmingly decided to split the town into two separate municipalities.
On April 15, 1919, Freehold Borough formally separated from Freehold Township. Freehold residents generally refer to the different municipalities simply as the Borough and the Township. The borough, the downtown area around the courthouse, retained all the existing government buildings around Court Street and Main Street. The borough also kept the designation as county seat. Freehold Township, the farming communities that surrounded the courthouse, set up a new city hall complex on Schanck Road. The township completely encircles the borough. On September 7, 1926, Freehold Borough annexed additional territory from the township.
The Borough in the 20th century

Freehold Borough initially prospered in the early 20th century. However, by mid-century, the Borough began to decline as downtown areas across the country shrank, and suburban areas began growing. In 1961, the A & M Karagheusian rug factory closed. This factory had long been the largest employer in the area, and its closure had a devastating effect on the economic stability of the borough. The borough managed to turn around its economic decline by establishing the downtown area as a center for restaurants and nightlife. Several well-known local restaurants on Main Street are now crowded every night of the week.
Freehold Borough was an important center of African American civil rights activity in New Jersey during the years leading up to the Brown v. Board of Education decision in 1954. In 2007, Jaye Sims became the first African American official to be elected to office.
Bruce Springsteen grew up in the borough. His family lived in various homes on Randolph St, Institute St and finally South St. In 1963, he graduated eighth grade from St. Rose of Lima School, and graduated from Freehold Borough High School in 1967. In 1973, he released his first album, and rocketed to international fame. Springsteen has always remained loyal to Freehold and makes reference to it in several of his famous songs, including "My Hometown". In 1996, he conducted a small benefit concert in Freehold for St. Rose of Lima.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the borough had a total area of 1.93 square miles (5.01 km2), including 1.93 square miles (5.00 km2) of land and <0.01 square miles (<0.01 km2) of water (0.10%). It is situated in the heart of Monmouth County and is located approximately 35 miles (56 km) south of New York City and 50 miles (80 km) northeast of Philadelphia. Freehold is also about 16 miles (26 km) west of Asbury Park on the Jersey Shore.
Freehold has an elevation of 174 feet (53 m) above sea level at its center.
The borough is completely surrounded by Freehold Township, making it part of 21 pairs of "doughnut towns" in the state, where one municipality entirely surrounds another.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Freehold Borough sits on the northern border between the humid subtropical climate (Cfa) zone and the humid continental climate (Dfa) zone, with the borough being one of the most northern localities in North America that has a humid subtropical climate. Cfa climates are characterized by all months having an average temperature above 32.0 °F (0.0 °C), at least four months with an average temperature at or above 50.0 °F (10.0 °C), at least one month with an average temperature at or above 71.6 °F (22.0 °C) and no significant precipitation difference between seasons.
| Climate data for Freehold Borough, New Jersey, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1893–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 73 (23) |
79 (26) |
87 (31) |
95 (35) |
96 (36) |
100 (38) |
106 (41) |
102 (39) |
99 (37) |
95 (35) |
83 (28) |
76 (24) |
106 (41) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 41.7 (5.4) |
44.4 (6.9) |
51.4 (10.8) |
63.0 (17.2) |
72.0 (22.2) |
81.1 (27.3) |
86.5 (30.3) |
84.6 (29.2) |
78.1 (25.6) |
66.6 (19.2) |
56.2 (13.4) |
46.7 (8.2) |
64.4 (18.0) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 32.3 (0.2) |
34.7 (1.5) |
41.4 (5.2) |
52.1 (11.2) |
61.3 (16.3) |
70.6 (21.4) |
76.0 (24.4) |
74.0 (23.3) |
67.1 (19.5) |
55.5 (13.1) |
45.9 (7.7) |
37.4 (3.0) |
54.0 (12.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 22.9 (−5.1) |
25.0 (−3.9) |
31.3 (−0.4) |
41.2 (5.1) |
50.6 (10.3) |
60.1 (15.6) |
65.5 (18.6) |
63.4 (17.4) |
56.1 (13.4) |
44.3 (6.8) |
35.7 (2.1) |
28.0 (−2.2) |
43.7 (6.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −14 (−26) |
−20 (−29) |
−2 (−19) |
17 (−8) |
28 (−2) |
35 (2) |
42 (6) |
41 (5) |
32 (0) |
20 (−7) |
7 (−14) |
−5 (−21) |
−20 (−29) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.87 (98) |
3.10 (79) |
4.20 (107) |
3.83 (97) |
3.81 (97) |
4.44 (113) |
4.65 (118) |
4.13 (105) |
4.19 (106) |
4.13 (105) |
3.54 (90) |
4.68 (119) |
48.57 (1,234) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.7 | 9.2 | 9.9 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 11.8 | 9.8 | 10.7 | 9.1 | 10.2 | 9.4 | 10.1 | 125.0 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Ecology
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. potential natural vegetation types, Freehold Borough would have an Appalachian Oak (104) vegetation type with an Eastern Hardwood Forest (25) vegetation form.
Demographics
2010 census
The 2010 United States census counted 12,052 people, 4,006 households, and 2,660 families in the borough. The population density was 6,180.8 per square mile (2,386.4/km2). There were 4,249 housing units at an average density of 2,179.1 per square mile (841.4/km2). The racial makeup was 65.72% (7,920) White, 12.57% (1,515) Black or African American, 0.52% (63) Native American, 2.89% (348) Asian, 0.07% (8) Pacific Islander, 15.35% (1,850) from other races, and 2.89% (348) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 42.87% (5,167) of the population.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 2,432 | — | |
| 1890 | 2,932 | 20.6% | |
| 1900 | 2,934 | 0.1% | |
| 1910 | 3,233 | 10.2% | |
| 1920 | 4,768 | 47.5% | |
| 1930 | 6,894 | 44.6% | |
| 1940 | 6,952 | 0.8% | |
| 1950 | 7,550 | 8.6% | |
| 1960 | 9,140 | 21.1% | |
| 1970 | 10,545 | 15.4% | |
| 1980 | 10,020 | −5.0% | |
| 1990 | 10,742 | 7.2% | |
| 2000 | 10,976 | 2.2% | |
| 2010 | 12,052 | 9.8% | |
| 2020 | 12,538 | 4.0% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 12,430 | 3.1% | |
| Population sources: 1880–1920 1880–1890 1890–1910 1910–1930 1940–2000 2000 2010 2020 |
|||
Of the 4,006 households, 33.6% had children under the age of 18; 44.3% were married couples living together; 13.6% had a female householder with no husband present and 33.6% were non-families. Of all households, 26.2% were made up of individuals and 13.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.98 and the average family size was 3.48.
24.5% of the population were under the age of 18, 10.4% from 18 to 24, 32.4% from 25 to 44, 21.7% from 45 to 64, and 11.0% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33.3 years. For every 100 females, the population had 111.7 males. For every 100 females ages 18 and older there were 112.0 males.
The Census Bureau's 2006–2010 American Community Survey showed that (in 2010 inflation-adjusted dollars) median household income was $52,000 (with a margin of error of +/− $3,634) and the median family income was $60,471 (+/− $3,989). Males had a median income of $29,752 (+/− $8,068) versus $34,976 (+/− $8,305) for females. The per capita income for the borough was $23,331 (+/− $1,602). About 13.1% of families and 16.01% of the population were below the poverty line, including 20.5% of those under age 18 and 14.2% of those age 65 or over.
Economy
Suburbanization within the vicinity of the Freeholds region has been due to its convenient location near the Jersey Shore, and proximity to cities such as New York, Newark, Trenton, and Philadelphia. The region has, thus, been a longtime premier shopping destination in Central New Jersey.
Commerce
Main Street
The borough is home to Downtown Freehold, located on East and West Main Street (County Route 537). This downtown section has various eateries, bars, boutiques, historical sites, and other excursions. Within this section of town, there have been plans to revitalize the downtown area, as outlined in the Freehold Center Core Revitalization Plan (2008), in which NJ Transit has sponsored a project in transforming the Freehold Center Bus Station into a Transit Village. This new designation would foster in the creation of a transit-oriented development zoning district around the bus station.
Freehold Raceway
Established in 1853, making it the nation's oldest half-mile harness racing track, Freehold Raceway offers horse lovers and bettors an opportunity to see harness racing. The raceway announced in September 2024 that they will close, with the final racing date being December 28.
Freehold Raceway Mall
Completed in August 1990, the Freehold Raceway Mall is a super-regional mall located in neighboring Freehold Township. The mall was constructed at a cost of $125 million on a site covering more than 175 acres (71 ha) across from the Freehold Raceway over U.S. 9, and it has a gross leasable area of 1,600,000 square feet (150,000 m2).
There are many other shopping destinations outside of the borough, including the Manalapan EpiCentre (formerly, the Manalapan Mall) in nearby Manalapan Township, the Jackson Premium Outlets in nearby Jackson Township, and The Shoppes in nearby Old Bridge Township.
Manufacturing
Freehold Borough and Township began to grow in commercial and industrial manufacturing of goods during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
A and M Karagheusian Mill
A & M Karagheusian, Inc. was a rug manufacturer headquartered at 295 Fifth Avenue in Manhattan. Manufacturing was located in Freehold Borough, New Jersey and operated for 60 years before closing in 1964. It employed 1,700 people at its peak operation in the 1930s. There was another factory in Roselle Park, New Jersey, that operated from May 19, 1923, to 1962.
Bruce Springsteen wrote about the Karagheusian Rug Mill’s closing in his 1984 song "My Hometown".
Brockway Glass
Brockway Glass Company built a facility on Center Street in 1955. Brockway Glass then proceeded to build additional facilities in the region in 1956, 1967, 1969 and 1976. The company ceased operations in the township in 1991, in which the site is now operated by the Freehold campus location for Iron Mountain, an enterprise information management services company.
Nestle
Nestle opened a production plant in 1948, which closed in 2023.
Parks and recreation

The Freeholds region is home to a wide array of nature spaces, including Monmouth Battlefield State Park, Turkey Swamp Park, and Lake Topanemus, providing assorted recreational opportunities. Smaller parks in the borough are operated by the Borough Recreation Commission, and they include Liberty Park, Veterans Park, and Vinyard Park.
The southernmost segment of the Henry Hudson Trail starts in the borough and runs northeast to the Raritan Bayshore area along an abandoned rail line to Matawan. There is a parking lot located at 119 Dutch Lane Road in Freehold Township. The trail is used by walkers, runners and bicyclists.
Lake Topanemus is a 71-acre (29 ha) suburban park located in Freehold Township, but is owned and operated by the borough. The pond's attractions, include freshwater fishing, paddle boating, and canoeing. The park is also known for its picturesque nature trails, playgrounds, outdoor calisthenics, and open fields.
Education
Freehold Borough's public school students in pre-kindergarten through eighth grade attend the Freehold Borough Schools. As of the 2022–23 school year, the district, comprised of three schools, had an enrollment of 1,641 students and 162.0 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 10.1:1. Schools in the district (with 2022–23 school enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics) are Freehold Learning Center with 566 students in grades PreK–2, Park Avenue Elementary School with 470 students in grades 3–5 and Freehold Intermediate School with 519 students in grades 6–8.
Students in public school for ninth through twelfth grades attend Freehold High School, as part of the Freehold Regional High School District (FRHSD). The Freehold Regional High School District also serves students from Colts Neck Township, Englishtown, Farmingdale, Freehold Township (which also has some students at Freehold Borough High School), Howell Township, Manalapan Township and Marlboro Township. As of the 2022–23 school year, the high school had an enrollment of 1,409 students and 97.8 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 14.4:1. Students may apply to attend one of the district's six specialized learning centers, including the Medical Sciences Learning Center hosted at Freehold High School. The FRHSD board of education has nine members, who are elected to three-year terms from each of the constituent districts. Each member is allocated a fraction of a vote that totals to nine points, with Freehold Borough allocated one member, who has 1.0 votes.
The independent Freehold Public Library is one of the remaining Carnegie-funded libraries in the state and is believed to be the only one with the name "Carnegie Library" engraved on its front. It is not part of the Monmouth County Library system.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Roads and highways

As of May 2010[update], the borough had a total of 31.31 miles (50.39 km) of roadways, of which 26.60 miles (42.81 km) were maintained by the municipality, 1.30 miles (2.09 km) by Monmouth County and 3.41 miles (5.49 km) by the New Jersey Department of Transportation.
U.S. Route 9, Route 33 Business, Route 79, County Route 522 and County Route 537 all pass through Freehold Borough.
Freehold Circle
Freehold Circle was located near the western boundary of Freehold Borough near Freehold Raceway. The circle carried traffic between U.S. Route 9, Route 33 Business and Manalapan Avenue (CR 24); it was eliminated in the 1980s due to the increased traffic load caused by a boom in commercial and residential development. Most notable of the commercial development is the Freehold Raceway Mall, in Freehold Township just south of the old circle on US 9, whose development in the late 1980s was a major impetus to redesign the circle. The former circle now features several jughandles, and most Manalapan Avenue traffic must use a connector road to Business Route 33 to reach the main intersection, but it is still known by locals as Freehold Circle. In the early 1940s, the Freehold Circle was the planned terminus of highway that would funnel traffic from South Amboy to the Jersey Shore by way of Matawan and Marlboro Township.
Public transportation
Rail
In the 19th and 20th centuries, Freehold Borough and Freehold Township had two major railways. One major railway in the area was the Freehold and Jamesburg Agricultural Railroad, which was owned and operated by the Camden & Amboy Railroad Company (C&A). Surveying for the line began on September 8, 1851, grading began on October 19, 1852, and the first track was laid on April 4, 1853. The first section of line was opened on July 18, 1853. The establishment of the Freehold & Jamesburg Agricultural Railroad caused the Freeholds region to become a transportation hub. The other major railway in the area was the Central Railroad of New Jersey, which had a branch that connected the still-active former Penn Central line from Jamesburg to CNJ's Seashore Branch and the New York and Long Branch line (now owned by NJ Transit) at Matawan.
The Freehold and Jamesburg Railroad was abandoned by the early 1930s. A 2.8-mile long (4.5 km) portion of the former railroad's right-of-way was later approved to be sold by the New Jersey Board of Public Utility Commissioners (PUC) to Jersey Central Power & Light Company in 1966, with occasional freight service still being used through the Freehold Industrial Track. Meanwhile, The Central Railroad of New Jersey went into bankruptcy in the early 1970s and entered into Conrail on April 1, 1976, with its freight service on the rails from Freehold to Matawan being terminated in 1979 (the rails were removed in 1980). Today, it is mostly a rail-trail, converting into the Henry Hudson Trail. Freehold's former train station for both of these important railway routes now serves as the central bus station for town.
The Monmouth Ocean Middlesex Line is a proposal by New Jersey Transit to restore passenger railway service to the region, by using the same tracks as the Freehold Industrial Track. The borough and its neighboring township would be potential stops for the 'MOM' Line.
As of now, the nearest train stations to the borough are located in Aberdeen-Matawan, Asbury Park, Long Branch, and South Amboy on the North Jersey Coast Line, and Metropark in Iselin, Metuchen, New Brunswick, and Princeton Junction on the Northeast Corridor Line.
Proposed NJ Transit Village
With the Borough of Freehold's determination to revitalize its downtown area, as outlined in the Freehold Center Core Revitalization Plan (2008), NJ Transit has sponsored a project in transforming the Freehold Center Bus Station into a "Transit Village". This new designation would foster in the creation of a Transit-oriented development (TOD) zoning district around by the Freehold Center Bus Station between West Main Street (County Route 537) and Throckmorton Street (County Route 522).
In 2019, Freehold Borough Council members began to authorize Planning Board members "to investigate if properties in the downtown district constitute an area in need of redevelopment. If board members determine redevelopment is warranted, they will prepare a redevelopment plan for the designated area." On April 20, 2020, borough council members had reached an agreement in adopting an ordinance that would purchase a new building to house as the municipal complex. The hopes of relocating the current municipal complex on West Main Street to this new location on Mechanic street would be in opening up more space for potential developers that could bid for the NJ 'Transit Village'.
Buses

NJ Transit bus service connects Freehold with communities along U.S. Route 9, to Newark Liberty International Airport, to New York City, and to Six Flags Great Adventure located in Jackson Township. The 131, 135 and 139 provide service to the Port Authority Bus Terminal in Midtown Manhattan, on the 67 to Newark, on the 64 and 67 to Jersey City and local service on the 836 and 838 routes. Bus service is available from Route 9 to Wall Street in New York's Financial District via the Academy Bus Line.
There are also several bus stops to the points listed above located along Route 9 in the borough and in neighboring Freehold Township.
Aviation
Following the closure of the Marlboro Airport, Old Bridge Airport in Old Bridge supply short-distance flights to surrounding areas and is the closest air transportation services. The nearest major commercial airports are Trenton-Mercer Airport, which serves several domestic destinations via Frontier Airlines and located 25 miles (40 km) west (about 38 minutes drive); and Newark Liberty International Airport, which serves as a major hub for United Airlines and located 32 miles (51 km) north (about 44 minutes drive) from Freehold Borough.
Healthcare
Freehold Borough is served by CentraState Healthcare System, which is affiliated with Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, located in neighboring Freehold Township. The regional hospital is a 287-bed medical facility. CentraState Healthcare system also provides healthcare through its various family practices in communities across western Monmouth and southern Middlesex counties in central New Jersey. CentraState Family Medicine Residency Program is one of Robert Wood Johnson Medical School's residency halls, which is located in Freehold Borough on Park Avenue. CentraState Healthcare System is the county's fourth-largest employer.
The next closest hospitals to the borough are Bayshore Community Hospital, located in nearby Holmdel Township, and the Old Bridge Division of Raritan Bay Medical Center, located in nearby Old Bridge Township. The closest major university hospitals to the borough are Jersey Shore University Medical Center in Neptune Township, Penn Medicine Princeton Medical Center in Plainsboro Township, Saint Peter's University Hospital and Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital in New Brunswick.
Points of interest
- Freehold Public Library
- Monmouth County Historical Association, a museum and library dedicated to the history of Monmouth County.
- Freehold Raceway, the oldest harness racetrack in the United States, dating to 1853.
- Hankinson-Moreau-Covenhoven House was constructed in the 1750s and used by the British as a headquarters during the Battle of Monmouth. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974
- St. Peter's Episcopal Church was built in 1771 based on a design by architect Robert Smith and was added to the National Register in 1998 as one of one five churches in the state dating back to the 1700s still standing.
- Freehold Jewish Center, a synagogue established in 1911 which was constructed as the Orthodox Jewish Congregation Agudath Achim.
- Metz Bicycle Museum exhibits antique bicycles dating back to the 1850s.
- Monmouth County Courthouse and Battle of Monmouth Monument
- Olive Branch Lodge No. 16 Free and Accepted Masons was instituted October 20, 1849.
-
Monument dedicated to the Battle of Monmouth, located on the premises for the Monmouth County Courthouse, 2021
Notable people
People who were born in, residents of, or otherwise closely associated with Freehold Borough include:
- Scott Conover (born 1968), former Detroit Lions offensive tackle and author of the children's book Can I Play Too? was raised in Freehold
- Anthony DeSclafani (born 1990), starting pitcher for the San Francisco Giants
- Robert Griswold (born 1996), swimmer
- Lewis Lane (1901–1977), pianist, composer, lecturer and musicologist
- Danny Lewis (1936–2015), NFL running back from 1958 to 1966, playing for the Detroit Lions, the Washington Redskins, and the New York Giants
- Joel Parker (1816–1888), 20th Governor of New Jersey, elected to two non-consecutive terms (1863–1866 and 1871–1874). A lawyer by profession, he served as Attorney General of New Jersey in 1875 and as a justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court, from 1880 to 1888
- Tim Perry (born 1965), former NBA player, most notably with the Phoenix Suns
- Darrell Reid (born 1982), former defensive tackle for the Denver Broncos and Indianapolis Colts
- Nehemiah Shumway (1761–1843), composer, farmer, principal of Freehold Academy
- J. R. Smith (born 1985), professional basketball player who plays for the Los Angeles Lakers
- Rebecca Soni (born 1987), Olympic gold medalist at the 2012 London Olympic Games who set world records in the 100-meter breaststroke (short course) and the 200-meter breaststroke (short and long course)
- Bruce Springsteen (born 1949), rock musician, was raised in Freehold Borough The borough is the subject of his song "My Hometown," from the Born in the U.S.A. album, which described racial and economic tensions in the 1960s (the "textile mill being closed" was the A & M Karagheusian rug mill at Center and Jackson Streets). Springsteen has also performed a humorous song about the borough called "In Freehold", which can be found on some bootleg live recordings.
See also
 In Spanish: Freehold (Nueva Jersey) para niños
In Spanish: Freehold (Nueva Jersey) para niños