Reduction (chemistry) facts for kids
Reduction is a chemical reaction that involves the gaining of electrons by one of the atoms involved in the reaction between two chemicals. The term refers to the element that accepts electrons, as the oxidation state of the element that gains electrons is lowered.
An example of a reduction is when iron reacts with oxygen, forming iron oxides such as those called rust. The iron is oxidized and the oxygen is reduced. This is called redox. A blast furnace reverses that reaction, using carbon monoxide as a reducing agent to reduce the iron.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
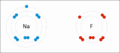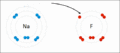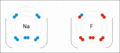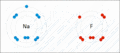
Sodium and fluorine bonding ionically to form sodium fluoride. Sodium loses its outer electron to give it a stable electron configuration, and this electron enters the fluorine atom exothermically. The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other. The sodium is oxidized; and the fluorine is reduced.
-
Oxides, such as iron(III) oxide or rust, which consists of hydrated iron(III) oxides Fe2O3·nH2O and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3), form when oxygen combines with other elements
-
Iron rusting in pyrite cubes
See also
 In Spanish: Reducción-oxidación para niños
In Spanish: Reducción-oxidación para niños