Mauritania facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Islamic Republic of Mauritania
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: شرف، إخاء، عدل
"Honour, Fraternity, Justice" |
|
|
Anthem: النشيد الوطني الموريتاني
"National Anthem of Mauritania" |
|
Location of Mauritania (in green) in western Africa
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Nouakchott 18°09′N 15°58′W / 18.150°N 15.967°W |
| Official languages | |
| Recognised national languages |
|
| Other languages | French |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion | Sunni Islam (official) |
| Demonym(s) | Mauritanian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential Islamic republic |
| Mohamed Ould Ghazouani | |
| Mokhtar Ould Djay | |
|
• President of the National Assembly
|
Mohamed Ould Meguett |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence | |
|
• Republic established
|
28 November 1958 |
|
• Independence from France
|
28 November 1960 |
|
• Current constitution
|
12 July 1991 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
1,030,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi) (28th) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
4,328,040 (128th) |
|
• Density
|
3.4/km2 (8.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2014) | ▼ 32.6 medium |
| HDI (2022) | low · 164th |
| Currency | Ouguiya (MRU) |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| ISO 3166 code | MR |
| Internet TLD | .mr |
|
|
Mauritania, formally the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. By land area Mauritania is the 11th-largest country in Africa and 28th-largest in the world; 90% of its territory is in the Sahara. Most of its population of some 4.3 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly a third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, on the Atlantic coast.
Despite an abundance of natural resources, including iron ore and petroleum, Mauritania remains poor; its economy is based primarily on agriculture, livestock, and fishing.
Contents
Etymology
Mauritania takes its name from the ancient Berber kingdom that flourished beginning in the third century BC and later became the Roman province of Mauretania, which flourished into the seventh century AD. The word "Mauri" is also the root of the name for the Moors.
History

Berbers occupied what is now Mauritania by the beginning of the third century AD. Groups of Arab tribes migrated to this area in the late seventh century, bringing with them Islam, Arab culture, and the Arabic language. In the early 20th century, Mauritania was colonized by France as part of French West Africa. It achieved independence in 1960, but has since experienced recurrent coups and periods of military dictatorship.
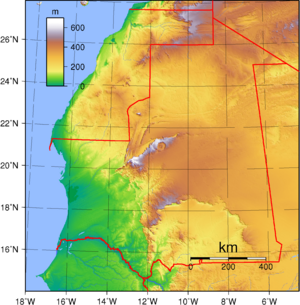
Geography
Mauritania lies in the western region of the continent of Africa, and is generally flat, its 1,030,700 square kilometers forming vast, arid plains broken by occasional ridges and clifflike outcroppings. It borders the North Atlantic Ocean, between Senegal and Western Sahara, Mali and Algeria. It is considered part of both the Sahel and the Maghreb. Approximately three-quarters of Mauritania is desert or semidesert. As a result of extended, severe drought, the desert has been expanding since the mid-1960s.
A series of scarps face southwest, longitudinally bisecting these plains in the center of the country. The scarps also separate a series of sandstone plateaus, the highest of which is the Adrar Plateau, reaching an elevation of 500 metres or 1,600 feet. Spring-fed oases lie at the foot of some of the scarps. Isolated peaks, often rich in minerals, rise above the plateaus; the smaller peaks are called guelbs and the larger ones kedias. The concentric Guelb er Richat is a prominent feature of the north-central region. Kediet ej Jill, near the city of Zouîrât, has an elevation of 915 metres (3,000 ft) and is the highest peak. The plateaus gradually descend toward the northeast to the barren El Djouf, or "Empty Quarter," a vast region of large sand dunes that merges into the Sahara Desert. To the west, between the ocean and the plateaus, are alternating areas of clayey plains (regs) and sand dunes (ergs), some of which shift from place to place, gradually moved by high winds. The dunes generally increase in size and mobility toward the north.
Belts of natural vegetation, corresponding to the rainfall pattern, extend from east to west and range from traces of tropical forest along the Sénégal River to brush and savanna in the southeast. Only sandy desert is found in the center and north of the country. Mauritania is home to seven terrestrial ecoregions: Sahelian Acacia savanna, West Sudanian savanna, Saharan halophytics, Atlantic coastal desert, North Saharan steppe and woodlands, South Saharan steppe and woodlands, and West Saharan montane xeric woodlands.
The Richat Structure, dubbed the "Eye of the Sahara", is a formation of rock resembling concentric circles in the Adrar Plateau, near Ouadane, west–central Mauritania.
Wildlife
Mauritania's wildlife has two main influences as the country lies in two biogeographic realms, the north sits in the Palearctic which extends south from the Sahara to roughly 19° north and the south in the Afrotropic realms. Additionally Mauritania is important for numerous birds which migrate from the Palearctic to winter there.
Most of the north to about 19° north is regarded as being in the palearctic, and is largely made up of the Sahara desert and adjacent littoral habitats. South of this is regarded as being in the Afrotropical biogeographic realm, which means that species of a predominantly Afrotropical distribution dominate the fauna. South of the Sahara is the South Saharan steppe and woodlands ecoregion which integrates into the Sahelian acacia savanna ecoregion. The southernmost part of the country lies in the West Sudanian savanna ecoregion.
Wetlands are important and the two main protected areas are the Banc d'Arguin National Park which protects rich, shallow coastal and marine ecosystems which integrates with the arid Sahara Desert and the Diawling National Park which forms the northern part of the delta of the Senegal River. Elsewhere in Mauritania wetlands are normally ephemeral and rely on the seasonal rainfall.
Government and politics
The Mauritanian Parliament is composed of a single chamber, the National Assembly. Composed of 176 members, representatives are elected for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies.
Until August 2017 the parliament had an upper house, the Senate. The Senate had 56 members, 53 members elected for a six-year term by municipal councilors with a third renewed every two years and three elected by Mauritanians abroad. It was abolished in 2017 after a referendum.
The President of Mauritania is directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in two rounds if needed for a five-year term (eligible for a second term). The Prime minister is appointed by the President.
Administrative divisions
The government bureaucracy is composed of traditional ministries, special agencies, and parastatal companies. The Ministry of Interior spearheads a system of regional governors and prefects modeled on the French system of local administration. Under this system, Mauritania is divided into 15 regions (wilaya or régions).
Control is tightly concentrated in the executive branch of the central government, but a series of national and municipal elections since 1992 have produced limited decentralization. These regions are subdivided into 44 departments (moughataa).
The regions and capital district and their capitals are:
| Region | Capital | # |
|---|---|---|
| Adrar | Atar | 1 |
| Assaba | Kiffa | 2 |
| Brakna | Aleg | 3 |
| Dakhlet Nouadhibou | Nouadhibou | 4 |
| Gorgol | Kaédi | 5 |
| Guidimaka | Sélibaby | 6 |
| Hodh Ech Chargui | Néma | 7 |
| Hodh El Gharbi | Ayoun el Atrous | 8 |
| Inchiri | Akjoujt | 9 |
| Nouakchott-Nord | Dar-Naim | 10 |
| Nouakchott-Ouest | Tevragh-Zeina | 10 |
| Nouakchott-Sud | Arafat | 10 |
| Tagant | Tidjikdja | 11 |
| Tiris Zemmour | Zouérat | 12 |
| Trarza | Rosso | 13 |
Economy
Despite being rich in natural resources, Mauritania has a low GDP. A majority of the population still depends on agriculture and livestock for a livelihood, even though most of the nomads and many subsistence farmers were forced into the cities by recurrent droughts in the 1970s and 1980s. Mauritania has extensive deposits of iron ore, which account for almost 50% of total exports. Gold and copper mining companies are opening mines in the interior such as Firawa mine. The country's gold production in 2015 is 9 metric tons.
The country's first deepwater port opened near Nouakchott in 1986.
In recent years drought and economic mismanagement have resulted in a buildup of foreign debt.
Demographics
As of 2018[update], Mauritania had a population of about 4.3 million, roughly a third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, on the Atlantic coast. The local population is composed of three main ethnicities: Bidhan or white Moors, Haratin or black moors, and West Africans. 30% Bidhan, 40% Haratin, and 30% others (mostly Black Sub-Saharans). Local statistics bureau estimations indicate that the Bidhan represent around 30% of citizens. They speak Hassaniya Arabic and are primarily of Arab-Berber origin. The Haratin constitute roughly 35% of the population, with many estimates putting them at around 40%. They are descendants of the original inhabitants of the Tassili n'Ajjer and Acacus Mountain sites during the Epipalaeolithic era. The remaining 30% of the population largely consists of various ethnic groups of West African descent. Among these are the Niger-Congo-speaking Halpulaar (Fulbe), Soninke, Bambara and Wolof.
Largest cities
Template:Largest cities of Mauritania
Religion
Mauritania is almost 100% Muslim, with most inhabitants adhering to the Sunni denomination. In 2020, the number of Christians in Mauritania was estimated at 10,000.
There are extreme restrictions on freedom of religion and belief in Mauritania; it is one of 13 countries in the world that punish atheism by death.
Languages
Arabic is the official and national language of Mauritania. The local spoken variety, known as Hassaniya, contains many Berber words and significantly differs from the Modern Standard Arabic that is used for official communication. Despite having no official status, French is used as an administrative language and as a medium of instruction in schools. It is also widely used in the media, business, and among educated classes.
Culture

Tuareg and Mauritanian silversmiths have developed traditions of traditional Berber jewellery and metalwork that have been worn by Mauritanian women and men. According to studies of Tuareg and Mauritanian jewellery, the latter are usually more embellished and may carry typical pyramidal elements.
Filming for several documentaries, films, and television shows have taken place in Mauritania, including Fort Saganne (1984), The Fifth Element (1997), Winged Migration (2001), Timbuktu (2014), and The Grand Tour (2024).
The TV show Atlas of Cursed Places (2020) that aired on the Discovery Channel & National Geographic Channel had an episode that mentions Mauritania as a possible location for the lost city of Atlantis. The location they consider is a geological formation consisting of a series of rings known as the Richat Structure, which is located in the Western Sahara.
The T'heydinn is part of Moorish oral tradition.
The libraries of Chinguetti contain thousands of medieval manuscripts.
Sports
Sports in Mauritania are influenced by its desert terrain and its location on the Atlantic coast. Football is the most popular sport in the country, followed by athletics and basketball. The country has several football stadiums, such as the Stade Municipal de Nouadhibou in Nouadhibou. Despite being ranked as the fourth-worst team in the world in 2012, Mauritania qualified for the 2019 Africa Cup of Nations. In 2023, Mauritania made headlines by defeating Sudan in the AFCON 2023 qualifiers.
Mauritania has been the recipient of international support for sports infrastructure. Morocco has committed to building a sports complex in the country.
Images for kids
-
The Portuguese Empire ruled Arguin (Portuguese: Arguim) from 1445, after Prince Henry the Navigator set up a feitoria, until 1633.
-
Nouakchott is the capital and the largest city of Mauritania. It is one of the largest cities in the Sahara.
See also
 In Spanish: Mauritania para niños
In Spanish: Mauritania para niños