Leskovac facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Leskovac
Лесковац (Serbian)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| City of Leskovac | |||
 |
|||
|
|||
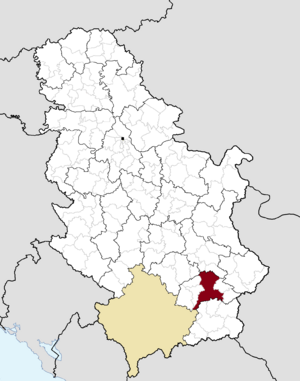
Location of the city of Leskovac within Serbia
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Region | Southern and Eastern Serbia | ||
| District | Jablanica | ||
| Settlements | 144 | ||
| Area | |||
| Area rank | 5th in Serbia | ||
| • Urban | 31.27 km2 (12.07 sq mi) | ||
| • Administrative | 1,025 km2 (396 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 228 m (748 ft) | ||
| Population
(2022 census)
|
|||
| • Rank | 6th in Serbia | ||
| • Urban | 58,338 | ||
| • Urban density | 1,865.62/km2 (4,831.9/sq mi) | ||
| • Administrative | 123,950 | ||
| • Administrative density | 120.93/km2 (313.20/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| Postal code |
16000
|
||
| Area code | +381(0)16 | ||
| Car plates | LE | ||
Leskovac (Serbian Cyrillic: Лесковац, pronounced [lěskoʋats]) is a city and the administrative center of the Jablanica District in southern Serbia. According to the 2022 census, the city of Leskovac has 123,950 inhabitants.
Contents
Etymology
Leskovac was historically called Glubočica, later evolving into Dubočica. These interchangeable variants derived from the Serbian word's, "glib", meaning mud and "duboko", meaning deep. Untamed rivers would often flood the area leaving swamps that once dried would spout hazelnut trees, or "leska" in Serbian, whilst "-ovac" is a common Slavic suffix, hence Leskovac. During Ottoman rule the town was referred to in Turkish as Leskovçe or Hisar (Turkish translation; fortress).
History
Early period
Archeological findings on Hisar Hill, located at the rim of Leskovac valley between the Jablanica and Veternica rivers, have established continual habitation between the Bronze Age until the 19th century. Hisar served as a fortification for many centuries and its surrounding plateau are abundant in Iron Age pottery largely associated with the Brnjica culture. Other archeological findings associated with the Illyrians, Thracians, Dacians, Greeks, Romans and Celts lay within Leskovac's surrounds. The Roman Empire conquered the area in the 1st century BC and would remain the dominant power until Slavic invasion and settlement in the late 6th and early 7th centuries, with the Serbs solidifying their presence.
The area Glubočica, later Dubočica and a synonym for Leskovac was first mentioned in the 12th century as lands bestowed upon the Nemanjić dynasty by Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos. The settlement of Leskovac per se was first mentioned by name in 1348 as an endowment by Serbian Emperor Dušan the Mighty to the Hilendar Monastery. The vicinity of modern-day Leskovac was contested territory during a series of conflicts fought between the Bulgarian Empire and medieval Serbian states between the 9th and 14th centuries.
The Battle of Dubočica took place on September 24, 1454, between the Serbian Despotate and the invading Ottoman Empire, and ended in a Serbian victory. Brankovic's Serbia was a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire during the first half of the 15th century and was repeatedly invaded, eventually becoming part of the Ottoman state.
Ottoman rule
Leskovac was annexed by the Ottomans in 1454 and allotted to the Rumelia Eyalet. The Nahija of Dubocica (later Leskovac) became part of Kruševac Sanjak with Leskovac possessing one of six kadiluks. During Ottoman rule, Leskovac was known in Turkish as Leskovçe, or more commonly Hisar (Turkish translation; fortress). The conquest in time brought Ottoman culture to Leskovac, influencing architecture, cuisine, customs, dress and language. Endowments by the ruling Ottoman aristocracy which financed the construction of mosques, tekije, madrasa, meter and Turkish baths marked the area. During this period, Leskovac was regarded for its quality horse tack, tanning, smithing and weaving. The townsfolk worked as craftsman, merchants and peri-urban farmers, residing in separate Serbian Orthodox and Muslim mahallah's whilst affluent Muslim families held prominent real estate and owned farmland. This cosmopolitan milieu was supplemented by officials, clergy, sipahi, and soldiers interlaced with Jewish, Greek, Vlach, Albanian and Ragusan traders. Leskovac was known in the wider region for its annual 15-day long fair.
Leskovac was severely damaged by fire in 1595 and again in 1690. In the Ottoman-Austrian War the towns Serbs overwhelmingly sided with Habsburg forces on arrival in 1689. Following the failed uprising many Serbs migrated north after the Ottomans recaptured Leskovac, razing the Serbian quarters as reprisals for collaboration. In 1790 Sultan Selim III administrative reforms granted Leskovac the seat of its own Eyalet governed by Şehsuvar Abdi Pasha, who was succeeded by his son Ismail Pasha in 1830, until the Leskovac Eyalet was annexed to the Niš Eyalet in 1839. The Serbian population of Leskovac (along with other south Serbian towns and villages) took part in the failed rebellion of 1841.
Before the Serbian–Turkish Wars (1876–1878), the county of Leskovac had a significant Muslim population, mostly Turkish and Albanian, which comprised one-third of its overall population. In 1873, the town had 2,500 Serbian houses and 1,000 Muslim houses. The Muslims in the town were Albanian- and Turkish-speaking. Albanians formed almost the entire Muslim population in the villages. Historian Miloš Jagodić has estimated that of ~17,033 Muslims who lived in the Leskovac county before the war, about 16,976 were Albanians who were expelled after the war.These estimates are corroborated in contemporary sources like the records of Austrian diplomat Johann Georg von Hahn. In the war almost the entire Muslim civilian population of Leskovac was expelled and the advancing Serbian Army and chetas entered the town on December 24, 1877. There were 2,122 Albanian abandoned household. Of the about 5,000 Muslims who had previously lived in the town, 120 were still living there in 1879 in the first post-war population count. The rest had left as refugees and most settled in cities like Mitrovica, Prizren and Kumanovo in Kosovo Vilayet.
From Turkish kasaba to Serbia's Little Manchester
Leskovac became part of Serbia which received full international recognition following the Treaty of Berlin in 1878. Before the war Leskovac was part of a network of textile industry hubs from the Black Sea to the central Balkans and collaborated closely with Bulgarian textile industry. Products from Leskovac were exported duty-free to Bulgaria which exported machinery to Serbia. Independence initially had a negative impact though trade barriers, tariffs and open hostilities between Serbia and Bulgaria necessitated the acquisition and development of technology for rope and industrial hemp processing. By the mid-1880s business development, particularly the textile sector enabled Leskovac to become the third largest urban area after Belgrade and Niš at the time. The establishment of a railway line linking Leskovac with Belgrade, Skopje and Thessaloniki in 1886 also significantly contributed to the development of the town. A vocational textile school opened 1890 and in 1903 the second hydroelectric power plant in Serbia was built on the nearby Vučjanka River.
Due to the towns burgeoning industriousness in the late 19th c. Leskovac became popularity nicknamed Serbia's Little Manchester (Serbian Cyrillic: Мали Манчестер) in honor of Manchester, England, a powerhouse of textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution. The growing customs dispute with Austria-Hungary following the May Coup precipitated protectionism throughout the 1900s which served to nourish the local economy.
World War I and Bulgarian Occupation
Following the Serbian campaign of 1915 Leskovac fell within the Bulgarian occupational zone. This period was marked by harsh repression with attempts at Bulgarisation of the local inhabitants. Numerous crimes were committed on the Leskovac citizenry with 2,000-4,000 victims being executed and a great many more massacred in the surrounding region. During the occupation Leskovac was also adversely affected by a typhus epidemic and widespread malnutrition. Bulgaria capitulation to the Entente on 30 September 1918, and Leskovac was liberated on 7 October 1918 in an offensive led by Field Marshal Petar Bojović's 1st Serbian Corps, which repelled the Austro-Hungarian 9th and German 11th Divisions. Cheering crowds gathered to welcome the Serbian Army's Dinarska and Dunavska divisions as they entered the city accompanied by French cavalry units.
The "Golden Age" of Leskovac
Following the war Leskovac continued its fast economic and social transformation. The townsfolk practised a cultural medley of both Oriental and European habits, whilst the social fabric was dominated by affluent, often competing industrialists families and greater social disparity within the community. Industrial development facilitated trade union agitation amongst an emerging urban working-class. In August 1920 Leskovac became one of the first municipalities to elect the Communist Party. Despite its victory the party was quickly suppressed by the authorities.
Despite the rise of Leskovac as a regional manufacturing centre the town still lacked basic infrastructure during the interwar period such as a running water supply, sewerage system, paved streets (with only three asphalted in 1938) and a permanent marketplace. Leskovac experienced a significant influx of largely peasant workers leading to poor housing conditions with many affected by squalor, a high mortality rate and labour exploitation. From 1929 to 1941, Leskovac was part of the Vardar Banovina of the renamed Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
World War II and Allied bombing
During the capitulation of Yugoslavia in the April War Leskovac was occupied by the Germans on April 12, 1941. Despite several attempts at assassination and sabotage the town remained relatively docile throughout the Nedić administration, with the exception of the Arapova Dolina massacre of 310 mostly Romani civilians. Pockets of Partisan insurgency remain limited to the surrounding countryside which began experiencing noteworthy military engagements during the Battle of Serbia with the July–August 1944 Toplica-Jablanica Operation.
On September 6, 1944, Leskovac was targeted in a catastrophic Allied bombing campaign which left much of the town heavily damaged with approximately 2,500-4,000 casualties and a total of 1,840 demolished or damaged residential buildings and factories. The bombing also caused significant damage to infrastructure and historical landmarks. Leskovac fell to the 47th Serbian Division of the National Liberation Army (Partisans) on October 11, 1944, following a German withdrawal during the Niš Operation. The new Communist authorities proceeded to purge the town of political and ideological opponents, summarily executing 707 people.
Socialist era
The city continued to be a major textile center until the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, but due to the economic isolation of Serbia resulting from ethnic wars, its remote location, and failure to privatize the mills, the industry collapsed resulting in depression of the economy in the area.
On 12 April 1999, during the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia a bridge near Leskovac (Grdelička klisura) was destroyed by a NATO aircraft as a passenger train was crossing. The act was highly condemned with the bridge being struck twice (the train itself having been bombed from the first attack).
21st Century
Contemporary Leskovac has become synonymous with Serbian culinary culture, particularly the national dishes of pljeskavica and ćevapi. The annual Roštiljijada grilled meat barbecue festival held since 1989 is the cities biggest tourist attraction drawing in thousands of visitors from both Serbia and abroad.
The once thriving textile industry of Leskovac has all but collapsed with only a small number of businesses still in operation. The effects of globalisation coupled with political sanctions have led to significant economic decline. Local businesses were sluggish in transitioning from a predominantly state capitalist economy towards greater deregulation and privatisation during the 2000s. Despite a modest increase in mostly foreign capital enterprise with some government support issues of corruption, high unemployment, ageing workforce and community, unreported employment, and population decline still persist.
Geography
Leskovac is situated in the heart of the vast and fertile valley of Leskovac (50 km (31 mi) long and 45 km (28 mi) wide), the small Veternica river, at the foot of Hisar, in the central part of the Leskovac valley. Leskovac lies at an altitude of 228 meters, in a basin that covers 2,250 km2 (869 sq mi). Around the valley are mountains Radan and Pasjača the west, Kukavica and Čemernik in the south and Babička Gora, Seličevica and Suva Planina to the east.
Climate
Leskovac has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) with continental influences, with long, hot summers and short but cold, cloudy winters.
| Climate data for Leskovac (1991–2020, extremes 1961–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.0 (68.0) |
24.8 (76.6) |
27.8 (82.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
38.6 (101.5) |
43.7 (110.7) |
41.3 (106.3) |
37.4 (99.3) |
35.0 (95.0) |
28.6 (83.5) |
21.4 (70.5) |
43.7 (110.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 4.8 (40.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.3 (55.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
23.4 (74.1) |
27.5 (81.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.5 (86.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
19.1 (66.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
5.7 (42.3) |
18.2 (64.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
2.4 (36.3) |
6.9 (44.4) |
11.8 (53.2) |
16.4 (61.5) |
20.4 (68.7) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.8 (62.2) |
11.5 (52.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
1.7 (35.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.6 (25.5) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
1.3 (34.3) |
5.3 (41.5) |
9.9 (49.8) |
13.5 (56.3) |
14.7 (58.5) |
14.3 (57.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
5.8 (42.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −30.5 (−22.9) |
−26.8 (−16.2) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
2.7 (36.9) |
5.4 (41.7) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−8.7 (16.3) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−21.7 (−7.1) |
−30.5 (−22.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 46.2 (1.82) |
45.5 (1.79) |
52.1 (2.05) |
62.8 (2.47) |
69.4 (2.73) |
61.7 (2.43) |
51.2 (2.02) |
45.1 (1.78) |
52.2 (2.06) |
60.7 (2.39) |
55.5 (2.19) |
58.2 (2.29) |
660.6 (26.01) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 13.9 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.9 | 14.2 | 11.0 | 8.5 | 7.3 | 9.7 | 10.4 | 11.3 | 14.0 | 138.2 |
| Average snowy days | 9.0 | 7.4 | 4.7 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 2.8 | 7.6 | 32.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 81.6 | 76.1 | 69.0 | 67.6 | 69.8 | 66.9 | 63.8 | 64.3 | 71.1 | 76.7 | 79.7 | 83.1 | 72.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 67.0 | 88.3 | 146.1 | 178.6 | 219.6 | 264.6 | 301.2 | 293.0 | 202.6 | 139.8 | 84.8 | 50.5 | 2,036.1 |
| Source: Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia | |||||||||||||
Rivers
The largest river in the region of Leskovac is the South Morava River, which flows south to north. Tributaries of the South Morava are: the Vlasina river, which collects water from Lake Vlasina and flows through Crna Trava and Vlasotince; the Veternica river, which flows through Leskovac; the Jablanica river, which springs from the foot of Goljak and flows through Medveđa and Lebane; the Pusta (Deserted) river, which starts on Radan mountain, fills Lake Brestovačko and flows through Bojnik. The river Vučjanka, which springs from the Kukavica mountain, flows through Vučje and is a tributary of the Veternica river. Also known in the Leskovac region are Kozaračka, Predejanska, Kopašnička and Sušica rivers.
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1878 | 9,718 | — |
| 1884 | 10,878 | +1.90% |
| 1890 | 12,211 | +1.95% |
| 1895 | 12,989 | +1.24% |
| 1900 | 13,973 | +1.47% |
| 1931 | 17,636 | +0.75% |
| 1948 | 113,158 | +11.55% |
| 1953 | 121,311 | +1.40% |
| 1961 | 134,250 | +1.27% |
| 1971 | 147,487 | +0.94% |
| 1981 | 159,001 | +0.75% |
| 1991 | 161,986 | +0.19% |
| 2002 | 156,252 | −0.33% |
| 2011 | 144,206 | −0.89% |
| 2016 | 138,132 | −0.86% |
| 2022 | 124,889 | −1.67% |
According to the 2011 census results, there are 144,206 inhabitants in the city of Leskovac.
Ethnic groups
In 2011 the city's population was 95,784 of whom majority are Serbs. Other significant ethnic groups include Roma, Macedonians and Yugoslavs. In January 2007, there were an estimated 500 persons of Chinese origin living in Leskovac. Apart from the city proper, there are 143 populated places in the city, of which the largest are Vučje and Grdelica, classified as "urban" (town) in census, with about 3000 residents each.
The ethnic composition of the city administrative area:
| Ethnic group | Population | % |
|---|---|---|
| Serbs | 133,623 | 92.66% |
| Roma | 7,700 | 5.34% |
| Macedonians | 291 | 0.20% |
| Montenegrins | 192 | 0.13% |
| Bulgarians | 91 | 0.06% |
| Yugoslavs | 88 | 0.06% |
| Croats | 55 | 0.04% |
| Albanians | 20 | 0.02% |
| Slovenians | 19 | 0.01% |
| Muslims | 19 | 0.01% |
| Germans | 19 | 0.01% |
| Hungarians | 16 | 0.01% |
| Greeks | 16 | 0.01% |
| Others | 2,061 | 1.43% |
| Total | 144,206 |
Vast majority of the people are Orthodox Christians (96%). There are also 3% Muslims. The rest are atheists or follow other religions. At one time the second largest city in Serbia, today Leskovac is blighted by economic problems with many working age people migrating out of the area.
Subdivisions
There are 144 villages located within the municipality:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Culture
Events
Roštiljijada
Roštiljijada (Barbecue week) is a grilled meat festival that has been organized in Leskovac for many years and takes place annually at the beginning of September. During the event, the main boulevard is closed for traffic for five days, and food stands are put up along the streets. The event brings visitors from all over Serbia as well as tourists. According to the TOL (Tourism Organization of Leskovac) in 2013, over 700,000 people visited the event. The organisers hold competitions, such as making the biggest burger, the Pljeskavica. The festival is the highlight of the season in Leskovac.
International Carnival
In 2009 Leskovac officially became an International Carnival city, admitted by The Association of European Carnival cities, which has over 50 members from Europe and America. The Leskovac Carnival is held at a time of Roštiljijada festival. Around 1200 people take part in the carnival, of which one-third part from abroad. The City Government considered separating this event in 2010. as a special tourist event which will be introduced as a special offer of the city.
Theater Marathon
Theater Marathon takes place every year in November and lasts 9 days. It runs performances of National Theaters from all over Serbia. This event takes place in the National Theater in Leskovac.
Leskovac International Film Festival
The first Leskovac International film festival was held in 2008. The idea of the film in the city is not that new. In 1996, a group of enthusiasts, with chairman Rade Jovic, organized the Festival which were shown films of domestic production. Today, many years later, Leskovac host an International Film Festival. The Festival presents awards in 3 categories:
- "Golden hazelnuts" - Best Director
- "Hazelnut leaf" - critics awards
- "Vox populi" - Audience Award.
Cultural heritage
- Monastery of John the Baptist, Leskovac
- Monastery of the Presentation of the Holy Mother of God, Leskovac
- Rudare Monastery
- Čukljenik Monastery
- Leskovac Cathedral
- Odžaklija Church
- Memorial Park to the Revolution (1971) by famed Yugoslav architect Bogdan Bogdanović
Sports
Leskovac has a proud sporting history and is home to several teams, including football club's GFK Dubočica, FK Sloga Leskovac, basketball team KK Zdravlje, and handball team RK Dubočica 54.
Economy and infrastructure
Economy of Leskovac is diverse, but it is still somewhat stagnating as a city in whole. Overall, industry has a minor growth, but its growth is safe and in the future, industry will certainly face another growth that will increase its status among Serbia's largest cities. Its main industry is light industry such as textile, household commodities and medical industries. Leskovac has mine of lead and zinc called "Leskovac Lece".
The first boom occurred after WW1 and lasted until 1941. It was "succeeded" in the late 1940s. During so called "Yugoslav economic miracle" (1950s – c.1980) Leskovac has developed into not just regional, but textile center in entire Southeast Europe. It became known as "Serbian Manchester". Leskovac Lece was constructed during that era. During the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, Leskovac was severely damaged like no other city in Europe at the time.
The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2022):
| Activity | Total |
|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 279 |
| Mining and quarrying | 18 |
| Manufacturing | 15,090 |
| Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply | 337 |
| Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities | 518 |
| Construction | 1,519 |
| Wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles | 5,577 |
| Transportation and storage | 1,256 |
| Accommodation and food services | 1,067 |
| Information and communication | 370 |
| Financial and insurance activities | 347 |
| Real estate activities | 105 |
| Professional, scientific and technical activities | 1,057 |
| Administrative and support service activities | 364 |
| Public administration and defense; compulsory social security | 1,506 |
| Education | 2,481 |
| Human health and social work activities | 2,853 |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 442 |
| Other service activities | 517 |
| Individual agricultural workers | 1,201 |
| Total | 36,906 |
Transportation
Leskovac is a traffic junction. International trains traveling from Europe to Skopje, Thessalonica and Athens pass through this city. Nineteen trains stop in Leskovac every day. The railway came to Leskovac in 1886. Leskovac today has one of the newest and most modern railway stations in Serbia.
Bus traffic is also very well developed, bearing in mind that Leskovac has been criss-crossed with roads. The most important is the E75 road which connects the borders of Hungary and Macedonia. Regional roads lead from Leskovac to Priština, Pirot and Bosilegrad. The distance from Leskovac to Niš is 45, to Belgrade 280, and to Sofia 155 kilometres (96 miles).
Leskovac has a regional airport, which is commonly used for sporting and agricultural flights. Also in summer the airport is used for air taxi. The nearest international airport is Niš Constantine the Great Airport located 45 km (28 mi) north of the city.
Environment
Leskovac was the first city in Serbia which had a sanitary landfill. Željkovac depot spreads over 80 hectares and is made by all European standards. In the landfill there is a center for atmospheric water purification, center for the selection and disposal systems for the detection of all types of pollution. Company Por Werner and Weber for Serbia, began construction of the center for collecting and recycling waste, and is the first city in the Balkans, where starting this job.
Notable residents
- Ahmed Ademović, trumpeter and soldier.
- Jovica Arsić, basketball coach.
- Mihajlo Babamilkić - politician.
- Obrad Belošević, basketball referee.
- Jacques Confino, physician and writer.
- Nikola Dekleva, doctor.
- Bojan Dimitrijević, actor.
- Sreten Dinić, educator.
- Nenad Filipović, athlete.
- Predrag Filipović, athlete.
- Miodrag Gligorijević "Bure", chef.
- Perica Hadži-Jovančić, historian.
- Kosta Ilić "Mumdžija", industrialists.
- Vlada Ilić - industrialist and politician.
- Bojan Janić, volleyball player.
- Zvonko Marić, physicist.
- Ljubiša Marković, artist.
- Sloboda Mićalović, actress.
- Gojko Mitić, actor.
- Vladimir Milošević, pianist.
- Maja Miljković, basketball player.
- Jovan Naumović, Yugoslav Army General
- Gligorije "Gorča" Petrović, industrialist
- Marko Perović, footballer.
- Antonije "Tonka" Popović, industrialist
- Trajko Rajković, basketball player.
- Nikola Skobaljić, medieval nobleman and military commander.
- Jovan Spasić, footballer.
- Kosta Stamenković, revolutionary and Yugoslav national hero.
- Predrag Stanković, footballer.
- Nebojša Stefanović, ultramarathon.
- Ljubiša Stojanović Louis, singer.
- Momir Stojanović, Serbian revolutionary voivode.
- Goran Stojiljković, athlete.
- Miodrag Stojković, geneticist.
- Ilija Strelja, Serbian revolutionary voivode.
- Şehsuvar Abdi Pasha, Ottoman pasha
- Dimitrije "Mita" Teokarević, industrialist
- Toma Zdravkovic, singer.
- Bratislav Živković, footballer.
- Jovan Vlajčić, industrialist
- Dragi Stamenković
International relations
Twin towns — sister cities
Leskovac is twinned with:
 Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina Bijeljina, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bijeljina, Bosnia and Herzegovina Elin Pelin (town), Bulgaria
Elin Pelin (town), Bulgaria Kumanovo, Macedonia
Kumanovo, Macedonia Kyustendil, Bulgaria
Kyustendil, Bulgaria Lanzhou, China
Lanzhou, China Novo Mesto, Slovenia
Novo Mesto, Slovenia Pazin, Croatia
Pazin, Croatia Plovdiv, Bulgaria
Plovdiv, Bulgaria Prizren, Republic of Kosovo
Prizren, Republic of Kosovo Silistra, Bulgaria
Silistra, Bulgaria Verviers, Belgium
Verviers, Belgium Zrenjanin, Serbia
Zrenjanin, Serbia
See also
 In Spanish: Leskovac para niños
In Spanish: Leskovac para niños