International Energy Agency facts for kids
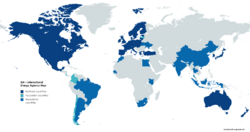
Member countries Association countries Accession countries
|
|
| Abbreviation | IEA |
|---|---|
| Established |
|
| Type | Autonomous intergovernmental organisation |
| Headquarters | 9, rue de la Fédération, Paris, France |
|
Membership
|
|
|
Official languages
|
English |
| Fatih Birol | |
|
Deputy Executive Director
|
Mary Burce Warlick |
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 association countries of the IEA represent 75% of global energy demand.
The IEA was set up under the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis to respond to physical disruptions in global oil supplies, provide data and statistics about the global oil market and energy sector, promote energy savings and conservation, and establish international technical collaboration. Since its founding, the IEA has also coordinated use of the oil reserves that its members are required to hold.
In subsequent decades, the IEA's role expanded to cover the entire global energy system, encompassing traditional fuels such as gas, and coal as well as cleaner and fast-growing energy sources and technologies including renewable energy sources; solar photovoltaics, wind power, biofuels as well as nuclear power, and hydrogen, and the critical minerals needed for these technologies.
The core activity of the IEA is providing policy advice to its member states and Associated countries to support their energy security and advance their transition to clean energy. Recently, it has focused in particular on supporting global efforts to accelerate clean energy transition, mitigate climate change, reach net zero emissions, and prevent global temperatures from rising above 1.5 °C. All IEA member countries have signed the Paris Agreement which aims to limit warming to 1.5 °C, and two thirds of IEA member governments have made commitments to emission neutrality by 2050.
The IEA's current executive director is Fatih Birol, who took office in late 2015. IEA publishes a range of reports and other information including its flagship publication, the annual World Energy Outlook, as well as the Net Zero by 2050 report.
History
The IEA was founded on November 18, 1974, after the 1973 oil crisis, to avoid future shocks by helping to ensure reliable energy supplies, promote energy efficiency, ensure energy security and encourage technological research and innovation.
The Agreement on an International Energy Program (IEP Agreement) established the mandates and structure of the IEA, chartering it as an autonomous organisation under the umbrella of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
The IEA operates autonomously, with its own budget and governance structure. The organization began with 16 founding member countries and has since expanded to 31, with the latest addition being Lithuania in 2022. Full members of the IEA must also be members of the OECD and are required to hold 90 days worth of oil imports as emergency stocks. These emergency stocks can be released to stabilize oil markets worldwide and have been activated five times: January 1991 due to the Gulf War, 2005 after devastation in the Gulf of Mexico from hurricanes Katrina and Rita, 2011 during the Libyan crisis, and twice in 2022 in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
In addition to the emergency release mechanism, the IEA's initial mandates include reducing dependence on oil, developing alternative energy sources, energy research and development, and collaboration with oil-producing companies and countries to create a stable energy market. Members are expected to draw up plans on demand reduction and efficiency measures that can be implemented during energy emergencies.
In 2015, the IEA's chief economist Fatih Birol was appointed executive director, the first time an official from within the organization was picked to lead it. They have a mandate to modernize the agency on three major pillars: broadening the IEA's mandate on energy security beyond oil to include natural gas and electricity; increasing engagement in emerging economies through new Association partnerships; and expanding the IEA's core focus on clean energy technology and energy efficiency.

The new category of "Association countries" was created in 2015, allowing countries that do not fit the criteria for IEA membership to become affiliated with the organization and participate in its work. China, Indonesia, and Thailand were the first to join and the IEA now has thirteen Association countries, including Ukraine since July 2022. IEA member and Association countries represent over 75% of global energy consumption.
In 2021, IEA chief Fatih Birol called on policymakers to do more to do more to accelerate the clean energy transition and reduce emissions, saying that "Clean-energy technologies are slowly but surely going to replace the existing energy industry."
After the IEA's 2022 Ministerial meeting, a bi-annual high-level meeting of IEA countries, member countries once again expanded the organisation's mandate to include accelerating the global clean energy transition by "supporting countries in the global effort to attain net zero greenhouse gas emissions in the energy sector by mid-century." The "IEA 3.0" mandate also doubles down on strengthening energy security and recognizes the importance of tracking critical minerals and materials to the clean energy transition.
Leadership
| No. | Name | Country of origin | Took office | Left office | Previous position | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ulf Lantzke | 1975 | 31 March 1984 | Special Advisor on Energy Issues to the Secretary General of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) | ||
| 2 | Helga Steeg | 1 July 1984 | 30 September 1994 | Director-General for Trade, Federal Ministry of Finance of the Federal Republic of Germany | ||
| 3 | Robert Priddle | 1 December 1994 | 31 December 2002 | Head of Consumer and Corporate Affairs, UK Department of Energy and Trade and Industry | ||
| 4 | Claude Mandil | 1 February 2003 | 31 August 2007 | Chairman and CEO of the Institut français du pétrole, 2000–2003 | ||
| 5 | Nobuo Tanaka | 1 September 2007 | 31 August 2011 | Director for Science, Technology and Industry at the OECD, 1992–2007 | ||
| 6 | Maria van der Hoeven | 1 September 2011 | 31 August 2015 | Minister of Economic Affairs of the Netherlands, 2007–2010 | ||
| 7 | Fatih Birol | 1 September 2015 | Incumbent | Chief Economist, International Energy Agency |
Structure
The IEA's structure includes a Governing Board, Ministerial Meetings, and Standing Groups and Committees.
The Governing Board constitutes the main decision-making body of the organisation. It is composed of member country representatives and meets three to four times a year. The Governing Board is responsible for the IEA's administrative proceedings and approving binding decisions in relation to energy developments.
The IEA Ministerial Meeting is the biennial gathering of energy ministers who determine the broad direction of the IEA. The Ministerial allows for the development of ideas which are subsequently put to the Governing Board.
Standing Groups meet multiple times a year and are made up of officials from member states. The IEA has several Standing Groups and Committees, focusing on energy research and technology, long-term cooperation, emergency preparedness, and other topics.
Membership
The 31 member countries and 13 association countries of the IEA represent 75% of global energy demand.
Member countries
Only OECD member states may join the IEA. Member are required to maintain total oil stock levels equivalent to at least 90 days of the previous year's net imports. Member countries commit to respond to significant oil disruptions through a collective action to allow more crude oil to enter the global market.
| Country | Membership | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1979 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 2001 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 2014 | ||
| 1992 | ||
| 1992 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 1976 | ||
| 1997 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 2022 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 2018 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 1977 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member (under a special Agreement) | |
| 1981 | ||
| 2 October 2007 | ||
| 7 March 2007 | ||
| 20 April 2001 | ||
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member | |
| 18 November 1974 | Founding member |
Accession countries
Accession countries are those going through the process of becoming full members. The process involves authorisation by the Governing Board, discussions with the executive director, and the sharing of information related to the criteria for membership with the Secretariat.
The following countries are currently undergoing the accession process:
Association countries
Association was formally launched in 2015 and currently includes 13 countries. The IEA collaborates with Association countries on a wide range of energy-related issues determined through joint programmes of work. Association countries may also participate in most Standing Groups and Ministerial meetings. Egypt and Argentina joined as Association countries in March 2022, and Ukraine was formally invited on 16 June 2022, and joined in July 2022.
 Argentina
Argentina Brazil
Brazil China
China Egypt
Egypt India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Kenya
Kenya Morocco
Morocco Senegal
Senegal Singapore
Singapore South Africa
South Africa Thailand
Thailand Ukraine
Ukraine
Areas of work
The IEA produces analyses on all energy sources and technologies, on global and regional markets, as well as specific country-level reports and studies on key technologies, minerals, and materials for the clean energy transition. It also produces comprehensive data and statistics for over 150 countries.
The IEA's analytical work is split into various categories including policy recommendations, tracking, market forecasts, technical roadmapping, and scenario analysis.
Data
The IEA publishes comprehensive data, statistics, and analysis that inform national energy policies and support long-term planning for energy sector investments. The IEA analyses and releases data and information on trends in energy supply, demand, prices, public research and development, and energy efficiency metrics. The data also serves to track short- and long-term trends in countries energy transitions.
The Policies and Measures Database (PAMS) makes available to the public data on government policies and programs to reduce carbon emissions, support energy efficiency, and improve the development and use of renewable and clean energy sources. The database compiles data from several IEA and International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) data sources dating back to 1999 and includes information on past, current, and planned policy measures.
Scenarios
IEA publications give projections based on sets of assumptions called scenarios. Currently-used scenarios include:
- Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS): Assumes implementation of governments' existing policies and firm commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Announced Pledges Scenario (APS): Assumes implementation of policies as in the STEPS, and also assumes fulfillment of looser pledges that are not yet backed by policy and legislation.
- Net Zero Scenario (NZE): Assumes implementation of the IEA's pathway to net zero emissions by 2050 while minimising cost and meeting key UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Older scenarios include:
- 450 Scenario: Environmental groups have become critical of the IEA's 450 Scenario (created to align with the 2009 Copenhagen Accord), contending it does not align with up-to-date climate science, nor is it consistent with the Paris climate agreement that aspires to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius. In March 2017, the IEA (along with IRENA) published a report that considers a safer climate scenario than their current 450S. This scenario offers improved chances of limiting global warming to less than two degrees, but – according to research organization Oil Change International – still falls short of adequately addressing climate science and the decarbonization required to reach agreed upon global climate limits. The IEA has stopped updating this safer climate scenario
- Sustainable Development Scenario: Concerns regarding the IEA's Sustainable Development Scenario (the successor to the 450 scenario) has also been raised by climate scientists and key financial institutions, who have called for 1.5°C scenario placed centrally in the World Energy Outlook. The IEA's Sustainable Development Scenario only gets to net-zero by 2070, two decades too late.
Key publications
World Energy Outlook (WEO)
Net Zero by 2050: a roadmap for the global energy sector
Net Zero by 2050 was published in May 2021 and presented the first comprehensive pathway for the global energy sector to reach net zero emissions by 2050. The report introduced the Net Zero Emissions scenario, showing how to transition to net zero by 2050 while maintaining secure and affordable energy supplies, extending energy access, and encouraging robust economic growth. The report was the basis for a game created by the IEA and the Financial Times in which players compete to see if they can reduce emissions to net zero.
Energy Technology Perspectives (ETP)
First issued in 2006, ETP is a bi-annual guidebook on clean energy technology. The publication focuses on challenges, growth areas, and strengths of emerging clean energy technologies and their contribution to global energy and environmental policy-making.
Global EV Outlook (GEVO)
Published annually with the support of the members of the Electric Vehicles Initiative, GEVO highlights and analyses recent developments in EVs and electric mobility. The publication combines historical analysis with projections to 2030 for topics such as charging infrastructure, CO2 emissions, energy use, and related policy developments. The report includes policy recommendations to advance EV adoption.
Oil Market Report
First published in 1983, the monthly Oil Market Report analyses the global oil market, providing data and forecasts aimed for an audience of industry, financial, and government officials as well as an academic and NGO audience. Country specific analysis on trade and production tracks both OECD and non-OECD states.
Electricity Market Report
The Electricity Market Report provides regular forecasts for global electricity demand, supply, generation and emissions, with a special focus on recent developments.
Gas Market Report
The Gas Market Report is updated quarterly, providing the latest developments and data for global gas markets.
Energy Efficiency
Energy Efficiency is an annual report on global progress and developments in the crucial role that efficient appliances, equipment, buildings, transport and industry play in reducing energy use and the resulting emissions.
Renewable Energy Market Update
The Renewable Energy Market Update surveys new additions in global renewable power capacity and demand for biofuel. The report, which is updated several times a year, also discusses important variables and policy implications that may affect projections for the years to come.
World Energy Investment
The annual World Energy Investment tracks investment across the energy world, examining how investors are assessing risks and opportunities across all areas of fuel and electricity supply, critical minerals, efficiency and research and development.
Tracking Clean Energy Progress
TCEP reports on the status of 46 critical energy technologies and sectors needed to achieve net zero emissions by mid-century, and provides recommendations on how to accelerate their development and deployment.
Country Reviews
Since 1976, the IEA has published in-depth energy policy reviews. These country policy reviews are typically conducted every five years for member countries, and cover the full range of the country's energy systems and policies, with recent reports placing particular focus on progress towards reaching climate goals. The most recent reports were on Norway, Poland, Belgium, and Canada. The IEA also produces in-depth energy reviews of its accession and association countries, as well as partner countries.
Energy Efficiency
In its focus on energy efficiency, the IEA convenes policy leaders and other stakeholders with an eye toward scaling up progress on energy efficiency as a way to mitigate climate change, contribute to energy security, and deliver economic, and support economies and communities. The IEA has created Energy Efficiency Indicators based on over ten years of data to highlight the drivers of individual nations' energy use in order to track energy efficiency and improve national policies. The data covers major sectors such as residential services, industry, and transport.
Clean Energy Transitions Programme
CETP's focus is to "accelerate global clean energy transitions, particularly in major emerging economies." The program supports governments whose energy policies will be key to the global energy transition and involves collaborative analytics, technology cooperation, stakeholder convenings, and training and capacity-building. CETP has identified Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Mexico, and South Africa as priority countries as well as the regions of Southeast Asia, Latin America and Africa.
People-Centered Clean Energy Transition
As part of its work on the energy transition, the IEA convenes the Global Commission for People-Centred Clean Energy Transitions to "ensure the benefits and costs involved in the transformation of our energy system are distributed fairly and in a way that protects the most vulnerable in society." The approach focuses on skill development, jobs, worker protections, economic development, equity and fairness, social inclusion, and engaging individuals as stakeholders in the process. The commission is composed of national leaders, government ministers, and representatives from civil society. In October 2021, the Commission published a report for twelve recommendations for a people-centered approach to the clean energy transition.
Resilience of the Energy Sector to Climate Change Impacts
Given the implications of climate change impacts for energy security, the IEA also works to understand climate impacts on energy systems and provide guidance on measures to improve their resilience to these impacts. This includes an assessment of hydropower under different climate scenarios and a report focused on climate hazards for power systems and measures to enhance their climate resilience. The IEA also provides an overview of the level of climate hazards in its member countries, along with key planning and policy documents to address energy sector climate resilience.
Technology Collaboration Programs (TCPs)
TCPs provide support to independent, international groups of government and industry experts to research, develop, and commercialise energy technologies and related issues. Over 6,000 experts are involved in TCPs across approximately 300 organisations in 55 countries. Examples of TCPs include the Energy in Buildings and Communities (EBC), Photovoltaic Power Systems (PVPS), and Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (HEV).
See also
 In Spanish: Agencia Internacional de la Energía para niños
In Spanish: Agencia Internacional de la Energía para niños
- World Energy Outlook
- Air Infiltration and Ventilation Centre
- Consensus Economics: Surveys of International Economic Forecasts
- Economics
- IEA Solar Heating and Cooling Programme
- International Energy Agency Energy in Buildings and Communities Programme
- IEA-ECBCS Annex 48 : Heat Pumping and Reversible Air Conditioning
- International Atomic Energy Agency
- International Partnership for Energy Efficiency Cooperation
- International Renewable Energy Agency
- Nuclear Energy Agency
- One Watt Initiative
- OPEC
- Peak oil
- REN21
- SolarPACES
- Task 40


