Ainu people facts for kids
| アィヌ | |
|---|---|
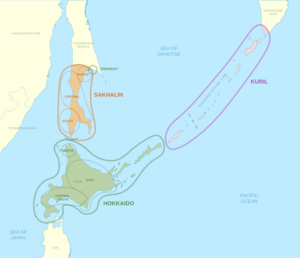
Historical homeland and distribution of Ainu people
|
|
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 11,450 surveyed in 2023 | |
| 300 (2021 census) | |
| Languages | |
| Ainu languages, Japanese, Russian | |
| Religion | |
| Ainu folk religion, Animism, Japanese Buddhism, Shinto, Russian Orthodoxy | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Jomon people, Satsumon, Okhotsk, Matagi, Emishi, Nivkh | |
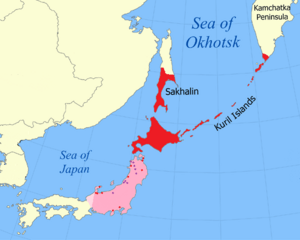
The Ainu are an indigenous ethnic group who reside in northern Japan and southeastern Russia, including Hokkaido and the Tōhoku region of Honshu, as well as the land surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, such as Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula, and the Khabarovsk Krai. They have occupied these areas, known to them as "Ainu Mosir" (Ainu: アイヌモシㇼ, lit. 'the land of the Ainu'), since before the arrival of the modern Yamato and Russians. These regions are often referred to as Ezochi (蝦夷地) and its inhabitants as Emishi (蝦夷) in historical Japanese texts. Along with the Yamato and Ryukyu ethnic groups, the Ainu people are one of the primary historic ethnic groups of Japan.
Official surveys of the known Ainu population in Hokkaido received 11,450 responses in 2023, and the Ainu population in Russia was estimated at 300 in 2021. Unofficial estimates in 2002 placed the total population in Japan at 200,000 or higher, as the near-total assimilation of the Ainu into Japanese society has resulted in many individuals of Ainu descent having no knowledge of their ancestry.
The Ainu are one of the few ethnic minorities native to the Japanese islands. They were subject to forced assimilation and colonization by the Japanese since at least the 18th century. Japanese assimilation policies in the 19th century around the Meiji Restoration included forcing Ainu peoples off their land. This, in turn, forced them to give up traditional ways of life such as subsistence hunting and fishing. Ainu people were not allowed to practice their religion and were placed into Japanese-language schools, where speaking the Ainu language was forbidden. In 1966, there were about 300 native Ainu speakers; in 2008, there were about 100. In recent years, there have been increasing efforts to revitalize the Ainu language.
Contents
Names
This people's most widely known ethnonym, Ainu (Ainu: アィヌ; Japanese: アイヌ; Russian: Айны), means 'human' in the Ainu language, particularly as opposed to kamui, 'divine beings'. Ainu also identify themselves as Utari ('comrades' or 'people'). Official documents use both names.
The name first appeared as Aino in a 1591 Latin manuscript titled De yezorum insula. This document gives the native name of Hokkaido as Aino moxori, or Ainu mosir, 'land of the Ainu'. The terms Aino and Ainu did not come into common use as ethnonyms until the early 19th century. The ethnonym first appeared in an 1819 German encyclopedia article. Neither European nor Japanese sources conceived of the Ainu as a distinct ethnic group until the late 1700s.
The Ainu were also called the Kuye by their neighbors. The Qing dynasty called Sakhalin Kuyedao ("island of the Ainu"). The island was also called Kuye Fiyaka. The word Kuye used by the Qing is "most probably related to kuyi, the name given to the Sakhalin Ainu by their Nivkh and Nanai neighbors." When the Ainu migrated onto the mainland, the Chinese described a "strong Kui (or Kuwei, Kuwu, Kuye, Kugi, i.e. Ainu) presence in the area otherwise dominated by the Gilemi or Jilimi (Nivkh and other Amur peoples)." Related names were in widespread use in the region, for example the Kuril Ainu called themselves koushi.
The Old Japanese exonym 蝦夷 (Emi1si) was coined according to the Kojiki-den from 蝦 ("shrimp") + 夷 ("barbarian") as a reference to their hairiness and savagery. The term is considered an insult by contemporary Ainu.
History
The Ainu are considered the native people of Hokkaido, southern Sakhalin, and the Kurils. Ainu toponyms support the historical view that the Ainu people lived in several places throughout northern Honshu. There is also a possibility that Ainu speakers lived throughout the Amur region as suggested by various Ainu loanwords found in the Uilta and Ulch languages. Ainu shares a number of cognates with Old Korean, that appear unlikely to be the result of a Japonic intermediary.
The ancestors of the Ainu, who were referred to as Emishi, came under Japanese subjugation starting in the 9th century and were pushed to the northern islands.
Ainu Culture period (Nibutani period)
Following the Zoku-Jōmon period, which began in the 5th century BC, and the subsequent Satsumon period, from around the 13th century the Ainu established their own culture by absorbing the surrounding culture while engaging in transit trade between Honshu and north-east Asia. This is called the Ainu Culture period or Nibutani period.
Active contact between the Wajin (ethnonym for Japanese, also known as Yamato people) and the Ainu of Ezogashima (now known as Hokkaidō) began in this period. The Ainu formed a society of hunter-gatherers, surviving mainly by hunting and fishing. They followed a religion that was based on natural phenomena.
After the Mongols conquered the Jin dynasty (1234), Karafuto (Sakhalin)-Ainu suffered raids by the Nivkh and Udege peoples. In response, the Mongols established an administration post at Nurgan (present-day Tyr, Russia) at the junction of the Amur and Amgun rivers in 1263, and forced the submission of the two peoples. In 1264, the Karafuto-Ainu invaded the land of the Nivkh people. They also started an expedition into the Amur region, which was then controlled by the Yuan dynasty, resulting in reprisals by the Mongols who invaded Sakhalin.
From the Nivkh perspective, their surrender to the Mongols essentially established a military alliance against the Ainu who had invaded their lands. According to the History of Yuan, a group of people known as the Guwei (骨嵬; Gǔwéi, the phonetic approximation of the Nivkh name for Ainu) from Sakhalin invaded and fought with the Jilimi (Nivkh people) every year. On November 30, 1264, the Mongols attacked the Ainu. The Karafuto-Ainu resisted the Mongol invasions but by 1308 had been subdued. They paid tribute to the Mongol Yuan dynasty at posts in Wuliehe, Nanghar, and Boluohe.
The Chinese Ming dynasty (1368–1644) placed Sakhalin under its "system for subjugated peoples" (ximin tizhi). From 1409 to 1411 the Ming established an outpost called the Nurgan Regional Military Commission near the ruins of Tyr on the Siberian mainland, which continued operating until the mid-1430s. There is some evidence that the Ming eunuch Admiral Yishiha reached Sakhalin in 1413 during one of his expeditions to the lower Amur, and granted Ming titles to a local chieftain.
The Ming recruited headmen from Sakhalin for administrative posts such as commander (指揮使; zhǐhuīshǐ), assistant commander (指揮僉事; zhǐhuī qiānshì), and "official charged with subjugation" (衛鎮撫; wèizhènfǔ). In 1431, one such assistant commander, Alige, brought marten pelts as tribute to the Wuliehe post. In 1437, four other assistant commanders (Zhaluha, Sanchiha, Tuolingha, and Alingge) also presented tribute. According to the Ming Veritable Records, these posts, like the position of headman, were hereditary and passed down the patrilineal line. During these tributary missions, the headmen would bring their sons, who later inherited their titles. In return for tribute, the Ming awarded them with silk uniforms.
Nivkh women in Sakhalin married Han Chinese Ming officials when the Ming took tribute from Sakhalin and the Amur River region. Due to Ming rule in Manchuria, Chinese cultural and religious influence such as Chinese New Year, the "Chinese god", and motifs such as dragons, spirals, and scrolls spread among the Ainu, Nivkh, and Amur natives such as the Udeghes, Ulchis, and Nanais. These groups also adopted material goods and practices such as agriculture, husbandry, heating, iron cooking pots, silk, and cotton.

The Manchu Qing dynasty, which came to power in China in 1644, called Sakhalin "Kuyedao" (Chinese: 庫頁島; pinyin: Kùyè dǎo; lit. 'island of the Ainu') or "Kuye Fiyaka" (ᡴᡠᠶᡝ
ᡶᡳᠶᠠᡴᠠ). The Manchus called it "Sagaliyan ula angga hada" (Island at the Mouth of the Black River). The Qing first asserted influence over Sakhalin after the 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk, which defined the Stanovoy Mountains as the border between the Qing and the Russian Empires. In the following year the Qing sent forces to the Amur estuary and demanded that the residents, including the Sakhalin Ainu, pay tribute. This was followed by several further visits to the island as part of the Qing effort to map the area. To enforce its influence, the Qing sent soldiers and mandarins across Sakhalin, reaching most parts of the island except the southern tip. The Qing imposed a fur-tribute system on the region's inhabitants.
The Qing dynasty ruled these regions by imposing upon them a fur tribute system, just as had the Yuan and Ming dynasties. Residents who were required to pay tributes had to register according to their hala (ᡥᠠᠯᠠ, the clan of the father's side) and gashan (ᡤᠠᡧᠠᠨ, village), and a designated chief of each unit was put in charge of district security as well as the annual collection and delivery of fur. By 1750, fifty-six hala and 2,398 households were registered as fur tribute payers, – those who paid with fur were rewarded mainly with Nishiki silk brocade, and every year the dynasty supplied the chief of each clan and village with official silk clothes (mangpao, duanpao), which were the gowns of the mandarin. Those who offered especially large fur tributes were granted the right to create a familial relationship with officials of the Manchu Eight Banners (at the time equivalent to Chinese aristocrats) by marrying an official's adopted daughter. Further, the tribute payers were allowed to engage in trade with officials and merchants at the tribute location. By these policies, the Qing dynasty brought political stability to the region and established the basis for commerce and economic development.
The Qing dynasty established an office in Ningguta, situated midway along the Mudan River, to handle fur from the lower Amur and Sakhalin. Tribute was supposed to be brought to regional offices, but the lower Amur and Sakhalin were considered too remote, so the Qing sent officials directly to these regions every year to collect tribute and to present awards. By the 1730s, the Qing had appointed senior figures among the indigenous communities as "clan chief" (hala-i-da) or "village chief" (gasan-da or mokun-da). In 1732, 6 hala, 18 gasban, and 148 households were registered as tribute bearers in Sakhalin. Manchu officials gave tribute missions rice, salt, other necessities, and gifts during the duration of their mission. Tribute missions occurred during the summer months. During the reign of the Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735–95), a trade post existed at Delen, upstream of Kiji (Kizi) Lake, according to Rinzo Mamiya. There were 500–600 people at the market during Mamiya's stay there.
Local native Sakhalin chiefs had their daughters taken as wives by Manchu officials as sanctioned by the Qing dynasty when the Qing exercised jurisdiction in Sakhalin and took tribute from them.
Japanese colonization
In 1635, Matsumae Kinhiro, the second daimyō of Matsumae Domain in Hokkaidō, sent Satō Kamoemon and Kakizaki Kuroudo on an expedition to Sakhalin. One of the Matsumae explorers, Kodō Shōzaemon, stayed in the island in the winter of 1636 and sailed along the east coast to Taraika (now Poronaysk) in the spring of 1637. The Tokugawa bakufu (feudal government) granted the Matsumae clan exclusive rights to trade with the Ainu in the northern part of the island. Later, the Matsumae began to lease out trading rights to Japanese merchants, and contact between Japanese and Ainu became more extensive. Throughout this period, Ainu groups competed with each other to import goods from the Japanese, and epidemic diseases such as smallpox reduced the population. In an early colonization attempt, a Japanese settlement was established at Ōtomari on Sakhalin's southern end in 1679.
In the 1780s, the influence of the Japanese Tokugawa Shogunate on the Ainu of southern Sakhalin increased significantly. By the beginning of the 19th century, the Japanese economic zone extended midway up the east coast, to Taraika. With the exception of the Nayoro Ainu located on the west coast in close proximity to China, most Ainu stopped paying tribute to the Qing dynasty. The Matsumae clan was nominally in charge of Sakhalin, but they neither protected nor governed the Ainu there. Instead they extorted the Ainu for Chinese silk, which they sold in Honshu as Matsumae's special product. To obtain Chinese silk, the Ainu fell into debt, owing much fur to the Santan (Ulch people), who lived near the Qing office. The Ainu also sold the silk uniforms (mangpao, bufu, and chaofu) given to them by the Qing, which made up the majority of what the Japanese knew as nishiki and jittoku. As dynastic uniforms, the silk was of considerably higher quality than that traded at Nagasaki, and enhanced Matsumae prestige as exotic items. Eventually the Tokugawa government, realizing that they could not depend on the Matsumae, took control of Sakhalin in 1807.
Mogami's interest in the Sakhalin trade intensified when he learned that Yaenkoroaino, the above-mentioned elder from Nayoro, possessed a memorandum written in Manchurian, which stated that the Ainu elder was an official of the Qing state. Later surveys on Sakhalin by shogunal officials such as Takahashi Jidayú and Nakamura Koichiró only confirmed earlier observations: Sakhalin and Sóya Ainu traded foreign goods at trading posts, and because of the pressure to meet quotas, they fell into debt. These goods, the officials confirmed, originated at Qing posts, where continental traders acquired them during tributary ceremonies. The information contained in these types of reports turned out to be a serious blow to the future of Matsumae's trade monopoly in Ezo.
From 1799 to 1806, the Tokugawa shogunate took direct control of southern Hokkaido. Japan proclaimed sovereignty over Sakhalin in 1807, and in 1809 Mamiya Rinzō claimed that it was an island. During this period, Ainu women were separated from their husbands and forcibly married to Japanese men. Meanwhile, Ainu men were deported to merchant subcontractors for five- and ten-year terms of service. Policies of family separation and assimilation, combined with the impact of smallpox, caused the Ainu population to drop significantly in the early 19th century. In the 18th century, there were 80,000 Ainu, but by 1868, there were only about 15,000 Ainu in Hokkaido, 2,000 in Sakhalin, and around 100 in the Kuril Islands.
Despite their growing influence in the area in the early 19th century as a result of these policies, the Tokugawa shogunate was unable to gain a monopoly on Ainu trade with those on the Asian mainland, even by the year 1853. Santan traders, a group composed mostly of the Ulchi, Nanai, and Oroch peoples of the Amur River, commonly interacted with the Ainu people independent of the Japanese government, especially in the northern part of Hokkaido. In addition to their trading ventures, Santan traders sometimes kidnapped or purchased Ainu women from Rishiri to become their wives. This further escalated Japan's presence in the area, as the Tokugawa shogunate believed a monopoly on the Santan trade would better protect the Ainu people.
Japanese annexation of Hokkaido
In 1869, the imperial government established the Hokkaidō Development Commission as part of the Meiji Restoration. Researcher Katarina Sjöberg quotes Yūko Baba's 1980 account of the Japanese government's reasoning:
... The development of Japan's large northern island had several objectives: First, it was seen as a means to defend Japan from a rapidly developing and expansionist Russia. Second ... it offered a solution to the unemployment for the former samurai class ... Finally, development promised to yield the needed natural resources for a growing capitalist economy.
As a result of the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875), the Kuril Islands—along with their Ainu inhabitants—came under Japanese administration. In 1899, the Japanese government passed an act labeling the Ainu as "former aborigines", with the idea that they would assimilate. This resulted in the Japanese government taking the land where the Ainu people lived and placing it under Japanese control. Also at this time, the Ainu were granted automatic Japanese citizenship, effectively denying them the status of an indigenous group.
The Ainu went from being a relatively isolated group of people to having their land, language, religion, and customs assimilated into those of the Japanese. Their land was distributed to the Yamato Japanese settlers to create and maintain farms in the model of Western industrial agriculture. It was known as "colonization" (拓殖) at the time, but later by the euphemism, "opening up undeveloped land" (開拓). Additionally, factories like flour mills and beer breweries, along with mining practices, resulted in the creation of infrastructure such as roads and railway lines during a development period that lasted until 1904. During this time, the Ainu were ordered to cease religious practices such as animal sacrifice and the custom of tattooing. The same act applied to the native Ainu on Sakhalin after its annexation as Karafuto Prefecture.
Assimilation after annexation
The Ainu have historically suffered from economic and social discrimination, as both the Japanese government and mainstream population regarded them as dirty and primitive barbarians. The majority of Ainu were forced to be petty laborers during the Meiji Restoration, which saw the introduction of Hokkaido into the Japanese Empire and the privatization of traditional Ainu lands. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the Japanese government denied the rights of the Ainu to their traditional cultural practices, such as hunting, gathering, and speaking their native language.
The legal denial of Ainu cultural practices mostly stemmed from the 1899 Hokkaido Former Aborigines Protection Act. This law and its associated policies were designed to fully integrate the Ainu into Japanese society while erasing Ainu culture and identity. The Ainu's position as manual laborers and their forced integration into larger Japanese society have led to discriminatory practices by the Japanese government that can still be felt today.
Intermarriage between Japanese and Ainu was actively promoted by the Ainu to lessen the chances of discrimination against their offspring. As a result, many Ainu today are indistinguishable from their Japanese neighbors, but some Ainu-Japanese are interested in traditional Ainu culture. For example, Oki, born as the child of an Ainu father and a Japanese mother, became a musician who plays the traditional Ainu instrument, the tonkori. There are also many small towns in the southeastern or Hidaka region of Hokkaido where ethnic Ainu live, such as in Nibutani (Niputay).
From the early 1870s, Christian missionary work was conducted among the Ainu. The Anglican Communion missionaries included the Rt. Rev. Philip Fyson, Bishop of Hokkaido, and the Rev. John Batchelor. Batchelor wrote extensively in English about the beliefs and daily life of the Ainu in Yezo (or Ezo), and his publications are a source of photographs of the Japanese and Ainu close to the missions.
Standard of living
The discrimination and negative stereotypes assigned to the Ainu have manifested in lower levels of education, income, and participation in the economy as compared to their ethnically Japanese counterparts. The Ainu community in Hokkaido in 1993 received welfare payments at a 2.3 times higher rate than that of Hokkaido as a whole. They also had an 8.9% lower enrollment rate from junior high school to high school and a 15.7% lower enrollment into college from high school. Due to this noticeable and growing gap, the Japanese government has been lobbied by activists to research the Ainu's standard of living nationwide. The Japanese government will provide ¥7 million (US$63,000), beginning in 2015, to conduct surveys nationwide on this matter.
Ainu and ethnic homogeneity in Japan
The existence of the Ainu has challenged the notion of ethnic homogeneity in post-WWII Japan. After the demise of the multi-ethnic Empire of Japan in 1945, successive governments forged a single Japanese identity by advocating monoculturalism and denying the existence of more than one ethnic group in Japan.
The Ainu were first recognised as an indigenous people in 1997, which began the process of claiming indigenous rights under national and international frameworks. Following the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in 2007, Hokkaido politicians pressured the government to recognize Ainu rights. Prime Minister Fukuda Yasuo answered a parliamentary question on May 20, 2008, by stating,
It is a historical fact that the Ainu are the earlier arrivers of the northern Japanese archipelago, in particular Hokkaido. The Japanese government acknowledges the Ainu to be an ethnic minority as it has maintained a unique cultural identity and has a unique language and religion. However, as there is no established international definition of "indigenous people", the government is not in a position to conclude whether the Ainu should be referred as "indigenous people"...
On June 6, 2008, the National Diet of Japan passed a non-binding, bipartisan resolution calling upon the government to recognize the Ainu as indigenous people.
In 2019, eleven years after this resolution, the Diet finally passed an act recognizing the Ainu as an indigenous people of Japan. Despite this recognition of the Ainu as an ethnically distinct group, political figures in Japan continue to define ethnic homogeneity as key to the overall Japanese national identity. For example, then Deputy Prime Minister Tarō Asō notably claimed in 2020, "No other country but this one has lasted for as long as 2,000 years with one language, one ethnic group, and one dynasty."
Origins
The Ainu are regarded as having descended from the indigenous Japanese hunter-gatherers who lived in Japan during the Jōmon period (c. 14,000 to 300 BCE).
The exact origins of the early Ainu remain unclear, but it is generally agreed to be linked to the Satsumon culture of the Epi-Jōmon period, with later influences from the nearby Okhotsk culture. The Ainu culture may be better described as an "Ainu cultural complex", taking into account the regional variable subgroups of Ainu peoples. While the Ainu can be considered a continuation of the indigenous Jomon culture, they also display links to surrounding cultures, pointing to a larger cultural complex flourishing around the Sea of Okhotsk. Some authors have also described the development of the Ainu culture as the "resistance" of a Jomon society to the emerging Japanese state.
One of their Yukar Upopo, or legends, tells that "[T]he Ainu lived in this place a hundred thousand years before the Children of the Sun came."
The historical Ainu economy was based on farming as well as hunting, fishing, and gathering.
The general consensus among historians is to associate the Ainu with the Satsumon culture, which was located in an area stretching from northern Honshu to Hokkaido. Linguists such as Juha Janhunen and Alexander Vovin argue for a Satsumon origin of Ainu dialects, with deeper links to cultures centered in Central or Northern Honshu. This is in part supported by Ainu-derived loanwords observed in Eastern Old Japanese and the probable distant link between the Ainu and the Emishi.
It has also been noted that the Okhotsk culture played a role in the formation of the later Ainu culture. The origin of the Okhotsk culture itself is subject to research. While Okhotsk remains display affinity to the modern Nivkh people of northern Sakhalin, both also display affinities to the Jōmon peoples of Japan, pointing to a possible heterogeneous makeup of Okhotsk society. Satsumon pottery has been found among Okhotsk sites, pointing to a complex network of contacts in the wider area around the Sea of Okhotsk.
The emergence of the Ainu culture is henceforth primarily attributed to the Satsumon culture, which later received some contributions from the Okhotsk culture via cultural contacts in northern Hokkaido after the Satsumon culture expanded northwards and into Sakhalin. This view has been corroborated by later analyses.
Archaeologists have considered that bear worship, which is a religious practice widely observed among the northern Eurasian ethnic groups (including the Ainu, Finns, Nivkh, and Sami), was also shared by the Okhotsk people. On the other hand, no traces of such a religious practice have ever been discovered from archaeological sites of the Jomon and Epi-Jomon periods, which were anterior to the Ainu cultural period. This implies that the Okhotsk culture contributed to the formation of the Ainu culture.
Relationship with the historical Emishi
While the view that the ancient Emishi were identical to the Ainu has been largely disproven by current research, the exact relationship between them is still under dispute. It is agreed that at least some Emishi spoke Ainu languages and were ethnically related to the Ainu. The Emishi may, however, have also included non-Ainu groups, which can either be associated with groups distantly related to the Ainu (Ainu-like groups) but forming their own ethnicity, or early Japonic-speakers outside the influence of the Yamato court. The Emishi display clear material culture links to the Ainu of Hokkaido. Based on Ainu-like toponyms throughout Tohoku, it is argued that the Emishi, like the Ainu, descended from the Epi-Jōmon tribes and initially spoke Ainu-related languages.
The term "Emishi" in the Nara period (710–794) referred to people who lived in the Tohoku region and whose lifestyle and culture differed markedly from that of the Yamato people; it was originally a highly cultural and political concept with no racial distinction.
From the mid-Heian period onward, Emishi who did not fall under the governance of the Yamato Kingship were singled out as northern Emishi. They began to be referred to as "Ezo" (Emishi).
The first written reference to "Ezo", which is thought to be Ainu, can be found in Suwa Daimyōjin Ekotoba, which was written in 1356. Indeed, Ainu have lived in Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands, Hokkaido, and the northern Tohoku region since the 13th century.
Culture
Traditional Ainu culture is quite different from Japanese culture. According to Tanaka Sakurako from the University of British Columbia, the Ainu culture can be included into a wider "northern circumpacific region", referring to various indigenous cultures of Northeast Asia and "beyond the Bering Strait" in North America. The Ainu culture developed from the 13th century (late Kamakura period) to the present day. While most Ainu in Japan now live outwardly similar lives to the Wajin (ethnic Japanese) due to assimilation policies, many still maintain their Ainu identity and respect for traditional Ainu ways, known as "Ainu puri". The distinctive Ainu patterns (Ainu mon'yō) and oral literature (Yukar) have been designated as Hokkaido Heritage.
Language
In 2008, the news block World Watch gave an estimate of fewer than 100 remaining speakers of the Ainu language. In 1993, linguist Alexander Vovin placed the number at fewer than 15 speakers, characterizing the language as "almost extinct". Because so few present-day speakers are left, study of the Ainu language is limited and is based largely on historical research. Historically, the status of the Ainu language was rather high and was used by early Russian and Japanese administrative officials to communicate with each other and with the Ainu people.
Despite the small number of native speakers of Ainu, there is an active movement to revitalize the language, mainly in Hokkaido but also elsewhere, such as in Kanto. Ainu oral literature has been documented both in hopes of safeguarding it for future generations and for use as a teaching tool for language learners. As of 2011, there were an increasing number of second-language learners, especially in Hokkaido.
The resurgence of Ainu culture and language is in large part due to the pioneering efforts of the late Ainu folklorist, activist, and former Diet member Shigeru Kayano, himself a native speaker. He first opened an Ainu language school in 1987, funded by Ainu Kyokai.
Although some researchers have attempted to show that the Ainu and Japanese languages are related, modern scholars have rejected the idea that the relationship goes beyond contact, such as the mutual borrowing of words. No attempt to show a relationship with Ainu to any other language has gained wide acceptance, and linguists currently classify Ainu as a language isolate. Most Ainu people speak either Japanese or Russian.
The Ainu language has no indigenous system of writing and has historically been transliterated using Japanese kana or Russian Cyrillic. As of 2019[update], it was typically written either in katakana or in the Latin alphabet.
Many of the Ainu dialects, especially those from different extremities of Hokkaido, are not mutually intelligible. However, all Ainu speakers understand the classic Ainu language of the Yukar, a form of Ainu epic. Without a writing system, the Ainu were masters of narration, with the Yukar and other forms of narration such as Uepeker (Uwepeker) tales being committed to memory and related at gatherings that often lasted many hours or even days.
Concepts expressed with prepositions in English, such as 'to', 'from', 'by', 'in', and 'at', appear as postpositional forms in Ainu. Whereas prepositions come before the word they modify, postpositions come after it. A single sentence in Ainu can comprise many added or agglutinated sounds or affixes that represent nouns or ideas.
Social structure

Ainu society was traditionally organized into small villages called kotan, typically located in river basins or along seashores where food was readily available, particularly in rivers where salmon traveled upstream. In early modern times, Ainu were forced to relocate their kotan near Japanese fishing grounds to provide labor. As a result, traditional kotan disappeared, and large villages of several dozen families were formed around fishing grounds. The Ainu social structure included chiefs, but judicial functions were not entrusted to them. Instead, an indefinite number of community members sat in judgment upon criminals. Capital punishment did not exist, nor did the community resort to imprisonment. Beating was considered a sufficient and final penalty.
Appearance and dress

Never shaving after a certain age, the men have full beards and moustaches. Men and women alike cut their hair level with the shoulders at the sides of the head, trimmed semi-circularly behind. The women tattoo (anchi-piri) their mouths and sometimes their forearms. The mouth tattoos start at a young age with a small spot on the upper lip, gradually increasing in size. The soot deposited on a pot hung over a fire of birch bark is used for color. Traditional Ainu dress consists of a robe spun from the inner bark of the elm tree, called attusi or attush. The various styles consist generally of a simple short robe with straight sleeves, folded around the body, and tied with a band around the waist. The sleeves end at the wrist or forearm, and the length generally is to the calves. Women also wear an undergarment of Japanese cloth. In winter, the skins of animals are worn, with leggings of deerskin and, in Sakhalin, boots made from the skin of dogs or salmon. Ainu culture regards earrings, traditionally made from grapevines, as gender-neutral. Women also wear a beaded necklace called a tamasay. Modern craftswomen weave and embroider traditional garments that command very high prices.
Dwellings
Their traditional habitations are reed-thatched huts, the largest about 20 ft (6 m) square, without partitions and having a fireplace in the center. There is no chimney; there is only a hole at the angle of the roof. One window sits on the eastern side, along with two doors. The house of the village head is used as a public meeting-place when one is needed. Another kind of traditional Ainu house is called chise. The chise is typically oriented east to west or parallel to a river, with the entrance on the west side also serving as a storeroom. It has three windows, including the sacred rorun-puyar on the east side, through which gods enter and leave and ceremonial tools are taken in and out. The Ainu regard this window as sacred and are told never to look in through it. A chise has a fireplace near the entrance. A husband and wife would traditionally sit on the fireplace's left side (called shiso). Children and guests would sit facing them on the fireplace's right side (called harkiso). The chise has a platform for valuables called iyoykir behind the shiso. The Ainu place sintoko (hokai) and ikayop (quivers) there.
Cuisine
Traditional Ainu cuisine consists of the meat of bears, foxes, wolves, badgers, oxen, and horses, as well as fish, fowl, millet, vegetables, herbs, and roots. The Ainu traditionally never eat raw fish or meat, always boiling or roasting it. They also cultivated crops such as millet (piyapa), foxtail millet (munchiro), and barnyard millet (menkur), which were used to make a type of sake called "tonoto" for ceremonial purposes. Salmon was particularly important, referred to as kamuy chep (god's fish) or shipe (true food). In autumn, large quantities of salmon were caught and processed into dried fish for preservation. This served not only as a staple food but also as a major trade item with the Japanese. The Ainu also made extensive use of the bulbs of the Cardiocrinum cordatum (turep), from which they extracted and preserved starch. This tradition of starch usage made it easy for them to adopt potatoes when they were introduced. Ainu cuisine is not commonly eaten outside Ainu communities. Only a few restaurants in Japan – mainly in Tokyo and Hokkaido – serve traditional Ainu dishes.
Hunting
The Ainu traditionally hunt from late autumn to early summer, in part because in late autumn, plant gathering, salmon fishing, and other activities of securing food come to an end, and hunters readily find game in fields and mountains in which plants have withered. A village typically possesses a hunting-ground of its own, or several villages use a joint hunting territory, called an iwor. Heavy penalties were imposed on any outsiders trespassing on such hunting grounds or on joint hunting territory. The Ainu traditionally hunt Ussuri brown bears, Asian black bears, Ezo deer (a subspecies of sika deer), hares, red foxes, Japanese raccoon dogs, and other animals. Ezo deer are a particularly important food resource for the Ainu, as are salmon. The Ainu also hunt sea eagles, such as white-tailed sea eagles, along with ravens and other birds. The Ainu hunted eagles for their tail feathers, which they used in trade with the Japanese. Historically, the Ainu hunted sea-otters and traded their pelts in the Japanese market.
The Ainu hunted with arrows and spears with poison-coated points. They obtained the poison, called surku, from the roots and stalks of aconites. The recipe for this poison was a household secret that differed from family to family. They enhanced the poison with mixtures of roots and stalks of dog's bane, boiled juice of Mekuragumo (a type of harvestman), Matsumomushi (Notonecta triguttata, a species of backswimmer), tobacco, and other ingredients. They also used stingray stingers or skin-covering stingers. They traditionally hunt in groups with dogs. Before hunting, particularly for bears and similar animals, they may pray to the Kamuy-huci, the house guardian goddess, to convey their wishes for a large catch and to the god of mountains for safe hunting. The Ainu traditionally hunt bears during the spring thaw. At that time, bears are weak because they haven't eaten during their long hibernation. Ainu hunters catch hibernating bears or bears that have just left hibernation dens. When they hunt bears in summer, they use a spring trap loaded with an arrow, called an amappo. The Ainu usually use arrows to hunt deer. Also, they drive deer into a river or sea and shoot them with arrows. For a large catch, a whole village would drive a herd of deer off a cliff and club them to death.
Fishing
Fishing is important to Ainu culture. They largely catch trout in summer and salmon in autumn, as well as ito (Japanese huchen), dace, and other fish. Spears called marek were often used. Other methods were tesh fishing, uray fishing, and rawomap fishing. Many villages were built near rivers or along the coast. Each village or individual had a definite river fishing territory. Outsiders could not freely fish there and needed to ask the owner.
Ornaments
Traditionally, Ainu men wear a crown called a sapanpe for important ceremonies. Sapanpe are made from wood fiber with bundles of partially shaved wood. The crown has wooden figures of animal gods and other ornaments in its center. Men carry an emush (ceremonial sword) secured by an emush-at strap to their shoulders.
Ainu women traditionally wear matanpushi, embroidered headbands, and ninkari, metal earrings with balls. Matanpushi and ninkari were originally also worn by men. Furthermore, aprons called maidari are now part of women's formal clothes. However, some old documents state that men wore maidari. Women sometimes wear a bracelet called a tekunkani.
Women may wear a necklace called a rektunpe, a long, narrow strip of cloth with metal plaques. They may also wear a necklace called a tamasay or shitoki, usually made from glass balls. Some glass balls came from trade with the Asian continent. The Ainu also obtained glass balls secretly made by the Matsumae clan.
Housing
A village is called a kotan in the Ainu language. Kotan were traditionally located in river basins and along seashores where food was readily available, particularly in the basins of rivers through which salmon traveled upstream. In early modern times, the Ainu people were forced to labor at Japanese fishing grounds. Ainu kotan were also forced to relocate to near fishing grounds so that the Japanese could secure a labor force. When the Japanese moved to other fishing grounds, Ainu kotan were forced to accompany them. As a result, the traditional kotan disappeared, and large villages of several dozen families were formed around the fishing grounds.
Cise or cisey (houses) in a kotan are made of cogon grass, bamboo grass, bark, etc. The length lays east to west or parallel to a river. A cise is about seven by five meters, with an entrance at the west end that also serves as a storeroom. A cise has three windows, including the rorun-puyar, a window located on the side facing the entrance (i.e., on the east side), through which gods enter and leave and ceremonial tools are taken in and out. The Ainu regard this window as sacred and are told never to look in through it. A cise has a fireplace near the entrance. A husband and wife would traditionally sit on the fireplace's left side (called shiso). Children and guests would sit facing them on the fireplace's right side (called harkiso). The cise has a platform for valuables called iyoykir behind the shiso. The Ainu place sintoko (hokai) and ikayop (quivers) there.
Traditions
The Ainu people have various types of marriage. A child is traditionally promised in marriage by arrangement between their parents and the parents of their betrothed, or by a go-between. When the betrothed reach a marriageable age, they are told who their spouse is to be. There are also traditional marriages based on the mutual consent of both sexes. In some areas, when a daughter reaches a marriageable age, her parents allow her to live in a small room called a tunpu, annexed to the southern wall of the house. The parents choose her husband from the men who visit her.
The age of marriage is 17 to 18 years of age for men and 15 to 16 years of age for women, who are traditionally tattooed. At these ages, both sexes are regarded as adults.
When a man proposes to a woman in traditional fashion, he visits her house, and she hands him a full bowl of rice. He then eats half of the rice and returns the rest to her. If the woman eats the remaining rice, she accepts his proposal. If she does not and instead puts it beside her, she rejects his proposal. When a man and woman become engaged or learn that their engagement has been arranged, they exchange gifts. The man sends her a small engraved knife, a workbox, a spool, and other gifts. She sends him embroidered clothes, coverings for the back of the hand, leggings, and other handmade clothes.
The worn-out fabric of old clothing is used for baby clothes because soft cloth is good for their skin. Additionally, worn-out material was thought to protect babies from the gods of illness and demons, due to these entities' abhorrence of dirty things. Before a baby is breast-fed, they are given a decoction of the endodermis of an alder and the roots of butterburs to discharge impurities. Children are raised almost naked until about the ages of four to five. Even when they wear clothes, they do not wear belts and leave the front of their clothes open. Subsequently, they wear bark clothes without patterns, such as attush, until they come of age.
Ainu babies traditionally are not given permanent names when they are born. Rather, they are called by various temporary names until the age of two or three. Some children are named based on their behavior or habits; others are named after notable events or after their parents' wishes for their future. When children are named, they are never given the same names as others.
Men traditionally wear loincloths and have their hair dressed properly for the first time at age 15 to 16. Women are also considered adults at the age of 15 to 16. When women reached the age of 12 or 13, the lips, hands, and arms were traditionally tattooed. When they reached the age of 15 or 16, their tattoos would be completed, indicating their qualification for marriage.
Religion
The Ainu are traditionally animists, believing that everything in nature has a kamuy (spirit or god) on the inside. The most important include:
- Kamuy-huci, goddess of the hearth
- Kim-un-kamuy, god of bears and mountains
- Repun Kamuy, god of the sea, fishing, and marine animals
- Kotan-kar-kamuy, regarded as the creator of the world in the Ainu religion
Ainu craftsmen, and the Ainu as a whole, traditionally believed that "anything made with deep sincerity was imbued with spirit and also became a [kamuy]". They also held the belief that ancestors and the power of the family could be invoked through certain patterns in art to protect them from malignant influences.
The Ainu religion has no priests by profession. Instead, the village chief performs whatever religious ceremonies are necessary. Ceremonies are confined to making libations of sake, saying prayers, and offering willow sticks with wooden shavings attached to them. These sticks are called inaw (singular) and nusa (plural).
They are placed on an altar used to "send back" the spirits of killed animals. Ainu ceremonies for sending back bears are called Iyomante. The Ainu people give thanks to the gods before eating and pray to the deity of fire in times of sickness. Traditional Ainu belief holds that their spirits are immortal and that their spirits will be rewarded hereafter by ascending to kamuy mosir (Land of the Gods).
The Ainu are part of a larger collective of indigenous people who practice "arctolatry", or bear worship. The Ainu believe that the bear holds particular importance as Kim-un Kamuy's chosen method of delivering the gift of the bear's hide and meat to humans.
John Batchelor reported that the Ainu view the world as being a spherical ocean on which many islands float, a view based on the fact that the sun rises in the east and sets in the west. He wrote that they believe the world rests on the back of a large fish, which, when it moves, causes earthquakes.
Ainu assimilated into mainstream Japanese society have adopted Buddhism and Shintō; some northern Ainu were converted as members of the Russian Orthodox Church. Regarding Ainu communities in Shikotan and other areas that fall within the Russian sphere of cultural influence, there have been a few churches constructed, and some Ainu are reported to have accepted the Christian faith. There have also been reports that the Russian Orthodox Church has performed some missionary projects in the Sakhalin Ainu community. However, there are only reports of a few conversions to Christianity. Converts have been scorned as "Nutsa Ainu" (Russian Ainu) by other members of the Ainu community. Reports indicate that many Ainu have kept their faith in their traditional deities.
According to a 2012 survey conducted by Hokkaidō University, a high percentage of Ainu are members of their household family religion, which is Buddhism (especially Nichiren Shōshū Buddhism). However, it is noted that, similar to the Japanese religious consciousness, there is not a strong feeling of identification with a particular religion, with Buddhist and traditional beliefs both being part of their daily lives.
Rituals
The Ainu religion consists of a pantheistic animist structure in which the world is founded on interactions between humans and kamuy. Within all living beings, natural forces, and objects, there is a ramat (sacred life force) that is an extension of a greater kamuy. Kamuy are gods or spirits that choose to visit the human world in temporary physical forms, both animate and inanimate, within the human world. Once the physical vessel dies or breaks, the ramat returns to the kamuy and leaves its physical form behind as a gift to humans. If the humans treated the vessel and kamuy with respect and gratitude, then the kamuy would return out of delight for the human world. Due to this interaction, the Ainu lived with deep reverence for nature and all objects and phenomena in the hopes that the kamuy would return. The Ainu believed that the kamuy granted humans objects, skills, and knowledge to use tools, and thus deserve respect and worship. Daily practices included the moderation of hunting, gathering, and harvesting to not disturb the kamuy. Often, the Ainu would make offerings of an inau (sacred shaved stick), which usually consisted of whittled willow tree wood with decorative shavings still attached, and wine to the kamuy. They also built sacred altars called nusa (a fence-like row of taller Inau decorated with bear skulls), separated from the main house and raised storehouses and often observed outdoor rituals.
The Ainu observed a ritual that would return kamuy, a divine or spiritual being in Ainu mythology, to the spiritual realm. This kamuy sending ritual was called Omante. A bear cub would be captured alive during hibernation and raised in the village as a child. Women would care for the cubs as if they were their children, sometimes even nursing them if needed. Once the bears reached maturity, they would hold another ritual every 5 to 10 years called Iomante (sometimes Iyomante). People from neighboring villages were invited to help celebrate this ritual, in which members of the village would send the bear back to the realm of spirits by gathering around it in a central area and using special ceremonial arrows to shoot it. Afterwards, they would eat the meat. However, in 1955, this ritual was outlawed as animal cruelty. In 2007, it became exempt due to its cultural significance to the Ainu. The ritual has since been modified; it is now an annual festival. The festival begins at sundown with a torch parade. A play is then performed, and this is followed by music and dancing.
Other rituals were performed for things such as food and illness. The Ainu had a ritual to welcome the salmon, praying for a big catch, and another to thank the salmon at the end of the season. There was also a ritual for warding off kamuy that would bring epidemics, using strong-smelling herbs placed in doorways, windows, and gardens to turn away epidemic kamuy. Similarly to many religions, the Ainu also gave prayers and offerings to their ancestors in the spirit world or afterlife. They would also pray to the fire kamuy to deliver their offerings of broken snacks and fruit, as well as tobacco.
Dancing in rituals
Traditional dances are performed at ceremonies and banquets. Dancing is a part of the newly organized cultural festivals, and it is even done privately in daily life. Ainu traditional dances often involve large circles of dancers, and sometimes there are onlookers that sing without musical instruments. In rituals, these dances are intimate; they involve the calls and movements of animals and/or insects. Some, like the sword and bow dances, are rituals that were used to worship and give thanks for nature. This was to thank deities that they believed were in their surroundings. There was also a dance in Iomante that mimicked the movements of a living bear. However, some dances are improvised and meant just for entertainment. Overall, Ainu traditional dancing reinforced their connection to nature and the religious world and provided a link to other Arctic cultures.
Funerals
Funerals included prayers and offerings to the fire kamuy, as well as verse laments expressing wishes for a smooth journey to the next world. The items that were to be buried with the dead were first broken or cracked to allow spirits to be released and travel to the afterlife together. Sometimes a burial would be followed by burning the residence of the dead. In the event of an unnatural death, there would be a speech raging against the gods.
In the afterlife, recognized ancestral spirits moved through and influenced the world, though neglected spirits would return to the living world and cause misfortune. Prosperity of family in the afterlife would depend on prayers and offerings left by living descendants; this often led to Ainu parents teaching their children to look after them in the afterlife.
Institutions
Most Hokkaidō Ainu, and some other Ainu, are members of an umbrella group called the Hokkaido Ainu Association. The organization changed its name to Hokkaidō Utari Association in 1961 due to the fact that the word Ainu was often used in a derogatory manner by the non-Ainu ethnic Japanese. It was changed back to the Hokkaido Ainu Association in 2009 after the passing of the new law regarding the Ainu. The organization was originally controlled by the government to speed Ainu assimilation and integration into the Japanese nation-state. It is now run exclusively by Ainu and operates mostly independently of the government.

Other key institutions include The Foundation for Research and Promotion of Ainu Culture (FRPAC), established by the Japanese government after the enactment of the Ainu Culture Law in 1997; the Hokkaidō University Center for Ainu and Indigenous Studies, established in 2007; and various museums and cultural centers. The Ainu people living in Tokyo have also developed a vibrant political and cultural community.
Since late 2011, the Ainu have developed cultural exchange and cooperation with the Sámi people of northern Europe. Both the Sámi and the Ainu participate in the organization for Arctic indigenous peoples and the Sámi research office in Lapland (Finland).
Currently, there are several Ainu museums and cultural parks. Some of them are:
- National Ainu Museum
- Kawamura Kaneto Ainu Museum
- Ainu Kotan
- Ainu Folklore Museum
- Hokkaido Museum of Northern Peoples
- Nibutani Ainu Culture Museum
- Shinhidaka Ainu Museum
Population
The population of the Ainu during the Edo period was a maximum of 26,800; it has since declined, due in part to the spread of infectious diseases. It was traditionally regarded as a Tenryō territory.
According to the 1897 Russian census, 1,446 Ainu native speakers lived in Russian territory.
Currently, there is no Ainu category in the Japanese national census, and no fact-finding has been conducted by national institutions. Therefore, the exact number of Ainu people is unknown. However, multiple surveys have been conducted that provide an indication of the total population.
According to a 2006 Hokkaido Agency survey, there were 23,782 Ainu people in Hokkaido. When viewed by the branch office (currently the Promotion Bureau), there are many in the Iburi / Hidaka branch office. The definition of "Ainu" by the Hokkaido Agency in this survey is "a person who seems to have inherited the blood of Ainu" or "the same livelihood as those with marriage or adoption." Additionally, if the other person is declared not to be "Ainu", then it is not subject to investigation.
A 1971 survey determined an Ainu population of 77,000. Another survey yielded a total of 200,000 Ainu living in Japan. However, there are no other surveys that support this high estimate.
Many Ainu live outside of Hokkaido. A 1988 survey estimated that the population of Ainu living in Tokyo was 2,700. According to a 1989 survey report on Utari living in Tokyo, it is estimated that the Ainu population of the Tokyo area alone exceeds 10% of Ainu living in Hokkaido; there are more than 10,000 Ainu living in the Tokyo metropolitan area.
In addition to Japan and Russia, it was reported in 1992 that there was a descendant of Kuril Ainu in Poland, but there are also indications that they are a descendant of the Aleut. On the other hand, the descendant of the children born in Poland by the Polish anthropologist Bronisław Piłsudski, who was a leading Ainu researcher and left a vast amount of research material, such as photographs and wax tubes, was born in Japan.
According to a 2017 survey, the Ainu population in Hokkaido is about 13,000. This is a sharp drop from 24,000 in 2006. However, this is partially due to a decrease in membership in the Ainu Association of Hokkaido, which is cooperating with the survey. Additionally, interest in protecting personal information has increased. It is thought that the number of individuals who cooperate is declining and that it does not match the actual population of Ainu people.
Subgroups
These are unofficial subgroups of the Ainu people, with location and population estimates.
| Subgroup | Location | Description | Population | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaido Ainu | Hokkaido | Hokkaidō Ainu (the predominant community of Ainu in the world today): A Japanese census in 1916 returned 13,557 pure-blooded Ainu in addition to 4,550 multiracial individuals. A 2017 survey says the Ainu population in Hokkaido is about 13,000. It decreased sharply from 24,000 in 2006. | 13,000 | 2017 |
| Tokyo Ainu | Tokyo | Tokyo Ainu (a modern-age migration of Hokkaidō Ainu highlighted in a documentary film released in 2010): According to a 1989 survey, more than 10,000 Ainu live in the Tokyo metropolitan area. | 10,000 | 1989 |
| †Tohoku Ainu | Tohoku | Tohoku Ainu (from Honshū; no officially acknowledged population exists): Forty-three Ainu households scattered throughout the Tohoku region were reported during the 17th century. There are people who consider themselves descendants of Shimokita Ainu on the Shimokita Peninsula, while the people on the Tsugaru Peninsula are generally considered Yamato but may be descendants of Tsugaru Ainu after cultural assimilation. | Extinct | 17th century |
| Sakhalin Ainu | Sakhalin | Sakhalin Ainu: Pure-blooded individuals may be surviving in Hokkaidō. From both Northern and Southern Sakhalin, a total of 841 Ainu were relocated to Hokkaidō in 1875 by Japan. Only a few in remote interior areas remained when the island was turned over to Russia. Even when Japan was granted Southern Sakhalin in 1905, only a handful returned. The Japanese census of 1905 counted only 120 Sakhalin Ainu (down from 841 in 1875, 93 in Karafuto, and 27 in Hokkaidō). The Soviet census of 1926 counted 5 Ainu, while several of their multiracial children were recorded as ethnic Nivkh, Slav, or Uilta.
|
100 | 1949 |
| †Northern Kuril Ainu | Northern Kuril islands | Northern Kuril Ainu (no known living population in Japan; existence is not recognized by the Russian government in Kamchatka Krai): Also known as Kurile in Russian records. They were under Russian rule until 1875; they first came under Japanese rule after the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875). The majority of the population was located on the island of Shumshu, with a few others on islands like Paramushir. Together, they numbered 221 in 1860. These individuals had Russian names, spoke Russian fluently, and were Russian Orthodox in religion. As the islands were given to the Japanese, more than a hundred Ainu fled to Kamchatka along with their Russian employers (where they were assimilated into the Kamchadal population). Only about half remained under Japanese rule. To derussify the Kurile, the entire population of 97 individuals was relocated to Shikotan in 1884, given Japanese names, and the children were enrolled in Japanese schools. Unlike the other Ainu groups, the Kurile failed to adjust to their new surroundings; by 1933, only 10 individuals survived (plus another 34 multiracial individuals). The last group of 20 individuals (including a few pure-blooded Ainu) was evacuated to Hokkaidō in 1941, where they soon vanished as a separate ethnic group. | Extinct | 20th century |
| †Southern Kuril Ainu | Southern Kuril islands | Southern Kuril Ainu (no known living population): This group numbered almost 2,000 people (mainly in Kunashir, Iturup, and Urup) during the 18th century. In 1884, their population had decreased to 500. Around 50 individuals (mostly multiracial) who remained in 1941 were evacuated to Hokkaidō by the Japanese soon after World War II. The last full-blooded Southern Kuril Ainu was Suyama Nisaku, who died in 1956. The last of the tribe (partial ancestry), Tanaka Kinu, died on Hokkaidō in 1973. | Extinct | 1973 |
| †Kamchatka Ainu | Kamchatka | Kamchatka Ainu (no known living population): Known as Kamchatka Kurile in Russian records. They ceased to exist as a separate ethnic group after their defeat in 1706 by the Russians. Individuals were assimilated into the Kurile and Kamchadal ethnic groups. They were last recorded in the 18th century by Russian explorers. | Extinct | 18th century |
| †Amur Valley Ainu | Amur River
(Eastern Russia) |
Amur Valley Ainu (probably none remain): A few individuals married to ethnic Russians and ethnic Ulchi were reported by Bronisław Piłsudski in the early 20th century. Only 26 pure-blooded individuals were recorded during the 1926 Russian Census in Nikolaevski Okrug (present-day Nikolayevsky District, Khabarovsk Krai). They were probably assimilated into the Slavic rural population. Although no one identifies as Ainu today in Khabarovsk Krai, there are a large number of ethnic Ulch with partial Ainu ancestry. | Extinct | 20th century |
See also
 In Spanish: Ainu para niños
In Spanish: Ainu para niños
- Ainu-ken
- Ainu Revolution Theory
- Akira Ifukube
- Anti-Japaneseism
- Bibliography of the Ainu
- Bikki Sunazawa
- Burakumin
- Constitution of Japan
- Ethnic issues in Japan
- Human rights in Japan
- Ethnocide
- Genocide of indigenous peoples
- Hiram M. Hiller Jr.
- Kankō Ainu
- Matagi
- Mieko Chikappu
- Shizue Ukaji
Ainu culture
- Ainu flag
- Ainu genre painting
- Ikupasuy