Malayan tiger facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Malayan tiger |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A Malayan tiger in water | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: |
P. t. jacksoni
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Panthera tigris jacksoni |
|
 |
|
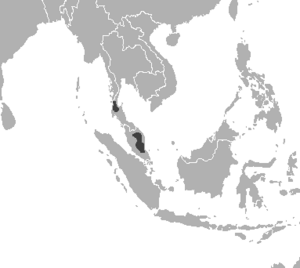
| Range map | |
The Malayan tiger (Panthera tigris jacksoni) is a new subspecies of the tiger that was discovered in 2004. People used to think they were Indo-Chinese tigers, But now they have their own subspecies. They have the same length and weight as the Indo-Chinese tiger. They live in southern Malaysia and they are an endangered species.
Contents
Characteristics
There is no clear difference between the Malayan and the Indochinese tigers, when specimens from the two regions are compared cranially or in pelage. No type specimen was designated.
Malayan tigers appear to be smaller than Indian ones. From measurements of 11 males and 8 females, the average length of a male is 8 ft 6 in (259 cm), and of a female 7 ft 10 in (239 cm).
Body length taken from 16 female tigers in the State of Terengganu ranged from 70 to 103 in (180 to 260 cm) and averaged 80.1 in (203 cm). Their height ranged from 23 to 41 in (58 to 104 cm), and their body weight from 52 to 195 lb (24 to 88 kg). Data from 21 males in the State of Terengganu showed that total length ranged from 75 to 112 in (190 to 280 cm), with an average of 94.2 in (239 cm). Their height ranged from 24 to 45 in (61 to 114 cm), and their body weight from 104 to 284.7 lb (47.2 to 129.1 kg).
Distribution and habitat
The geographic division between Malayan and Indochinese tigers is unclear as tiger populations in northern Malaysia are contiguous with those in southern Thailand. In Singapore tigers were extirpated in the 1950s, and the last one shot in 1932.
Between 1991 and 2003, tiger signs were reported from early-succession vegetation fields, agricultural areas outside forests in Kelantan, Terengganu, Pahang, and Johor, and many riparian habitats outside forests in Pahang, Perak, Kelantan, Terengganu, and Johor. Most of the major rivers that drain into the South China Sea had some evidence of tigers, whereas those draining into the Straits of Malacca in the west did not.
Tiger signs were not reported from Perlis, Penang, and Malacca, and the federal territories of Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya in the west coast. The total potential tiger habitat was 66,211 km2 (25,564 sq mi), which comprised 37,674 km2 (14,546 sq mi) of confirmed tiger habitat, 11,655 km2 (4,500 sq mi) of expected tiger habitat and 16,882 km2 (6,518 sq mi) of possible tiger habitat. All the protected areas greater than 402 km2 (155 sq mi) in size had tigers.
In September 2014 two conservation organisations announced that a camera trap survey of seven sites in the three separate habitats from 2010 to 2013 had produced an estimate of the surviving population from 250 to 340 healthy individuals, with a few additional isolated small pockets probable. According to the report, the decline meant that the species might have to be moved to the "Critically Endangered" category in the IUCN list.
Ecology and behaviour
Malayan tigers prey on sambar deer, barking deer, wild boar, Bornean bearded pigs and serow. Malayan tigers also prey on sun bears, young elephants and rhino calves. Whether their principal prey includes adult gaur and tapir is unknown. Occasionally, livestock is also taken; however, tiger predation reduces the numbers of wild boar which can become a serious pest in plantations and other croplands. Studies indicate that in areas where large predators (tigers and leopards) are extinct, wild pigs are over 10 times more numerous than in areas where tigers and leopards are still present.
Tigers occur at very low densities 1.1–1.98 tigers per 100 km² in the rainforest as a result of low prey densities, thus to maintain viable tiger populations of minimum of 6 breeding females, reserves need to be larger than 1000 km². Information on dietary preference, morphological measurements, demographic parameters, social structure, communication, home range sizes, dispersal capabilities are all lacking.
Threats
Habitat fragmentation due to development projects and agriculture are serious threats. Commercial poaching occurs at varying levels in all tiger range states. In Malaysia there is a substantial domestic market in recent years for tiger meat and manufactured tiger bone medicines.
Conservation
Tigers are included on CITES Appendix I, banning international trade. All tiger range states and countries with consumer markets have banned domestic trade as well.
The Malaysian Conservation Alliance for Tigers (MYCAT) is "an alliance of non-governmental organisations comprising the Malaysian Nature Society (MNS), Traffic Southeast Asia, Wildlife Conservation Society-Malaysia Programme and WWF-Malaysia." It also includes the Department of Wildlife and National Parks.
In 2007, they implemented a hotline to report tiger-related crimes, such as poaching. In order to deter poaching, they organize "Cat Walks", a citizen patrol in danger zones. MYCAT has a goal of increasing the tiger population.
In captivity
The Cincinnati Zoo was the first zoo in North America to begin a captive breeding program for Malayan tigers with the importation of a male and three females from Asia between 1990 and 1992. The breeding program was as a Tiger SSP in 1998. There are also a few Malayan Tigers in the Zoo Taiping and Night Safari.
As of 2011 there were 54 of this subspecies in North American zoos. The 54 individuals are located in 25 institutions and are descended from only 11 founders. Therefore, the plan of retaining a target of 90% genetic diversity over the next century is not possible unless other founders are added.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tigre malayo para niños
In Spanish: Tigre malayo para niños






