Engineering facts for kids

Engineering is the use of science and math to design or make things. People who do engineering are called engineers. They learn engineering at a college or university. Engineers usually design or build things. Some engineers also use their skills to solve technical problems. There are different types of engineers that design everything from computers and buildings to watches and websites.
Contents
History

Engineering has existed since ancient times, when humans devised inventions such as the wedge, lever, wheel and pulley.
The term engineering is derived from the word engineer, which itself dates back to 1390 when an engine'er (literally, one who operates an engine) referred to "a constructor of military engines." In this context, now obsolete, an "engine" referred to a military machine, i.e., a mechanical contraption used in war (for example, a catapult). Notable examples of the obsolete usage which have survived to the present day are military engineering corps, e.g., the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.
The word "engine" itself is of even older origin, ultimately deriving from the Latin ingenium (c. 1250), meaning "innate quality, especially mental power, hence a clever invention."
Later, as the design of civilian structures, such as bridges and buildings, matured as a technical discipline, the term civil engineering entered the lexicon as a way to distinguish between those specializing in the construction of such non-military projects and those involved in the discipline of military engineering.
Ancient era

The pyramids in Egypt, the Acropolis and the Parthenon in Greece, the Roman aqueducts, Via Appia and the Colosseum, Teotihuacán, the Great Wall of China, the Brihadeeswarar Temple of Thanjavur, among many others, stand as a testament to the ingenuity and skill of ancient civil and military engineers. Other monuments, no longer standing, such as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, and the Pharos of Alexandria were important engineering achievements of their time and were considered among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
The earliest civil engineer known by name is Imhotep. As one of the officials of the Pharaoh, Djosèr, he probably designed and supervised the construction of the Pyramid of Djoser (the Step Pyramid) at Saqqara in Egypt around 2630–2611 BC. Ancient Greece developed machines in both civilian and military domains. The Antikythera mechanism, the first known mechanical computer, and the mechanical inventions of Archimedes are examples of early mechanical engineering. Some of Archimedes' inventions as well as the Antikythera mechanism required sophisticated knowledge of differential gearing or epicyclic gearing, two key principles in machine theory that helped design the gear trains of the Industrial Revolution, and are still widely used today in diverse fields such as robotics and automotive engineering.
Ancient Chinese, Greek, Roman and Hungarian armies employed military machines and inventions such as artillery which was developed by the Greeks around the 4th century B.C., the trireme, the ballista and the catapult. In the Middle Ages, the trebuchet was developed.
Renaissance era
The first steam engine was built in 1698 by Thomas Savery. The development of this device gave rise to the Industrial Revolution in the coming decades, allowing for the beginnings of mass production.
With the rise of engineering as a profession in the 18th century, the term became more narrowly applied to fields in which mathematics and science were applied to these ends. Similarly, in addition to military and civil engineering, the fields then known as the mechanic arts became incorporated into engineering.
Modern era

The inventions of Thomas Newcomen and James Watt gave rise to modern mechanical engineering. The development of specialized machines and machine tools during the industrial revolution led to the rapid growth of mechanical engineering both in its birthplace Britain and abroad.
John Smeaton was the first self-proclaimed civil engineer and is often regarded as the "father" of civil engineering. He was an English civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours, and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent physicist. Smeaton designed the third Eddystone Lighthouse (1755–59) where he pioneered the use of 'hydraulic lime' (a form of mortar which will set under water) and developed a technique involving dovetailed blocks of granite in the building of the lighthouse. His lighthouse remained in use until 1877 and was dismantled and partially rebuilt at Plymouth Hoe where it is known as Smeaton's Tower. He is important in the history, rediscovery of, and development of modern cement, because he identified the compositional requirements needed to obtain "hydraulicity" in lime; work which led ultimately to the invention of Portland cement.
The United States census of 1850 listed the occupation of "engineer" for the first time with a count of 2,000. There were fewer than 50 engineering graduates in the U.S. before 1865. In 1870 there were a dozen U.S. mechanical engineering graduates, with that number increasing to 43 per year in 1875. In 1890 there were 6,000 engineers in civil, mining, mechanical and electrical.
There was no chair of applied mechanism and applied mechanics at Cambridge until 1875, and no chair of engineering at Oxford until 1907. Germany established technical universities earlier.
The foundations of electrical engineering in the 1800s included the experiments of Alessandro Volta, Michael Faraday, Georg Ohm and others and the invention of the electric telegraph in 1816 and the electric motor in 1872. The theoretical work of James Maxwell (see: Maxwell's equations) and Heinrich Hertz in the late 19th century gave rise to the field of electronics. The later inventions of the vacuum tube and the transistor further accelerated the development of electronics to such an extent that electrical and electronics engineers currently outnumber their colleagues of any other engineering specialty. Chemical engineering developed in the late nineteenth century. Industrial scale manufacturing demanded new materials and new processes and by 1880 the need for large scale production of chemicals was such that a new industry was created, dedicated to the development and large scale manufacturing of chemicals in new industrial plants. The role of the chemical engineer was the design of these chemical plants and processes.

Aeronautical engineering deals with aircraft design process design while aerospace engineering is a more modern term that expands the reach of the discipline by including spacecraft design. Its origins can be traced back to the aviation pioneers around the start of the 20th century although the work of Sir George Cayley has recently been dated as being from the last decade of the 18th century. Early knowledge of aeronautical engineering was largely empirical with some concepts and skills imported from other branches of engineering.
The first PhD in engineering (technically, applied science and engineering) awarded in the United States went to Josiah Willard Gibbs at Yale University in 1863; it was also the second PhD awarded in science in the U.S.
Only a decade after the successful flights by the Wright brothers, there was extensive development of aeronautical engineering through development of military aircraft that were used in World War I. Meanwhile, research to provide fundamental background science continued by combining theoretical physics with experiments.
In 1990, with the rise of computer technology, the first search engine was built by computer engineer Alan Emtage.
Branches of Engineering


Engineering is a big subject. Here are a few of the many types of engineers:
- Aerospace engineers design space vehicles or airplanes.
- Biomedical engineers design and work with medical equipment.
- Chemical engineers use chemicals to make products like drugs and medicines or fertilizers for crops.
- Civil engineers work on roads, bridges, buildings and other public structures.
- Computer engineers design and build computers and the parts that computers are made of.
- Electrical engineers work with electricity and design electrical equipment, from small things like radios and computers to large things like the wires that carry electricity across the country.
- Electronic engineers work with electronics, which are used to build computer parts and electrical equipment.
- Environmental engineers design and implement solutions to remediate and restore the environment.
- Manufacturing engineers design and improve the machines and assembly lines that make things. They work with robots, hydraulics and air-operated devices to help companies work faster and better with fewer mistakes.
- Mechanical engineers design machines or things that move, like cars and trains. A mechanical engineer also might help design electricity generating stations, oil refineries, and factories.
- Mechatronics engineers work in multiple fields of engineering that include mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, telecommunications engineering, control engineering and computer engineering.
- Marine Engineers design, build, test and repair boats, ships, underwater craft, focusing primarily on their internal systems.
- Nanotechnology engineers study very small things, like strings of atoms and how they are put together.
- Nuclear engineers design and build nuclear plants. They also study the characteristic behaviors of certain radioactive or unstable elements.
- Structural engineers are dealing with design and analysis of buildings and large non-building structures to withstand both the gravity and wind loads as well as natural disasters.
- Software engineers design and write programs for computers.
- Systems engineers look at how complicated things work and try to make them faster and smarter.
Engineers do not only work with machines. They also work a lot with other people. Many engineering projects are large and very complicated. Often different kinds of engineers work together and help each other. As an example, computer engineers need help from electrical engineers to build a computer. The computer needs programs written by software engineers. The computer could be used by aerospace engineers to control an airplane. An airplane is a big mechanical system with many parts, so a mechanical engineer and a systems engineer are also needed.
Study
Most (but not all) engineers have had years of training. Much of their training involves working within a limited budget and materials.
Images for kids
-
The steam engine, the major driver in the Industrial Revolution, underscores the importance of engineering in modern history. This beam engine is on display in the Technical University of Madrid.
-
The Ancient Romans built aqueducts to bring a steady supply of clean and fresh water to cities and towns in the empire.
-
The application of the steam engine allowed coke to be substituted for charcoal in iron making, lowering the cost of iron, which provided engineers with a new material for building bridges. This bridge was made of cast iron, which was soon displaced by less brittle wrought iron as a structural material
-
Offshore platform, Gulf of Mexico
-
The solar furnace at Odeillo in the Pyrénées-Orientales in France can reach temperatures up to 3,500 °C (6,330 °F)
-
The InSight lander with solar panels deployed in a cleanroom
-
Design of a turbine requires collaboration of engineers from many fields, as the system involves mechanical, electro-magnetic and chemical processes. The blades, rotor and stator as well as the steam cycle all need to be carefully designed and optimized.
-
A drawing for a booster engine for steam locomotives. Engineering is applied to design, with emphasis on function and the utilization of mathematics and science.
-
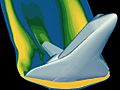
A computer simulation of high velocity air flow around a Space Shuttle orbiter during re-entry. Solutions to the flow require modelling of the combined effects of fluid flow and the heat equations.
-
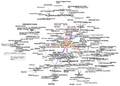
Graphic representation of a minute fraction of the WWW, demonstrating hyperlinks
-
Robotic Kismet can produce a range of facial expressions.
-
Engineers, scientists and technicians at work on target positioner inside National Ignition Facility (NIF) target chamber
-
The International Space Station is used to conduct science experiments in space
-
Leonardo da Vinci, seen here in a self-portrait, has been described as the epitome of the artist/engineer. He is also known for his studies on human anatomy and physiology.
See also
 In Spanish: Ingeniería para niños
In Spanish: Ingeniería para niños