Molecule facts for kids
A molecule is the smallest amount of a chemical substance that can exist. If a molecule were split into smaller pieces, it would be a different substance.
Molecules are made up of atoms that are stuck together in a particular shape or form. Not all combinations of atoms are equally possible; atoms make certain shapes in preference to others. Also, they have different valency. For example, oxygen atoms always have two bonds with other atoms, carbon atoms always have four bonds with other atoms, and nitrogen atoms always have three bonds with other atoms.
In the kinetic theory of gases, the term molecule is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. According to this definition, noble gas atoms are considered molecules as they are in fact monoatomic molecules.
In gases like air, the molecules are just flying around. In liquids like water, the molecules are stuck together but they can still move. In solids like sugar, the molecules can only vibrate. In the fourth state of matter known as plasma, the atoms are ionized and cannot form molecules.
With a molecular formula, you can write down the numbers of all atoms in a molecule. For example, the molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6. That means that one molecule of glucose is made up of six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms.
Bonding
For a molecule to exist, atoms have to stick together. This happens when two atoms share electrons. Instead of circling just one atom, the electron now circles around two. This is called a covalent bond. Sometimes, more than one electron is shared. The more electrons are shared, the stronger the bond gets and the stronger the atoms stick together.
Bonds can also be broken apart. Since most bonds require energy to form, they also give off energy when they are broken. But before most bonds break, the molecule has to be heated. Then the atoms start to move, and when they move too much, the bond breaks. Molecules that require less energy to break than they give off when broken are called fuels. For example, a candle will just sit there and nothing happens. But when you use a match to light it, it will burn for a long time. The match brings the energy to break the first bonds, which release enough energy to break the bonds below them, until the candle has burned down.
There are also ionic bonds.
Images for kids
-
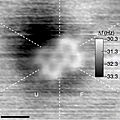
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) image of a PTCDA molecule, in which the five six-carbon rings are visible.
-
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of pentacene molecules, which consist of linear chains of five carbon rings.
-
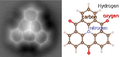
Structure and STM image of a "cyanostar" dendrimer molecule.
-
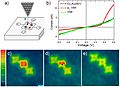
Hydrogen can be removed from individual H2TPP molecules by applying excess voltage to the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope (STM, a); this removal alters the current-voltage (I-V) curves of TPP molecules, measured using the same STM tip, from diode like (red curve in b) to resistor like (green curve). Image (c) shows a row of TPP, H2TPP and TPP molecules. While scanning image (d), excess voltage was applied to H2TPP at the black dot, which instantly removed hydrogen, as shown in the bottom part of (d) and in the rescan image (e). Such manipulations can be used in single-molecule electronics.
See also
 In Spanish: Molécula para niños
In Spanish: Molécula para niños