Electrolysis of water facts for kids
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas. This happens when an electric current being passed through the water. This technique can be used to produce breathable oxygen or hydrogen fuel. However, that method is more expensive than the industrial way to produce hydrogen fuel from natural gas.
In pure water, a redox reaction can be watched. At the cathode a reduction happens and on the anode an oxidation. Normally, the reaction is balanced with either an acid or a base as shown in the equations below.
- the oxidation at anode: 2 H2O(l) → O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 4e−
That two reactions are half reactions. They are balanced with an acid. Commonly hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid is used. However, the half reactions can also be balanced with a base, for example with sodium hydroxide.
- the reduction at cathode: 2 H2O(l) + 2e− → H2(g) + 2 OH−(aq)
- the oxidation at anode: 4 OH−(aq) → O2(g) + 2 H2O(l) + 4 e−
Combining one pair of half reactions leads to an overall reaction, which is then the decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen.
- complete reaction: 2 H2O(l) → 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
Images for kids
-
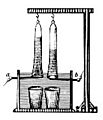
Device invented by Johann Wilhelm Ritter to develop the electrolysis of water
-
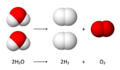
Diagram showing the overall chemical equation.
-
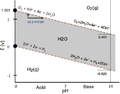
Pourbaix diagram for water, including equilibrium regions for water, oxygen and hydrogen at STP. The vertical scale is the electrode potential of hydrogen or non-interacting electrode relative to an SHE electrode, the horizontal scale is the pH of the electrolyte (otherwise non-interacting). Neglecting overpotential, above the top line the equilibrium condition is oxygen gas, and oxygen will bubble off of the electrode until equilibrium is reached. Likewise, below the bottom line, the equilibrium condition is hydrogen gas, and hydrogen will bubble off of the electrode until equilibrium is reached.
-
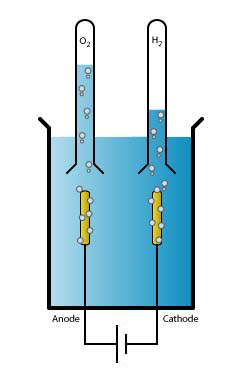
Hoffman voltameter connected to a direct current power supply
-
Illustrating inputs and outputs of simple electrolysis of water, for production of hydrogen.
See also
 In Spanish: Electrólisis del agua para niños
In Spanish: Electrólisis del agua para niños