Calvin cycle facts for kids
The Calvin cycle (also known as the Benson-Calvin cycle) is the set of chemical reactions that take place in chloroplasts during photosynthesis.
The cycle is light-independent because it takes place after the energy has been captured from sunlight.
The Calvin cycle is named after Melvin C. Calvin, who won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry for finding it in 1961. Calvin and his colleagues, Andrew Benson and James Bassham, did the work at the University of California, Berkeley.
Contents
Context
Using the radioactive carbon-14 isotope as a tracer, Calvin, Andrew Benson and their team mapped the complete route that carbon travels through a plant during photosynthesis. They traced the carbon-14 from soaking up its atmospheric carbon dioxide to its conversion into carbohydrates and other organic compounds. The single-celled algae Chlorulla was used to trace the carbon-14.
The Calvin group showed that sunlight acts on the chlorophyll in a plant to fuel the manufacture of organic compounds, not directly on carbon dioxide as previously believed.
Steps
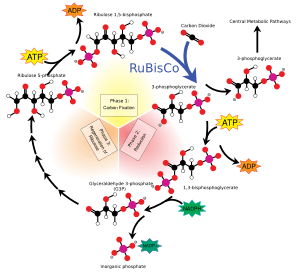
The steps in the cycle are as follows:
1. Grab: A five-carbon carbon catcher called RuBP (Ribulose bisphosphate) catches one molecule of carbon dioxide and forms a six-carbon molecule.
2. Split: the enzyme RuBisCO (with the energy of ATP and NADPH molecules) breaks the six-carbon molecule into two equal parts.
3. Leave: A trio of carbons leave and become sugar. The other trio moves on to the next step.
4. Switch: Using ATP and NADPH, the three carbon molecule is changed into a five carbon molecule.
5. The cycle starts over again.
The product
The carbohydrate products of the Calvin cycle are three-carbon sugar phosphate molecules, or 'glucose triose phosphates' (G3P). Each step of the cycle has its own enzyme which speeds up the reaction.
fi:Yhteyttäminen#Valoreaktiot ja pimeäreaktiot
See also
 In Spanish: Ciclo de Calvin para niños
In Spanish: Ciclo de Calvin para niños