Sakaiminato, Tottori facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sakaiminato
境港市
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Downtown Sakaiminato, near Sakaiminato Station
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||

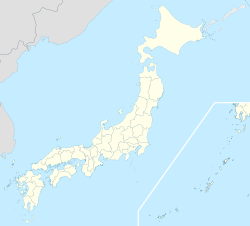
Location of Sakaiminato in Tottori Prefecture
|
|||||||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||||||
| Region | Chūgoku (San'in) | ||||||||||
| Prefecture | Tottori | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| • Total | 29.10 km2 (11.24 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population
(1 June 2016)
|
|||||||||||
| • Total | 32,012 | ||||||||||
| • Density | 1,100.07/km2 (2,849.2/sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) | ||||||||||
| City hall address | 3000, Agarimichichō, Sakaiminato-shi, Tottori-ken 684-8501 | ||||||||||
| Climate | Cfa | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
Sakaiminato (境港市, Sakaiminato-shi) is a city in Tottori Prefecture, Japan. As of 31 December 2021[update], the city had an estimated population of 32,012 in 13178 households and a population density of 1110 persons per km². The total area of the city is 272.06 square kilometres (105.04 sq mi).
Contents
Geography
Sakaiminato is located in far western Tottori Prefecture, at the northern end of the Yumigahama Peninsula. It is surrounded on three sides by Lake Nakaumi, the Sea of Japan, and the Sakai Channel, which connects them. Across the Sakai Channel or across the Eshima Ohashi Bridge, it borders the city of Matsue in Shimane Prefecture. Sakaiminato is located on a sandbar, and the land is very flat, with an average elevation of two meters above sea level.
Surrounding municipalities
Climate
Sakaiminato has a Humid climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm, wet summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Sakaiminato is 15.5 °C (59.9 °F). The average annual rainfall is 1,903.3 mm (74.93 in) with July as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 27.3 °C (81.1 °F), and lowest in January, at around 4.9 °C (40.8 °F). Its record high is 38.5 °C (101.3 °F), reached on 22 August 2018, and its record low is −9.7 °C (14.5 °F), reached on 27 January 1904.
| Climate data for Sakaiminato (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1883−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.7 (67.5) |
24.6 (76.3) |
26.7 (80.1) |
31.2 (88.2) |
32.9 (91.2) |
35.0 (95.0) |
37.5 (99.5) |
38.5 (101.3) |
36.9 (98.4) |
33.6 (92.5) |
27.7 (81.9) |
22.3 (72.1) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.8 (55.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
23.1 (73.6) |
26.0 (78.8) |
29.9 (85.8) |
31.5 (88.7) |
27.0 (80.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
11.0 (51.8) |
19.7 (67.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.9 (40.8) |
5.3 (41.5) |
8.3 (46.9) |
13.3 (55.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.9 (78.6) |
27.3 (81.1) |
23.2 (73.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
12.4 (54.3) |
7.3 (45.1) |
15.5 (59.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
1.6 (34.9) |
3.9 (39.0) |
8.4 (47.1) |
13.6 (56.5) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.1 (75.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
8.4 (47.1) |
3.9 (39.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.7 (14.5) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
1.8 (35.2) |
7.0 (44.6) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
8.3 (46.9) |
2.3 (36.1) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−9.7 (14.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 188.4 (7.42) |
136.0 (5.35) |
139.7 (5.50) |
111.2 (4.38) |
123.3 (4.85) |
170.8 (6.72) |
215.2 (8.47) |
140.9 (5.55) |
212.8 (8.38) |
133.5 (5.26) |
145.9 (5.74) |
193.2 (7.61) |
1,903.3 (74.93) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 32 (13) |
25 (9.8) |
6 (2.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
14 (5.5) |
75 (30) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 19.6 | 15.0 | 13.2 | 10.4 | 9.1 | 9.9 | 11.0 | 9.4 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 13.0 | 18.5 | 150 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1 cm) | 7.1 | 5.8 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.4 | 17.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 72 | 69 | 68 | 70 | 77 | 79 | 76 | 77 | 74 | 73 | 74 | 74 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 63.0 | 81.8 | 137.9 | 183.9 | 208.9 | 162.0 | 174.3 | 207.1 | 147.5 | 154.8 | 109.2 | 74.7 | 1,705.1 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
Demography
Per Japanese census data, the population of Sakaiminato has been as follows.
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1920 | 21,199 | — |
| 1930 | 24,267 | +14.5% |
| 1940 | 22,386 | −7.8% |
| 1950 | 29,746 | +32.9% |
| 1960 | 32,714 | +10.0% |
| 1970 | 34,145 | +4.4% |
| 1980 | 38,278 | +12.1% |
| 1990 | 37,282 | −2.6% |
| 2000 | 36,843 | −1.2% |
| 2010 | 35,219 | −4.4% |
Etymology
The name of Sakaiminato in the Japanese language is formed from two kanji characters. The first, 境, means "border", and the second, 港 means "port".
History
The area of Sakaiminato was part of ancient Hōki Province and number remains from the Yayoi period and Kofun period have been found within city limits. In the Muromachi period, the area was dominated by the powerful Amago clan from Izumo Province and occupied an important position as a landing point for rice and navy anchorage. During the Sengoku period, it came under the control of the Mōri clan, and during the Edo Period, it was part of the holdings of the Ikeda clan of Tottori Domain. Following the Meiji restoration, the port prospered as a strategic point for domestic shipping routes in the Sea of Japan, and was designated as a trading port in 1896 for continental trade with Busan, Incheon, and Wonsan on the Korean Peninsula. The town of Sakai was established on October 21, 1889 with the establishment of the modern municipalities system. It was raised to city status on April 1, 1956, changing its name to Sakaiminato at that time.
Economy
The seaport of Sakaiminato has a long history as a seaport for the San'in Region. Following World War II the city has served as the base of the fishing industry for all of Western Japan. Consequently, marine product processing is also a major industry in the city.
Education
Sakaiminato has six public elementary schools and three public junior high schools operated by the town government. The city has two public high schools operated by the Tottori Prefectural Board of Education.
Transportation
Airport
- Miho-Yonago Airport
Railway
- Yonago Airport - Nakahama - Takamatsuchō - Amariko - Agarimichi - Babasakichō - Sakaiminato
Highways
 National Route 431
National Route 431
Seaports
- Port of Sakaiminato; The port at Sakaiminato serves the DBS Cruise ferry Eastern Dream, which connects Japan to Donghae, South Korea, and Vladivostok, Russia.
Sister cities
Sakaiminato is twinned with:
 Hunchun, China
Hunchun, China
Former twin towns
 Wonsan, North Korea (revoked in 2006). Sakaiminato was the only Japanese municipality to have a twin town agreement with a North Korean city from 1992 to 2006. In 2006, Mayor Katsuji Nakamura revoke the agreement in response to North Korea's announcement of a nuclear test along with the Japanese government's decision to impose economic sanctions. Actual twin town activities had already come to an end by 2002, after which the cities had only sent each other a letter once per year.
Wonsan, North Korea (revoked in 2006). Sakaiminato was the only Japanese municipality to have a twin town agreement with a North Korean city from 1992 to 2006. In 2006, Mayor Katsuji Nakamura revoke the agreement in response to North Korea's announcement of a nuclear test along with the Japanese government's decision to impose economic sanctions. Actual twin town activities had already come to an end by 2002, after which the cities had only sent each other a letter once per year.
Local attractions
- Tottori Domain Battery Sites, National Historic Site
Notable people from Sakaiminato
- Shigeru Mizuki, the creator of GeGeGe no Kitaro, a character seen in many forms throughout Japan. Although he was born in Osaka, Mizuki was raised in Sakaiminato. The spirit of Kitaro can be found in Sakaiminato, on Kitaro Road, a street dedicated to all the characters that appear in Mizuki's stories. Over one hundred bronze statues of the story's characters line both sides of the road.
- Shōji Ueda
Gallery
See also
 In Spanish: Sakaiminato (Tottori) para niños
In Spanish: Sakaiminato (Tottori) para niños