World map facts for kids
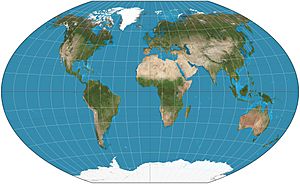
a low-error map projection adopted by the National Geographic Society for reference maps
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of the earth. While this is true of any map, these distortions reach extremes in a world map. Many techniques have been developed to present world maps that address diverse technical and aesthetic goals.
Charting a world map requires global knowledge of the earth, its oceans, and its continents. From prehistory through the Middle ages, creating an accurate world map would have been impossible because less than half of Earth's coastlines and only a small fraction of its continental interiors were known to any culture. With exploration that began during the European Renaissance, knowledge of the Earth's surface accumulated rapidly, such that most of the world's coastlines had been mapped, at least roughly, by the mid-1700s and the continental interiors by the twentieth century.
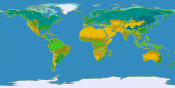
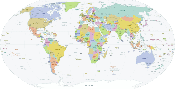
Maps of the world generally focus either on political features or on physical features. Political maps emphasize territorial boundaries and human settlement. Physical maps show geographical features such as mountains, soil type, or land use. Geological maps show not only the surface, but characteristics of the underlying rock, fault lines, and subsurface structures. Choropleth maps use color hue and intensity to contrast differences between regions, such as demographic or economic statistics.
Map projections
All world maps are based on one of several map projections, or methods of representing a globe on a plane. All projections distort geographic features, distances, and directions in some way. The various map projections that have been developed provide different ways of balancing accuracy and the unavoidable distortion inherent in making world maps.
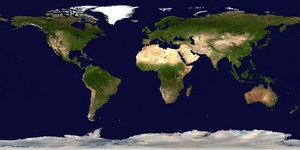
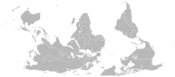
Perhaps the best-known projection is the Mercator Projection, originally designed as a nautical chart.
-
Mercator projection
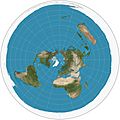
(82°S and 82°N) -
Polar azimuthal equidistant projection
-
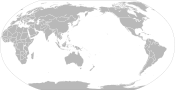
Pacific-centric map
(more commonly used in East Asian and Oceania countries) -
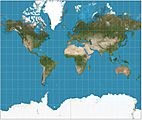
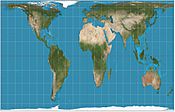
Gall–Peters projection, an equal-area map projection
-
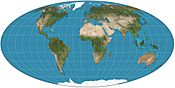
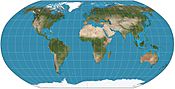
Robinson projection, formerly used by National Geographic Society
Thematic maps
A thematic map shows geographical information about one or a few focused subjects. These maps "can portray physical, social, political, cultural, economic, sociological, agricultural, or any other aspects of a city, state, region, nation, or continent".
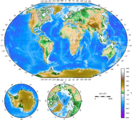
-
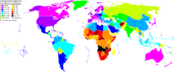
Topographical map of the world
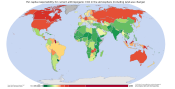
-
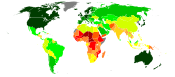
United Nations Human Development Index by country as of 2016
-
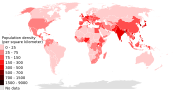
World map showing life expectancy
Historical maps
Early world maps cover depictions of the world from the Iron Age to the Age of Discovery and the emergence of modern geography during the early modern period. Old maps provide information about places that were known in past times, as well as the philosophical and cultural basis of the map, which were often much different from modern cartography. Maps are one means by which scientists distribute their ideas and pass them on to future generations.
-
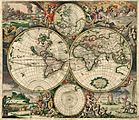
The world, Abraham Ortelius's Typus Orbis Terrarum, first published in 1564
-
Hypothetical reconstruction of the world map of Anaximander (610–546 BC)
-
World map according to Posidonius (150–130 BC),
drawn in 1628 -
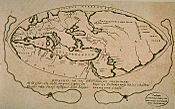
Tabula Rogeriana world map by Muhammad al-Idrisi in 1154
north is to the bottom -
World map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Kunyu Wanguo Quantu (Ming dynasty, 1602)
See also
 In Spanish: Mapamundi para niños
In Spanish: Mapamundi para niños
- Wikipedia's clickable world map
- Global Map
- Globe
- International Map of the World
- List of map projections
- List of world map changes
- Mappa mundi
- Maps of the world
- Rhumbline network
- Theorema Egregium
- Time zone