Thar Desert facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Thar DesertGreat Indian Desert |
|
|---|---|

Thar Desert in Rajasthan, India
|
|
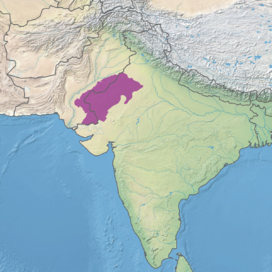
Map of the Thar Desert ecoregion
|
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Indomalayan |
| Biome | Deserts and xeric shrublands |
| Borders | Northwestern thorn scrub forests and Rann of Kutch seasonal salt marsh |
| Geography | |
| Area | 238,254 km2 (91,990 sq mi) |
| Countries | India and Pakistan |
| States of India and provinces of Pakistan | India: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab, Pakistan: Punjab and Sindh |
| Coordinates | 27°N 71°E / 27°N 71°E |
| Climate type | Hot |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | vulnerable |
| Protected | 41,833 km2 (18%) |
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of 200,000 km2 (77,000 sq mi) in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-largest hot subtropical desert.
About 85% of the Thar Desert is in India, and about 15% is in Pakistan. The Thar Desert is about 4.56% of the total geographical area of India. More than 60% of the desert lies in the Indian state of Rajasthan; the portion in India also extends into Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana. The portion in Pakistan extends into the provinces of Sindh and Punjab (the portion in the latter province is referred to as the Cholistan Desert). The Indo-Gangetic Plain lies to the north, west and northeast of the Thar desert, the Rann of Kutch lies to its south, and the Aravali Range borders the desert to the east.
The most recent paleontological discovery in 2023 from the Thar Desert in India, dating back to 167 million years ago, pertains to a herbivorous dinosaur group known as dicraeosaurids. This discovery marks the first of its kind to be unearthed in India and is also the oldest specimen of the group ever recorded in the global fossil record.
History of desertification
Ice-age desertification
During the Last Glacial Maximum 20,000 before present, an approximately 2,400,000 square kilometres (930,000 sq mi) ice sheet covered the Tibetan Plateau, causing excessive radiative forcing i.e. the ice in Tibet reflected at least four times more radiation energy per unit area into space than ice at higher latitudes, which further cooled overlying atmosphere at that time. This impacted the regional climate. Without the thermal low pressure caused by the heating, there was no monsoon over the Indian subcontinent. This lack of monsoon caused extensive rainfall over the Sahara, expansion of the Thar Desert, more dust deposited into the Arabian Sea, a lowering of the biotic life zones on the Indian subcontinent, and animals responded to this shift in climate with the Javan rusa deer migrating into India.
Desertification due to drying up of Sarasvati river
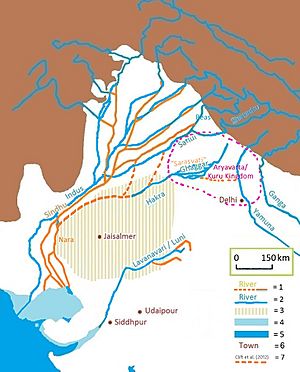
1 = ancient river
2 = today's river
3 = today's Thar desert
4 = ancient shore
5 = today's shore
6 = today's town
7 = dried-up Harappan Hakkra course, and pre-Harappan Sutlej paleochannels ().
10,000-8,000 years ago a paleo channel of Ghaggar-Hakra River - identified with the paleo Sarasvati River, after confluence with Sutlej flowed into the Nara river - a delta channel of the Indus River, changed its course, leaving the Ghaggar-Hakra as a system of monsoon-fed rivers which did not reach the sea and now ends in the Thar desert.
Around 5,000 years ago when the monsoons that fed the rivers diminished further, the Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) prospered in this area, with the rise of numerous IVC urban sites at Kalibangan (Rajasthan), Banawali and Rakhigarhi (Haryana), Dholavira and Lothal (Gujarat) along this course.
4,000 years ago when monsoons diminished even further, the dried-up Harkra become an intermittent river, and the urban Harappan civilisation declined, becoming localized in smaller agricultural communities.
Geography

The northeastern part of the Thar Desert lies between the Aravalli Hills. The desert stretches to Punjab and Haryana in the north, to the Great Rann of Kutch along the coast, and to the alluvial plains of the Indus River in the west and northwest. Much of the desert area is covered by huge, shifting sand dunes that receive sediments from the alluvial plains and the coast. The sand is highly mobile due to the strong winds that rise each year before the onset of the monsoon. The Luni River is the only river in the desert. Rainfall is 100 to 500 mm (4 to 20 in) per year, almost all of it between June and September.
Saltwater lakes within the Thar Desert include the Sambhar, Kuchaman, Didwana, Pachpadra, and Phalodi in Rajasthan and Kharaghoda in Gujarat. These lakes receive and collect rainwater during monsoon and evaporate during the dry season. The salt comes from the weathering of rocks in the region.
Lithic tools belonging to the prehistoric Aterian culture of the Maghreb have been discovered in Middle Paleolithic deposits in the Thar Desert.
Climate
The climate is arid and subtropical. Average temperature varies with season, and extremes can range from near-freezing in the winter to more than 50 °C in the summer months. Average annual rainfall ranges from 100 to 500 mm, and occurs during the short July-to-September southwest monsoon.
The desert has both a very dry part (the Marusthali region in the west) and a semidesert part (in the east) that has fewer sand dunes and slightly more precipitation.
Desertification control

The soil of the Thar Desert remains dry for much of the year, so it is prone to wind erosion. High-velocity winds blow soil from the desert, depositing some of it on neighboring fertile lands, and causing sand dunes within the desert to shift. To counteract this problem, sand dunes are stabilised by first erecting micro windbreak barriers with scrub material and then by afforestation of the treated dunes—planting the seedlings of shrubs (such as phog, senna, and castor oil plant) and trees (such as gum acacia, Prosopis juliflora, and lebbek tree). The 649-km-long Indira Gandhi Canal brings fresh water to the Thar Desert. It was built to halt any spreading of the desert into fertile areas.
Protected areas
There are several protected areas in the Thar Desert:
- In India:
- The Desert National Park, in Rajasthan, covers 3,162 km2 (1,221 sq mi) and represents the Thar Desert ecosystem; it includes 44 villages. Its diverse fauna includes the great Indian bustard (Chirotis nigricaps), blackbuck, chinkara, fox, Bengal fox, wolf, and caracal. Seashells and massive fossilized tree trunks in this park record the geological history of the desert.
- The Tal Chhapar Sanctuary covers 7 km2 (2.7 sq mi) and is an Important Bird Area. It is located in the Churu district, 210 km (130 mi) from Jaipur, in the Shekhawati region of Rajasthan. This sanctuary is home to large populations of blackbuck, fox, caracal, partridge, and sand grouse.
- The Sundha Mata Conservation Reserve covers 117.49 km2 (45.36 sq mi) and is located in the Jalore District of Rajasthan.
- In Pakistan:
- The Nara Desert Wildlife Sanctuary covers 6,300 km2 (2,400 sq mi); it is located in is located in Mirpurkhas District. It contains the largest population of the endangered mugger crocodile in Pakistan.
- The Rann of Kutch Wildlife Sanctuary located in Badin District is an Important Bird Area and Ramsar Site, with 30 species of mammals, 112 bird species, 20 reptiles, and 22 important plant species.
- The Lal Suhanra Biosphere Reserve and National Park is a UNESCO declared biosphere reserve, which covers 65,791 hectares (254.02 sq mi) the Cholistan region of the Greater Thar Desert.
Biodiversity
Fauna
Some wildlife species that are fast vanishing in other parts of India are found in the desert in large numbers, including the blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra), chinkara (Gazella bennettii), and Indian wild ass (Equus hemionus khur) in the Rann of Kutch. This may be partly because they are well adapted to this environment: they are smaller than similar animals that live in other environments, and they are mainly nocturnal. It may also be because grasslands in this region have not been transformed into cropland as fast as in other regions, and because a local community, the Bishnois, has made special efforts to protect them.
Other mammals in the Thar Desert include a subspecies of red fox (Vulpes vulpes pusilla) and the caracal, and a number of reptiles dwell there too.
The region is a haven for 141 species of migratory and resident desert birds, including harriers, falcons, buzzards, kestrels, vultures, short-toed eagles (Circaetus gallicus), tawny eagles (Aquila rapax), greater spotted eagles (Aquila clanga), and laggar falcons (Falco jugger).
The Indian peafowl is a resident breeder in the Thar region. The peacock is designated as the national bird of India and the provincial bird of the Punjab (Pakistan). It can be seen sitting on khejri or pipal trees in villages or Deblina.
-
Peafowl eating pieces of chapati in Tharparkar District, Sindh
Flora
The natural vegetation of this dry area is classified as northwestern thorn scrub forest occurring in small clumps scattered more or less openly. Density and size of patches increase from west to east following the increase in rainfall. The natural vegetation of the Thar Desert is composed of these tree, shrub, and herb species:
- Trees and shrubs: Vachellia jacquemontii, Balanites roxburghii, Ziziphus zizyphus, Ziziphus nummularia, Calotropis procera, Suaeda fruticosa, Crotalaria burhia, Aerva javanica, Clerodendrum multiflorum, Leptadenia pyrotechnica, Lycium barbarum, Grewia tenax, Commiphora mukul, Euphorbia caducifolia, Euphorbia neriifolia, Cordia sinensis, Maytenus emarginata, Capparis decidua, Mimosa hamata
- Herbs and grasses: Ochthochloa compressa, Dactyloctenium scindicum, Cenchrus biflorus, Cenchrus setiger, Lasiurus scindicus, Cynodon dactylon, Panicum turgidum, Panicum antidotale, Dichanthium annulatum, Sporobolus marginatus, Saccharum spontaneum, Cenchrus ciliaris, Desmostachya bipinnata, Eragrostis species, Ergamopagan species, Phragmites species, Tribulus terrestris, Typha species, Sorghum halepense, Citrullus colocynthis
The endemic floral species include Calligonum polygonoides, Prosopis cineraria, Acacia nilotica, Tamarix aphylla, and Cenchrus biflorus.
People
The Thar people are the natives of the area. The Thar Desert is the most widely populated desert in the world, with a population density of 83 people per km2. In India, the inhabitants comprise Hindus, Jains, Sikhs, and Muslims. In Pakistan, inhabitants include both Muslims and Hindus.
About 40% of the total population of Rajasthan lives in the Thar Desert. The main occupations of the inhabitants are agriculture and animal husbandry.
Jodhpur, the largest city in the region, lies in the scrub forest zone at the desert's perimeter. Bikaner and Jaisalmer are the largest cities located entirely in the desert.
-
A girl from the Gadia Lohars nomadic tribe of Marwar, cooking her food.
Water and housing in the desert
In the true desert areas, the only sources of water for animals or humans are small, scattered ponds - some that are natural (tobas) and some that are human-made (johads). The persistence of water scarcity heavily influences life in all areas of the Thar, prompting many inhabitants to adopt a nomadic lifestyle. Most of the permanent human settlements are located near the two seasonal streams of the Karon-Jhar hills. Potable groundwater is also rare in the Thar Desert. Much of it tastes sour due to dissolved minerals. Potable water is mostly available only deep underground. When wells are dug that happen to yield sweet tasting water, people tend to settle near them, but such wells are difficult and dangerous to dig, sometimes claiming the lives of the well-diggers.
Crowded housing conditions are common in some areas.
Economy
Agriculture
The Thar is one of the most heavily populated desert areas in the world with the main occupations of its inhabitants being agriculture and animal husbandry.
Agricultural production is mainly from kharif crops, which are grown in the summer season and seeded in June and July. These are then harvested in September and October and include bajra, pulses such as guar, jowar (Sorghum vulgare), maize (zea mays), sesame and groundnuts.
Livestock
-
Thari cow breed originating from Tharparkar, Sindh, popular since World War I
Agroforestry
P. cineraria wood is reported to contain high calorific value and provide high-quality fuel wood. The lopped branches are good as fencing material. Its roots also encourage nitrogen fixation, which produces higher crop yields.
Ecotourism
Desert safaris on camels have become increasingly popular around Jaisalmer. Domestic and international tourists frequent the desert seeking adventure on camels for one to several days. This ecotourism industry ranges from cheaper backpacker treks to plush Arabian night-style campsites replete with banquets and cultural performances. During the treks, tourists are able to view the fragile and beautiful ecosystem of the Thar Desert. This form of tourism provides income to many operators and camel owners in Jaisalmer, as well as employment for many camel trekkers in the desert villages nearby. People from various parts of the world come to see the Pushkar ka Mela (Pushkar Fair) and oases.
Industry
The government of India initiated departmental exploration for oil in 1955 and 1956 in the Jaisalmer area, Oil India Limited discovered natural gas in 1988 in the Jaisalmer basin.
History
The Desert National Park in Jaisalmer district has a collection of 180-million-year- old animal and plant fossils.
Jaisalmer State's historical foundations are in the large empire ruled by the Bhati dynasty. The empire stretched from what is now Ghazni in modern-day Afghanistan to what is Sialkot, Lahore and Rawalpindi in modern-day Pakistan to the region that is Bhatinda and Hanumangarh in modern-day India. The empire crumbled over time because of continuous invasions from central Asia. According to Satish Chandra, the Hindu Shahis of Afghanistan made an alliance with the Bhatti rulers of Multhan because they wanted to end the slave raids that were made by the Turkic ruler of Ghazni, but the alliance was broken apart by Alp Tigin in 977 CE. Bhati dominions continued to shift southwards: they ruled Multan, then finally got pushed into Cholistan and Jaisalmer, where Rawal Devaraja built Dera Rawal / Derawar. Jaisalmer was founded as the new capital in 1156 by Maharawal Jaisal Singh and the state took its name from the capital. On 11 December 1818 Jaisalmer became a British protectorate through the Rajputana Agency.
Because the kingdom's main source of income had long been levies on caravans, its economy suffered after Bombay became a major port, and sea trade largely replaced trade along the traditional land routes. Maharawals Ranjit Singh and Bairi Sal Singh tried to reverse the economic decline, but the kingdom nevertheless became impoverished. To make matters worse, there was a severe drought and a resulting famine from 1895 to 1900, during the reign of Maharawal Salivahan Singh, which caused the widespread loss of the livestock upon which the increasingly agriculturally based kingdom had come to rely.
In 1965 and 1971, population exchanges took place in the Thar between India and Pakistan; 3,500 Muslims shifted from the Indian section of the Thar to Pakistani Thar, whilst thousands of Hindu families also migrated from Pakistani Thar to the Indian section.
See also
 In Spanish: Desierto de Thar para niños
In Spanish: Desierto de Thar para niños
- Arid Forest Research Institute
- Arid Lands Information Network
- Aridification
- Cholistan Desert
- Nara desert
- Cyclone Phet – tracked directly over the desert
- Deforestation
- Geography of India
- History of Thar
- List of deserts by area
- Marwar
- Pokhran
- Thari people

























