Economy of India facts for kids
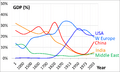
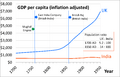
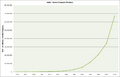
The Economy of India is the fifth largest in the world with a GDP (a year's goods and services) of $2.94 trillion (U.S.). If you consider PPP (purchasing power parity: how much that money can buy in India compared to other countries), the economy is third largest (worth $10.51 trillion U.S.). However, due to India's huge population, the economy was still only $6,209 (considering PPP) per person per year in 2015.
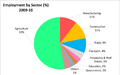
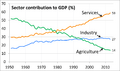
India's economy includes agriculture, handicrafts, industries, and a lot of services. The service sector is the main source of economic growth in India today, though two-thirds of Indian people earn their living directly or indirectly through agriculture. In recent times, due to its many well-educated people who can speak English, India became a pioneer in information technology.
For most of India's independent history, it had strict government controls in many areas such as telecommunications (communication over long distances), banking and foreign direct investment. Since the early 1990s, India has slowly opened up its markets by reducing government control on foreign trade and investment.This was started by Manmohan Singh under the leadership of P.V.Narasimha Rao.From then, the Indian Economy grew at a rapid pace.
The social and economic problems India faces are the increasing population, poverty, lack of infrastructure (buildings, roads, etc.) and growing unemployment. Although poverty has gone down 10% since the 1980s, a quarter of India's citizens still cannot pay for enough food.
Images for kids
-
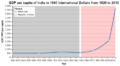
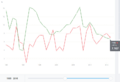
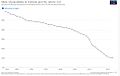
Estimated GDP per capita of India and United Kingdom during 1700–1950 in 1990 US$ according to Maddison. However, Maddison's estimates for 18th-century India have been criticized as gross underestimates, Bairoch estimates India had a higher GDP per capita in the 18th century, and Parthasarathi's findings show higher real wages in 18th-century Bengal and Mysore. But there is consensus that India's per capita GDP and income stagnated during the colonial era, starting in the late 18th century.
-
Rice fields near Puri, Odisha on India's east coast.
-
India exports more than 100,000 tonnes of processed cashew kernels every year. There are more than 600 cashew processing units in Kollam alone.
-
Many famous stones such as the Koh-i-Noor and Hope Diamond (above), came from India.
-
Visakhapatnam Port in the Bay of Bengal.
-
Indian coal production is the 3rd highest in the world according to the 2008 Indian Ministry of Mines estimates. Shown above is a coal mine in Jharkhand.
-
Durgapur Steel plant, West Bengal.
-
Air India became the first Asian carrier to induct a jet aircraft, with the Boeing 707–420 Gauri Shankar.
-
State Bank of India is the largest bank in India.
-
Infosys Media Centre in Bangalore, India. Infosys is one of the largest Indian IT companies.
-
Bactrian camel ride at Nubra Valley in Ladakh.
-
Poomparai village in the Hilly region of Kodaikanal hill station
-
The Reserve Bank of India's headquarters in Mumbai, India.
-
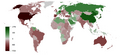
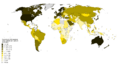
Gini index of India compared to other countries per World Bank data tables as of 2018[update]
-
University of Calcutta, established in 1857, was the first multidisciplinary and secular Western-style institution in Asia.
See also
 In Spanish: Economía de la India para niños
In Spanish: Economía de la India para niños