Hadrosaur facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hadrosaurids |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Mounted skeleton of Parasaurolophus cyrtocristatus, Field Museum of Natural History | |
 |
|
| Mounted skeleton of Edmontosaurus annectens, Oxford University Museum | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | †Ornithischia |
| Suborder: | †Ornithopoda |
| Clade: | †Hadrosauromorpha |
| Family: | †Hadrosauridae Cope, 1869 |
| Type species | |
| †Hadrosaurus foulkii Leidy, 1858
|
|
| Subgroups | |
|
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Hadrosaurs (meaning "bulky lizards") were the family of duck-billed herbivorous dinosaurs. They were the most common dinosaurs.
Hadrosaurs ranged in size from 10 to 65 ft (3 to 20 m) long. They had horny, toothless beaks and hundreds of cheek teeth in the sides of their jaws. The duck-billed dinosaurs had the most teeth; they had up to about 960 cheek teeth. Hadrosaurs lived during the later Cretaceous, and their fossils have been found in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Characteristics
Hadrosaurs had a stiff tail that was probably used for balance. They had hoof-like nails on their feet, and bumpy skin. They ran on two legs, holding their tail and head in a horizontal position. They may have walked on all four legs while grazing. Hadrosaurs probably lived near bodies of water, migrating to high ground to lay eggs. It used to be thought that they had webbed hands, but this was an artifact of the fossilization process.
It is a very interesting thing that, as Bakker says, the duckbills were so common, yet they had no obvious defence against the large carnivores. Perhaps herd organisation and running speed were sufficient. Their eating apparatus must have been an advantage as compared to other herbivores.
An exceptional fossil
One of the most complete hadrosaur specimens was found in 1999 in Hell Creek Formation of North Dakota and is known as "Dakota". This fossil is so well preserved that scientists have been able to calculate its muscle mass and learn that it was more muscular than previously thought, probably giving it the ability to outrun predators such as Tyrannosaurus rex.
This mummified hadrosaur fossil comes complete with skin (not merely skin impressions), ligaments, tendons, and possibly some internal organs. It is being analyzed in the world's largest CT scanner, operated by the Boeing Co. The machine usually is used for detecting flaws in space shuttle engines and other large objects, but previously none so large as this. Researchers hope the technology will help them learn more about the fossilized insides of the creature.
They found a gap of about a centimeter between each vertebra, indicating that there may have been a disk or other material between them, allowing more flexibility and meaning the animal was actually longer than shown in a museum. Skin impressions have been found from the following hadrosaurs: Edmontosaurus annectens, Corythosaurus casuarius, Brachylophosaurus canadensis, Gryposaurus notabilis, Parasaurolophus walkeri, Lambeosaurus magnicristatus, Lambeosaurus lambei, Saurolophus osborni, and Saurolophus angustirostris.
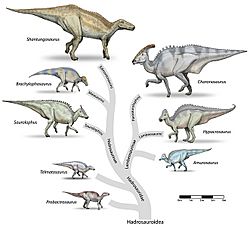
Two clades
- Two clearly different clades can be seen. One, the Hadrosaurines (sometimes called Paralophosurines), had solid crests or no crests, and were larger. The Lambeosaurines had hollow crests and were smaller.
Lambeosaurines had narrower beaks than hadrosaurines, which suggests that Lambeosaurus and its relatives could feed more selectively than their broad-beaked, crestless counterparts.
Examples
Images for kids
-
Skeleton of Maiasaura posed with a nest; the naming of this genus was one of numerous important developments in the Dinosaur Renaissance
-
Skull of Lambeosaurus, the type taxon of Lambeosaurinae
-
Skull of Saurolophus, the type taxon of Saurolophinae
-
Early restoration by Charles R. Knight of hadrosaurs as semi-aquatic animals that could only chew soft water plants, a popular idea at the time.
-
Edmontosaurus dentary with teeth, typical of hadrosauridae
See also
 In Spanish: Hadrosáuridos para niños
In Spanish: Hadrosáuridos para niños