Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Hundred Years' War | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
|
Armagnac party |
Burgundian party |
England |
||||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||||
The Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War was a conflict between two cadet branches of the French royal family – the House of Orléans (Armagnac faction) and the House of Burgundy (Burgundian faction) from 1407 to 1435. It began during a lull in the Hundred Years' War against the English and overlapped with the Western Schism of the papacy.
Contents
Causes
The leaders of both parties were closely related to the French king through the male line. For this reason, they were called "princes of the blood", and exerted much influence on the affairs of the kingdom of France. Their rivalries and disputes for control of the government would serve as much of the basis for the conflict. The Orléans branch of the family, also referred to as House of Valois-Orléans, stemmed from Louis I, Duke of Orléans, younger son of King Charles V of France (r. 1364–1380). The House of Valois-Burgundy originated from Charles V's youngest brother, Philip the Bold, the Duke of Burgundy. Both their respective namesake duchies of Orléans and Burgundy were held in the status of appanage, as none of its holders were first in the line of succession to the French throne.
The war's causes were rooted in the reign of Charles VI of France (Charles V's eldest son and successor) and a confrontation between two different economic, social and religious systems. On the one hand was France, very strong in agriculture, with a strong feudal and religious system, and on the other was England, a country whose rainy climate favoured pasture and sheep farming and where artisans, the middle classes and cities were important. The Burgundians were in favour of the English model (the more so since the County of Flanders, whose cloth merchants were the main market for English wool, belonged to the Duke of Burgundy), while the Armagnacs defended the French model. In the same way, the Western Schism induced the election of an Armagnac-backed antipope based at Avignon, Pope Clement VII, opposed by the English-backed pope of Rome, Pope Urban VI.
With Charles VI mentally ill, from 1393, his wife Isabeau of Bavaria presided over a regency counsel, on which sat the grandees of the kingdom. The uncle of Charles VI, Philip the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, who acted as regent during the king's minority (from 1380 to 1388), was a great influence on the queen (he had organized the royal marriage during his regency). This influence progressively shifted to Louis I, Duke of Orléans, the king's brother, and it was suspected, the queen's lover. On the death of Philip the Bold, his son John the Fearless (who was less linked to Isabeau) again lost influence at court. The other uncle of Charles VI, John, Duke of Berry, served as a mediator between the Orléans party (what would become the Armagnacs) and the Burgundy party, whose rivalry would increase bit by bit and in the end, result in a true civil war.
To oppose the territorial expansion of the Dukedom of Burgundy, the Duke of Orléans acquired Luxembourg in 1402. While Louis of Orléans, getting 90% of his income from the royal treasury, bought lands and strongholds in the eastern marches of the kingdom that the Burgundians considered their private hunting ground, John the Fearless (lacking the fiery prestige of his father) saw royal largess towards him drying up (Philip received 200,000 livres per year, but John had to satisfy himself with 37,000).
The Duke of Orléans, son-in-law of Gian Galeazzo Visconti and holding the title for more or less hypothetical fiefdoms in the peninsula, wanted to let Charles VI intervene militarily in his favor. What is more, it seems he wanted to let the Anglo-French truce break down, even so far as provoking Henry IV of England to a duel, which John the Fearless could not allow, since Flemish industry depended totally on imported English wool and would have been ruined by an embargo on English goods.
The quarrel at first respected all forms of courtesy: John the Fearless adopted the nettle as his emblem, whilst Louis of Orléans chose the gnarled stick and the duke of Burgundy the plane or rabot (distributing "rabotures", or badges, to his supporters).
Outbreak of the war
The king's brother, Louis of Orléans, "who whinnied like a stallion after almost all the beautiful women", was accused of having wanted to ... or worse, "esforcier", Margaret of Bavaria, the duchess of Burgundy. ..... Louis was certainly close to the queen and benefited from the benevolence of his brother the king, whenever he was out of crisis; he thus succeeded in ousting the Burgundians on the counsel.
Ousted from power and toyed with by Louis, this was too much for John the Fearless. Taking advantage of rising anger among the taxpayers, always under pressure in peacetime, and noting that their taxes serve to finance court festivities, John began to campaign for support, financing demagoguery (promising, for example, tax cuts and state reforms, that is, a controlled monarchy). He thus won over the merchants, the small people and the university.
John threatened Paris in 1405 with a demonstration of his power, but even this did not prove sufficient to restore his influence. He thus decided to get rid of his exasperating rival, having him murdered on rue Vieille du Temple in Paris on 23 November 1407, whilst he was leaving the queen's residence at Hôtel Barbette, a few days after she had given birth to her twelfth child. Thomas de Courteheuse then sent word to Louis that the king, Charles VI of France, urgently needed him at hôtel Saint-Paul. Leaving the Hôtel Barbette, Louis was stabbed by fifteen masked criminals led by Raoulet d'Anquetonville, a servant of the Duke of Burgundy. Louis's escort of valets and guards were powerless to protect him. John had the support of Paris's population and university, whom he had won over by promising the establishment of an ordinance like that of 1357. Thus able to take power, he could also publicly acknowledge the assassination – far from hiding it, he publicized it in an elegy in praise of tyrannicide by the Sorbonne university theologian Jean Petit. Finally, the assassination unleashed a civil war that would last almost 30 years.
Civil war
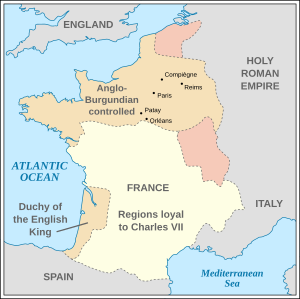
Intending to avenge his father, Charles of Orléans (Louis's son) backed the enemies of the Dukes of Burgundy wherever he could but even so, in 1409, a peace concluded at Chartres seemed to bring an end to hostilities. However, on 15 April 1410, at the marriage of Charles and Bonne d'Armagnac at Gien, the Duke of Orléans, his new father-in-law and the grandees of France formed a league against John and his supporters. The marriage gave the Orléans faction a new head to replace Louis (Charles's new father-in-law, Bernard VII, Count of Armagnac, who became the natural protector of the Duke) and a new name (the Armagnac party). Other members of the league included the Dukes of Berry, Bourbon and Brittany, as well as the Counts of Clermont and Alençon.
Bernard VII recruited warbands in the Midi that fought with unheard-of ferocity: the Écorcheurs. At their head, he ravaged the vicinity of Paris and advanced into the Saint-Marcel suburb. A new treaty, signed at Bicêtre on 2 November 1410, suspended hostilities, but both sides had taken up arms again as early as spring 1411. In October 1411, with an army 60,000 strong, the Duke of Burgundy entered Paris and attacked the Bretons allied to the Armagnacs, who had retrenched at La Chapelle. He had to withdraw in the end but, in the night of 8 to 9 November, he left via the porte Saint-Jacques, marched across Saint-Cloud and decisively defeated the Écorcheurs. Then John the Fearless pursued the princes of Orléans and their allies to Bourges, which Orléans was besieging, but the royal army appeared in front of the city on 11 June 1412. Another peace was signed at Bourges on 15 July and confirmed at Auxerre on 22 August.
The English took advantage of the situation by punctually supporting the two parties or buying their neutrality. The Armagnacs concluded a treaty with Henry IV of England in 1412, to prevent an Anglo-Burgundian alliance, so they yielded Guyenne to him and recognized his suzerainty over Poitou, Angoulême and Périgord. All the same, John the Fearless managed the English well, since an English wool embargo could ruin the cloth merchants of Flanders.
In 1413, John the Fearless supported the Cabochien Revolt that brought about a slaughter in Paris. The Parisian population, terrified, called on the Armagnacs for aid. Their troops retook the city in 1414. When Henry V of England renewed hostilities in 1415, the duke of Burgundy remained neutral, leaving Henry able to defeat the French army (essentially provided by the Armagnacs), at the battle of Agincourt in October 1415.
On May 29, 1418, thanks to the treason of a certain Perrinet Leclerc and the support of the craftsmen and university, Paris was delivered to Jean de Villiers de L'Isle-Adam, captain of a troop favouring the duke of Burgundy. On the following 12 June, Bernard VII and other Armagnacs were slaughtered by a mob. John thus became master of Paris once again, and so he entered into negotiations with the English in which he seemed willing to welcome the king of England's claim on the French throne. It thus became imperative for the Dauphin to negotiate a rapprochement with the Burgundians, again to avoid an Anglo-Burgundian alliance. John the Fearless, on his part, had become master of a large part of the kingdom after his capture of Paris, but his finances were at rock bottom. John was thus in favor of meeting the Dauphin, Charles VII of France, in order to sign up to an advantageous peace, so several meetings were thus organized.
Assassination of John the Fearless
However, having set the precedent for assassinations, on 10 September 1419, John himself was murdered on the bridge at Montereau-Fault-Yonne, whilst in the town for an interview with Charles. Both sides agreed to meet on the bridge. Charles's men accused the Burgundians of not keeping their promise to break off their alliances with the English. They, on high alert because they had heard that Jean intended to kidnap or attack the dauphin, reacted swiftly when the Lord of Navailles raised his sword. In the ensuing scuffle, the duke was killed. This act prevented all appeasement, and thereby enabled a continuation of English military successes with the collusion of Burgundy.
Aftermath
Philip the Good, the new Duke of Burgundy, then entered into an alliance with the English, which resulted in the Treaty of Troyes. This treaty disinherited the Dauphin Charles and handed the succession to Henry V through a marriage to Charles VI's daughter, Catherine of Valois. The treaty named Henry "regent and heir of France" (although the English only had effective control over northern France and Guyenne) until Charles's death. The treaty was denounced by the Armagnacs, who reasoned "that the king belongs to the crown and not vice versa". Despite his expectations, Henry V predeceased his sickly father-in-law by a few months, in 1422. In 1429, the intervention of Joan of Arc culminated in a successful coronation campaign that allowed Charles VII to be crowned at Reims Cathedral, the traditional coronation site of French kings, on 17 July 1429. The ten-year-old Henry VI of England was crowned as King of France on 16 December 1431 at Notre-Dame de Paris.
End of the war
Engaged in a patient reconquest of French territory, Charles VII wished to isolate the English from the Burgundians. In 1435, he concluded the treaty of Arras with Philip the Good, ending the civil war. Philip the Good was personally exempted from rendering homage to Charles VII (for having been complicit in his father's murder). This agreement officially put an end to the war and allowed Charles VII to recapture practically all the English continental possessions, leaving them in 1453 with Calais alone. Philip the Good later secured the release of Charles, Duke of Orléans, ending the feud between the two houses.
See also
- Journal d'un bourgeois de Paris