Central Valley facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Central Valley |
|
|---|---|
| Great Central Valley, Great Valley, The Valley, Golden Empire | |
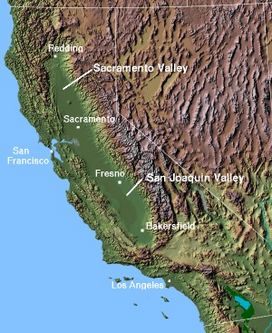
Topography, major regions, and cities of the Central Valley
|
|
| Length | 450 mi (720 km) |
| Width | 40 to 60 mi (64 to 97 km) |
| Area | 18,000 sq mi (47,000 km2) |
| Depth | 2,000 to 6,000 ft (610 to 1,830 m) |
| Geology | |
| Type | Alluvial |
| Age | 2–3 million years |
| Geography | |
| Location | California, United States |
| Population centers | Redding, Chico, Yuba City, Sacramento, Stockton, Porterville, Tulare, Modesto, Manteca, Turlock, Merced, Fresno, Visalia, Bakersfield, Clovis |
| Borders on | Sierra Nevada (east), Cascade Range, Klamath Mountains (north), Coast Range, San Francisco Bay (west), Tehachapi Mountains (south) |
| Traversed by | Interstate 5, Interstate 80, State Route 99 |
| Rivers | Sacramento River, San Joaquin River, Kings River |
The Central Valley (also called the Great Central Valley) is a very large valley in the middle of California, in the United States. About 42,000 square miles (108,779 square kilometers) in size, it is about the size of the state of Tennessee. It consists of two connected, differently named valleys, the Sacramento Valley and the San Joaquin Valley.
The Sierra Nevada Mountains border the valley on the east side, while the Coast Range borders it on the west side. The Sacramento River flows through the north part of the Central Valley. This part of the valley is also called the Sacramento Valley. The San Joaquin River flows through the larger south part of the Central Valley. also called the San Joaquin Valley. Both rivers merge eventually and empty into the Pacific Ocean via San Francisco Bay. The capital of California, Sacramento, is located in the north part of the Central Valley. In total, the Central Valley is around 450 miles (720 km) long.
The Central Valley has 18 California counties. 15 of these counties are among the 25 most productive farmland in California. Overall, the Central Valley economy depends on farming. However, this has led to serious environmental damages, such as pesticides and selenium and other bad materials being washed into the rivers and polluting the San Francisco Bay.
Contents
Geography
The valley floor is a flat, smooth land area covering about 42,000 square miles (108,779 square kilometers) in size, 450 miles (720 km) long, and 40 miles (64 km) wide. It covers 18 California counties. These counties are:
- Shasta
- Tehama
- Glenn
- Butte
- Colusa
- Sacramento
- El Dorado
- Sutter
- Yuba
- Yolo
- Placer
- San Joaquin
- Stanislaus
- Merced
- Madera
- Fresno
- Kings
- Tulare
- Kern
-from north to south.
Mountain ranges

The Sierra Nevada mountains are on the east side of the valley. These mountains are very tall and steep. Lots of rivers and streams flow off the Sierra Nevada. The highest mountain in the Sierra Nevada is Mount Whitney (14,495') which is also the tallest mountain in California and the rest of the United States (except for Alaska and Hawaii). On the west side, there is the California Coast Ranges, an extension of the Pacific Coast Ranges. Its highest point is approximately 8,848'.
Rivers
The Sacramento River begins in the north part of the Central Valley, near Mount Shasta. It actually begins in the Cascade Range, which are mountains north of the Central Valley, though most of its length is in the Central Valley. The Sacramento River flows south about 447 miles (719 km) to San Francisco Bay. Some of its tributaries include the Pit River, Feather River, and American River. All these rivers come off the Sierra Nevada.
The San Joaquin River begins at the south Sierra Nevada, and flows west and north into the Central Valley and to San Francisco Bay. Altogether, its length is sone 330 miles (530 km). The San Joaquin is more polluted than the Sacramento, and about 63 miles (101 km) of it is actually dry.
Together, the Sacramento-San Joaquin river system is the water supply of 22-23 million people in California.
Climate
The climate of the Sacramento Valley (north Central Valley) and San Joaquin Valley are very different. The Sacramento Valley has a Mediterranean climate. This means that it has warm, dry summers and cool, wet winters. The San Joaquin Valley is much hotter and drier. Most of it is Mediterranean steppe, which is similar to Mediterranean except that it is warmer and drier. Some of it, however, can be close to desert climate. This section of the Central Valley is said to have the worst air quality in California.
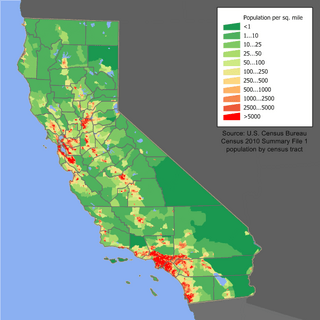
Population
Subregions and their counties commonly associated with the valley include:
- North Sacramento Valley (all or parts of Shasta, Tehama, Glenn, Butte and Colusa counties)
- Sacramento Metropolitan area (all or parts of Sacramento, El Dorado, Solano, Sutter, Yuba, Yolo and Placer counties)
- North San Joaquin (all or parts of San Joaquin, Stanislaus and Merced counties)
- South San Joaquin (all or parts of Madera, Fresno, Kings, Tulare and Kern counties)
The four main population centers in the Central Valley area are roughly equidistant from the next. From south to north, they are Bakersfield, Fresno, Sacramento and Redding. These four cities act as hubs for regional commerce and transportation.
Metropolitan areas
As of 2010, some 7.2 million people lived in the Central Valley; it was the fastest-growing region in California. It includes 12 Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSA) and 1 Micropolitan Statistical Area (μSA). Below, they are listed by MSA and μSA population. The largest city is Fresno followed by the state capital Sacramento. The following metropolitan and micropolitan statistical areas are listed from largest to smallest:
| SMSA | Population |
|---|---|
| Sacramento Metropolitan Area | 2,527,123 |
| Fresno Metropolitan Area | 930,450 |
| Bakersfield Metropolitan Area | 839,361 |
| Stockton Metropolitan Area | 696,214 |
| Modesto Metropolitan Area | 518,522 |
| Visalia–Porterville Metropolitan Area | 449,253 |
| Merced Metropolitan Area | 259,898 |
| Chico Metropolitan Area | 220,266 |
| Redding Metropolitan Area | 177,774 |
| Yuba City Metropolitan Area | 167,497 |
| Hanford–Corcoran Metropolitan Area | 153,765 |
| Madera Metropolitan Area | 152,925 |
| Red Bluff Micropolitan Area | 63,601 |
Ethnography
After English and Spanish, Punjabi is the third most commonly spoken language in the Central Valley. The valley has the largest Sikh population in the nation.
Economy and agriculture
Farming (agriculture) has always been the main economy of the Central Valley. Except for the city of Sacramento, where the focus is on the government, the rest is mostly agricultural. Immigrants provide a large amount of the work done in farms in the Central Valley. Overall, 12.3% of jobs in the Central Valley are directly agriculture related. Not including Sacramento County, the percentage is 16%.
Transportation
The main road transport routes through the Central Valley are Interstate 5 and California State Route 99. These two highways run from north to south. Interstate 5 is the larger of the two, and carries more traffic. Highway 99 is older than Interstate 5. The Highway 99 separates from Route 5 at the south end of the Central Valley, and joins again at the north end of the valley.
The Burlington Northern Santa Fe Railway (BNSF) and the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) go through the Central Valley as well. Some of their branch lines include:
- BNSF:
- BNSF Bakersfield Subdivision
- BNSF Stockton Subdivision
- UP:
- Union Pacific Railroad Martinez Subdivision
- Fresno Subdivision
Amtrak is one of the main rail service providers in the Central Valley, and is also popular in much of the rest of California.
Water supply
The 715-mile (1,150 km) California Aqueduct, the longest aqueduct in California, runs through the Central Valley. Water from the northern Central Valley and the Sierra Nevada goes into this aqueduct. The Central Valley Project is another major water supply project in the Central Valley. This project includes:
- Shasta Dam and Shasta Lake (reservoir)
- Delta Cross Channel
- Delta-Mendota Canal
- Friant Dam
- Madera Canal
- Friant-Kern Canal
- Contra Costa Canal
- Folsom Dam