Jurassic facts for kids
The Jurassic is the second and middle geological period in the Mesozoic era and the eighth period in the Phanerozoic eon. It began 201.3 million years ago, and ended 145 million years ago. The Jurassic period happened between the Triassic and Cretaceous periods.
Climate
During the Jurassic period, the climate was hotter and wetter than it is today. Carbon dioxide levels and sea levels were also higher than today.
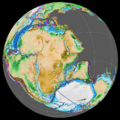
The Kimmeridge Clay of the Upper Jurassic was laid down in an environment which does not exist on the earth today. Much of Western Europe was covered by a high sea level. The supercontinent Pangaea was beginning to break up, causing a narrow Atlantic Ocean. Because of this, the United Kingdom was covered by a shallow and largely anoxic sea, perhaps less than 100 metres deep, with occasional landmasses.
This was shallower water than the Blue Lias of the Lower Jurassic. It was often low in oxygen, which caused its organic material to decompose, but only partially. The Jurassic's mudstones are organic-rich, and gave rise to most of the North Sea oil.
Plate tectonics
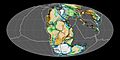
During the early or Lower Jurassic, the supercontinent Pangaea broke up into the northern supercontinent Laurasia and the southern supercontinent Gondwana. This was the start of the break-up of Pangaea, a process which took a long time to complete. The process of pulling apart in geology is called rifting.
Floods of lava flowed from fissures (splits) and volcanos. By the end of the Jurassic, South America had begun to part from Africa. In the western part of North America, mountain ranges began to form. This continued as the American tectonic plates gradually moved west. The westward-moving North American plates gradually rode over the Pacific Ocean plates to form the Rocky Mountains.
Paleontology
On sea and land, evolutionary trends which started in the Upper Triassic continued through the Jurassic. Archosaurian reptiles dominated the land biota. Reptile groups radiated and filled many niches. Dinosaurs, pterosaurs, marine reptiles (Ichthyosaurs, Plesiosaurs, turtles) all flourished.
Amongst Invertebrates, there was much change. Modern predators like starfish, crabs, and hole-boring gastropods took over the sea floor, eating the benthic fauna in huge numbers. Brachiopods lost their grip on the in-shore habitats; molluscan bivalves took their place.
Early mammals existed, but mostly as small creatures living in burrows, on the margins of a reptilian world. The first fossils of small dinosaurs with feathers, called Anchiornis, come from the Jurassic period. The first fossil bird, Archaeopteryx, comes from the Upper Jurassic.
Land plants
The dominant land plants were the gymnosperms (conifers). Ferns, large horsetails,'monkey puzzle' trees, ginkgos and cycads were common. These trees were not easy to digest, compared to modern flowering plant trees (Angiosperms). They must have spent longer in the gut than the food of modern herbivores. That would make increased size an advantage for sauropods, which did indeed become much larger in the Jurassic than any any land life had before.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Portrait of Alexandre Brongniart, who coined the term "Jurassic"
-
Middle Jurassic strata in Neuquén Province, Argentina
-
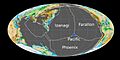
The breakup of Gondwanaland took place during the Late Jurassic, the Indian Ocean opened up as a result
-
Holotype specimen of Platysuchus, a telosaurid thalattosuchian
-
Fossil of Ichthyosaurus somersetensis at the Natural History Museum, London
-
Skeleton of Rhamphorhynchus muensteri at Teylers Museum, Haarlem
-
Archaeopteryx lithographica from the Late Jurassic (Tithonian) of Germany
-
Skeleton of Heterodontosaurus, a primitive ornithischian from the Early Jurassic of South Africa
-
Skeleton of Mamenchisaurus sinocanadorum from the Middle-Late Jurassic of China
-
Lichnomesopsyche daohugouensis , an extinct mesopsychid scorpionfly from the Late Jurassic of China
-
Vadasaurus herzogi, a rynchocephalian from the Upper Jurassic Solnhofen Limestone of Germany
-
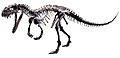
Skeleton of Ceratosaurus, a ceratosaurid from the Late Jurassic of North America
-
Skeleton of Monolophosaurus, a basal tetanuran from the Middle Jurassic of China
-
Restoration of Yi qi, a scansoriopterygid from the Middle to Late Jurassic of China
See also
 In Spanish: Jurásico para niños
In Spanish: Jurásico para niños