Turkish language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Turkish |
|
|---|---|
| Türkçe | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈt̪yɾkˌtʃe] |
| Native to | Albania, Azerbaijan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Hungary, Iraq, Kosovo, Lebanon, Republic of Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Northern Cyprus, Palestine, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Syria, Turkey, Uzbekistan, and by immigrant communities in Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, The Netherlands, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and other countries of the Turkish diaspora |
| Region | Anatolia, Cyprus, Balkans, Caucasus, Central Europe, Western Europe |
| Native speakers | over 77 million worldwide (date missing) |
| Language family | |
| Writing system | Latin alphabet (Turkish variant) |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | *See Cyprus Dispute. **In municipalities with more than 20% Turkish speakers. ***Turkish is one of regional languages. |
| Regulated by | Turkish Language Association |
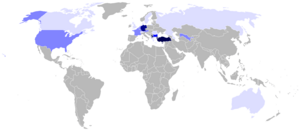
Countries with significant Turkish-speaking populations
|
|
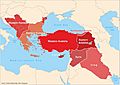
Turkish (Türkçe) is a language spoken in Turkey, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Greece and other countries of the former Ottoman Empire as well as by several million ethnic Turkish immigrants in Europe.
Turkish is a Turkic language and is believed to be an Altaic language. Like Finnish, Estonian and Hungarian, Turkish uses vowel harmony. Word order is usually subject-object-verb.
Turkish used to be written with the Arabic alphabet from about 900 to 1928. However, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk changed it to the Latin alphabet. The Turkish government justified the move as making it much easier to learn to increasing literacy. The literacy rate indeed increased greatly after the reform, from around 10.5% (in 1927) to over 90% (today). However, some say that the move was also to distance the country from the Ottoman Empire, whose documents can no longer be read except by a few scholars.
Turkish is a majority language in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus but it has a distinct dialect. It can be known as Cypriot Turkish.
The Latin alphabet was made to reflect the actual sounds of spoken Turkish, rather than simply transcribing the old Ottoman script into a new form. The Turkish alphabet has 29 letters, seven of which (Ç, Ğ, I, İ, Ö, Ş, and Ü) have been modified from their Latin originals for the phonetic requirements of the language. It represents modern Turkish pronunciation with a high degree of accuracy and specificity. It is the current official alphabet and the latest in a series of distinct alphabets used in different eras.
Turkish is most closely related to other Turkic languages, including Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Uzbek and Kazakh. Another theory is that it is one of the many Altaic languages, which also include Japanese, Mongolian, and Korean.
Simple phrases
- Merhaba = Hello (formal)
- Selam = Hello
- Nasılsın? = How are you?
- İyiyim = I'm fine
- Teşekkür ederim = Thank you (formal)
- Teşekkürler = Thanks
- Sağ ol = Thank you
- Benim adım ... = My name is ...
- Türkçe bilmiyorum. = I don't speak Turkish.
- İngilizce biliyor musunuz? = Do you speak English?
- Tekrarlar mısınız? = Can you repeat it?
- Evet = Yes
- Hayır = No
- Belki = Maybe
- Biraz = A little
- Acıktım. = I'm hungry.
- Dur! = Stop!
- Yapma! = Don't do it!
- İstemiyorum. = I don't want it.
- Tabii = Sure
- Bekledim. = I waited.
Images for kids
-
Map of the main subgroups of Turkish dialects across Southeast Europe and the Middle East.
-
Road sign at the European end of the Bosphorus Bridge in Istanbul. (Photo taken during the 28th Istanbul Marathon in 2006)
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma turco para niños
In Spanish: Idioma turco para niños