Permafrost facts for kids
In geology, permafrost is soil that stays at or below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years. It is also called cryotic soil. Most permafrost is on land close to the North and South poles.
Landforms
Permafrost processes manifest themselves in large-scale land forms, such as palsas and pingos and smaller-scale phenomena, such as patterned ground found in arctic, periglacial and alpine areas.
-
Pingos near Tuktoyaktuk, Northwest Territories, Canada
-
Stone rings on Spitsbergen
-
Solifluction on Svalbard
-
Cracks forming at the edges of the Storflaket permafrost bog in Sweden.
Images for kids
-
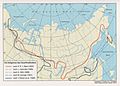
Southern limit of permafrost in Eurasia according to Karl Ernst von Baer (1843), and other authors.
-
A peat plateau complex south of Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories
-
Thawing permafrost in Herschel Island, Canada, 2013
-
Permafrost and ice in Herschel Island, Canada, 2012
-
Permafrost thaw ponds on peatland in Hudson Bay, Canada in 2008.
-
Permafrost polygons on Mars imaged by the Phoenix lander.
-
False-color Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter image of polygonal surface pattern.
-
Heat pipes in vertical supports maintain a frozen bulb around portions of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline that are at risk of thawing.
See also
 In Spanish: Permafrost para niños
In Spanish: Permafrost para niños