RuBisCO facts for kids
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, better known as RuBisCO, is an enzyme that catalyzes the first major step of carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle. Carbon fixation is a process by which the atoms of atmospheric carbon dioxide are made available to organisms in the form of energy-rich molecules such as glucose. RuBisCO splits 6-C molecules into two equal parts.
RuBisCO is very important in biology and ecology because it catalyzes the primary chemical reaction by which inorganic carbon permanently enters the biosphere.
RuBisCO is also the most abundant protein in leaves and the most abundant protein on Earth. It accounts for 50% of soluble leaf protein (20-30% of total leaf nitrogen) and 30% of soluble leaf protein in plants (5-9% of total leaf nitrogen).
Given its important role in the biosphere, there are currently efforts to genetically engineer crop plants to contain more efficient RuBisCO.
Images for kids
-
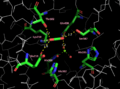
Active site of RuBisCO of Galdieria sulphuraria with CO2: Residues involved in both the active site and stabilizing CO2 for enzyme catalysis are shown in color and labeled. Distances of the hydrogen bonding interactions are shown in angstroms. Mg2+ ion (green sphere) is shown coordinated to CO2, and is followed by three water molecules (red spheres). All other residues are placed in grayscale.
See also
 In Spanish: RuBisCO para niños
In Spanish: RuBisCO para niños