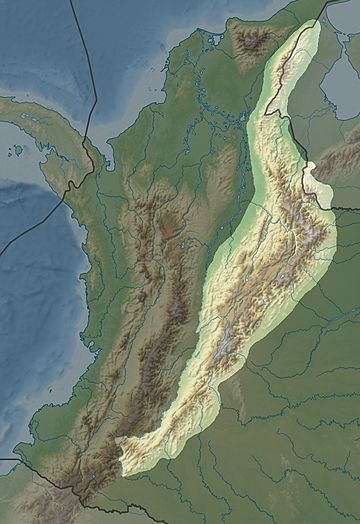
Cordillera Oriental (Colombia) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cordillera Oriental (Eastern Ranges) |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Ritacuba Blanco |
| Elevation | 5,410 m (17,750 ft) |
| Listing | Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Serranía de los Yariguíes, Serranía de las Quinchas, Sierra Nevada del Cocuy, Serranía del Perijá |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 1,200 km (750 mi) SW-NE |
| Area | 144,252 km2 (55,696 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
| Country | Colombia |
| Parent range | Andes |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Neoproterozoic-Holocene |
| Mountain type | Andean Subduction-related orogen |
The Cordillera Oriental (English: Eastern Ranges) is the widest of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Huila Department to Norte de Santander Department where it splits into the Serranía del Perijá and the Cordillera de Mérida in Venezuelan Andes. The highest peak is Ritacuba Blanco at 5,410 m (17,750 ft) in the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy.
Contents
Geography
The western part of the Cordillera Oriental belongs to the Magdalena River basin, while the eastern part includes the river basins of the Amazon River, Orinoco River, and Catatumbo River. Within it, the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy (with the only snowy peaks in this mountain range) stand out. The mountain range contains the most páramos in the world.
The Cordillera Oriental montane forests ecoregion covers the eastern slopes of the cordillera and its northern end. The Magdalena Valley montane forests cover the western slopes. The Northern Andean páramo covers the highest elevations.
Protected areas
- Cueva de los Guácharos
- Chingaza National Natural Park
- Yariguíes National Park
- Sierra Nevada del Cocuy
- Sumapaz Páramo
- Tamá National Natural Park
- Los Estoraques Unique Natural Area
- Lake Iguaque
- Guanentá Alto Río Fonce Flora and Fauna Sanctuary
- Catatumbo Barí National Natural Park
- Los Picachos National Natural Park
- Pisba National Natural Park
Regional geology
| Age | Paleomap | VMM | Guaduas-Vélez | W Emerald Belt | Villeta anticlinal | Chiquinquirá- Arcabuco |
Tunja- Duitama |
Altiplano Cundiboyacense | El Cocuy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maastrichtian |  |
Umir | Córdoba | Seca | eroded | Guaduas | Colón-Mito Juan | ||||||
| Umir | Guadalupe | ||||||||||||
| Campanian | Córdoba | ||||||||||||
| Oliní | |||||||||||||
| Santonian | La Luna | Cimarrona - La Tabla | La Luna | ||||||||||
| Coniacian | Oliní |
Villeta
|
Conejo | Chipaque | |||||||||
|
Güagüaquí
|
Loma Gorda | undefined | La Frontera | ||||||||||
| Turonian |  |
Hondita | La Frontera | Otanche | |||||||||
| Cenomanian | Simití | hiatus | La Corona | Simijaca | Capacho | ||||||||
| Pacho Fm. | Hiló - Pacho | Churuvita | Une | Aguardiente | |||||||||
| Albian |  |
Hiló | Chiquinquirá | Tibasosa | Une | ||||||||
| Tablazo | Tablazo | Capotes - La Palma - Simití | Simití | Tibú-Mercedes | |||||||||
| Aptian | Capotes | Socotá - El Peñón | Paja | Fómeque | |||||||||
| Paja | Paja | El Peñón | Trincheras | Río Negro | |||||||||
| La Naveta | |||||||||||||
| Barremian | 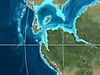 |
||||||||||||
| Hauterivian | Muzo |
Cáqueza
|
Las Juntas | ||||||||||
| Rosablanca | Ritoque | ||||||||||||
| Valanginian | Ritoque | Furatena | Útica - Murca | Rosablanca | hiatus | Macanal | |||||||
| Rosablanca | |||||||||||||
| Berriasian | 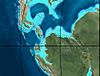 |
Cumbre | Cumbre | Los Medios | Guavio | ||||||||
| Tambor | Arcabuco | Cumbre | |||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Cordillera Oriental (Colombia) para niños
In Spanish: Cordillera Oriental (Colombia) para niños
- Geography of Colombia
- Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Bogotá savanna, Tenza Valley
- Cordillera Central, Occidental, Andean Region, Venezuelan Andes, continuation of this mountain system

