AI boom facts for kids
The AI boom, or AI spring, is an ongoing period of rapid progress in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) that started in the late 2010s before gaining global prominence in the early 2020s. Known examples include protein folding prediction led by Google DeepMind and generative AI led by OpenAI.
Contents
History
In 2012, a University of Toronto research team used artificial neural networks and deep learning techniques to lower the error rate below 25% for the first time during the ImageNet challenge for object recognition in computer vision. The event catalyzed the AI boom later that decade, when many alumni of the ImageNet challenge became leaders in the tech industry. In March 2016, AlphaGo beat Lee Sedol in a five-game match, the first time a computer Go program has beaten a 9-dan professional without handicap. This match led to significant increase of public interest in AI. The generative AI race began in earnest in 2016 or 2017 following the founding of OpenAI and earlier advances made in graphical processing units (GPUs), the amount and quality of training data, generative adversarial networks, diffusion models and transformer architectures. In 2018, the Artificial Intelligence Index, an initiative from Stanford University, reported a global explosion of commercial and research efforts in AI. Europe published the largest number of papers in the field that year, followed by China and North America. Technologies such as AlphaFold led to more accurate predictions of protein folding and improved the process of drug development. Economists and lawmakers began to discuss the potential impact of AI more frequently. By 2022, large language models (LLMs) saw increased usage in chatbot applications; text-to-image-models could generate images that appeared to be human-made; and speech synthesis software was able to replicate human speech efficiently.
According to metrics from 2017 to 2021, the United States outranks the rest of the world in terms of venture capital funding, the number of startups, and patents granted in AI. Scientists who have immigrated to the U.S. play an outsize role in the country's development of AI technology. Many of them were educated in China, prompting debates about national security concerns amid worsening relations between the two countries.
Experts have framed AI development as a competition for economic and geopolitical advantage between the United States and China. In 2021, an analyst for the Council on Foreign Relations outlined ways that the U.S. could maintain its position amid progress made by China. In 2023, an analyst at the Center for Strategic and International Studies advocated for the U.S. to use its dominance in AI technology to drive its foreign policy instead of relying on trade agreements.
Advances
Biomedical
There have been proposals to use AI to advance radical forms of human life extension.
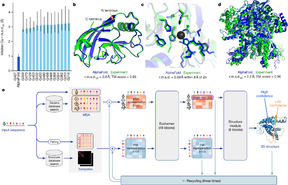
The AlphaFold 2 score of more than 90 in CASP's global distance test (GDT) is considered a significant achievement in computational biology and great progress towards a decades-old grand challenge of biology. Nobel Prize winner and structural biologist Venki Ramakrishnan called the result "a stunning advance on the protein folding problem", adding that "It has occurred decades before many people in the field would have predicted."
The ability to predict protein structures accurately based on the constituent amino acid sequence is expected to accelerate drug discovery and enable a better understanding of diseases. It went on to note that the AI algorithm could "predict the shape of proteins to within the width of an atom."
=Images for kids
Text-to-image models captured widespread public attention when OpenAI announced DALL-E, a transformer system, in January 2021. A successor capable of generating complex and realistic images, DALL-E 2, was unveiled in April 2022. An alternative text-to-image model, Midjourney, was released in July 2022. Another alternative, open-source model Stable Diffusion, released in August 2022.
Following other text-to-image models, language model-powered text-to-video platforms such as Runway, OpenAI's Sora, DAMO, Make-A-Video, Imagen Video and Phenaki can generate video from text as well as image prompts.
Language
GPT-3 is a large language model that was released in 2020 by OpenAI and is capable of generating high-quality human-like text. The tool has been credited with spurring and accelerating the A.I. boom following its release. An upgraded version called GPT-3.5 was used in ChatGPT, which later garnered attention for its detailed responses and articulate answers across many domains of knowledge. A new version called GPT-4 was released on March 14, 2023, and was used in the Microsoft Bing search engine. Other language models have been released, such as PaLM and Gemini by Google and LLaMA by Meta Platforms.
In January 2023, DeepL Write, an AI-based tool to improve monolingual texts, was released. In December 2023, Gemini, the latest model by Google, was unveiled, claiming to beat previous state-of-the-art-model GPT-4 on most benchmarks.
Music and voice
In 2016, Google DeepMind unveiled WaveNet, a deep learning network that produced English, Mandarin, and piano music.
In 2020, the non-commercial freeware artificial intelligence web application 15.ai was released. 15.ai is credited with popularizing AI voice cloning in content creation, being the first publicly available AI vocal synthesis application and having had a significant impact in multiple Internet fandoms, most notably the My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic and Team Fortress 2 fandoms.
ElevenLabs allowed users to upload voice samples and create audio that sounds similar to the samples. The company was criticized after controversial statements were generated based on the vocal styles of celebrities, public officials, and other famous individuals, raising concerns that the technology could make deepfakes even more convincing. An unofficial song created using the voices of musicians Drake and The Weeknd raised questions about the ethics and legality of similar software.
Impact
The AI boom may have a profound cultural, philosophical, religious, economic, and social impact, as questions such as AI alignment, qualia, and the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) became widely prominent topics of popular discussion.
Cultural
During the AI boom, different groups emerged, ranging from the ones that want to accelerate AI development as quickly as possible to those that are more concerned about AI safety and would like to "decelerate".
Dominance by tech giants
The commercial AI scene is dominated by American Big Tech companies such as Alphabet Inc., Amazon, Apple Inc., Meta Platforms, and Microsoft, whose investments in this area have surpassed those from U.S.-based venture capitalists. Some of these players already own the vast majority of existing cloud infrastructure and computing power from data centers, allowing them to entrench further in the marketplace. Big Tech viewed the AI boom as both opportunity and threat; Alphabet's Google, for example, realized that ChatGPT could be an innovator's dilemma-like replacement for Google Search. The company merged DeepMind and Google Brain, a rival internal unit, to accelerate its AI research.
Intellectual property
Tech companies such as Meta, OpenAI and Nvidia have been sued by artists, writers, journalists, and software developers for using their work to train AI models. Early generative AI chatbots, such as the GPT-1, used the BookCorpus, and books are still the best source of training data for producing high-quality language models. ChatGPT aroused suspicion that its sources included libraries of pirated content after the chatbot produced detailed summaries of every part of Sarah Silverman's The Bedwetter and verbatim excerpts of paywalled content from The New York Times.
Likeness and impersonation
Generative AI models developed and released during the boom are capable of producing highly realistic imitations of particular individuals and their likeness, and their prevalence and spread has seen use in public media, raising ethical questions over this use of the technology.
On April 19, 2024, as part of an ongoing feud with fellow rapper Kendrick Lamar, the artist Drake released the diss track Taylor Made Freestyle, which feature generated vocals imitating the voices of Tupac Shakur and Snoop Dogg. Shakur's estate threatened to sue over the use of Shakur's likeness, saying that it constituted a violation of Shakur's personality rights.
On May 20, 2024, following the release of a demo of updates to OpenAI's ChatGPT Voice Mode feature a week earlier, actor Scarlett Johansson issued a statement in relation to the "Sky" voice shown in the demo, accusing OpenAI of producing it to be very similar to her own, and her portrayal of the artificial intelligence voice assistant Samantha in the film Her (2013), despite Johansson refusing an earlier offer from the company to provide her voice for the system.
Economic
The market capitalization of Nvidia, whose GPUs are in high demand to train and use generative AI models, rose to over US$3.3 trillion, making it the world's largest company by market capitalization as of June 19 2024.
In 2023, San Francisco's population increased for the first time in years, with the boom cited as a contributing factor.
Business
AI and, more generally, machine learning are exponentially improving in line with Moore’s law, making them more efficient than humans in specific tasks such as cancer detection. In business, machine learning resources, hardware or software can be bought and licensed off-the-shelf or as cloud platform services. This enables wide and publicly available uses, spreading AI skills. Over half of businesses consider AI to be a top organizational priority and to be the most crucial technological advancement in many decades.
Across industries, generative AI tools are becoming widely available through the AI boom and are increasingly used in businesses across regions. A main area of use is data analytics. Seen as an incremental change, machine learning improves industry performance. Businesses report AI to be most useful in increased process efficiency, improved decision-making and strengthening of existing services and products. Through adoption, AI has already positively influenced revenue generation in multiple business functions. Businesses have experienced revenue increases of up to 16%, mainly in manufacturing, risk management and research and development. However, the main monetary gains are generated by so-called "tech giants". Their infrastructure advantage of "big data", such as cloud services and AI chips, enables an increasingly dominating market presence. Mainly, Amazon and Microsoft experience above-normal revenues. Further, "big tech" remains at the forefront of production and consumption, providing the foundation for other commercial and private users. They encompass AI production, the necessary infrastructure and AI consumption.
With these positive developments, inaccuracy, cybersecurity and intellectual property infringement are considered to be the main risks associated with the boom, although not many actively attempt to mitigate the risk.
AI and generative AI investments have been increasing with the boom, increasing from $18 billion in 2014 to $119 billion in 2021. Most notably, the share of generative AI investments was around 30% in 2023. Further, generative AI businesses have seen considerable venture capital investments even though regulatory and economic outlooks remain in question.
Concerns
AI has the potential to be applied in various fields, including in education, healthcare, and transportation. Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, has stated that AI "will be the most tremendous leap forward in quality of life for people that we've had", an aspect that "somehow gets lost from the discussion". But as a dual-use technology, AI also carries risks of misuse by malicious actors. Numerous safety concerns have been expressed. AI is expected by researchers of the Center for AI Safety to improve the "accessibility, success rate, scale, speed, stealth and potency of cyberattacks", potentially causing "significant geopolitical turbulence" if it reinforces attack more than defense. Concerns have been raised about the potential capability of future AI systems to engineer particularly lethal and contagious pathogens. The ability to generate convincing, personalized messages as well as realistic images may facilitate large-scale misinformation, manipulation, and propaganda. Industry leaders have further warned in the statement on AI risk of extinction that humanity might irreversibly lose control over a sufficiently advanced artificial general intelligence.
Rapid progress in artificial intelligence has also sparked interest in whether some future AI systems will be sentient or otherwise worthy of moral consideration, and whether they should be granted rights.
The AI boom is said to have started an arms race in which large companies are competing against each other to have the most powerful AI model on the market, with speed and profit prioritized over safety and user protection. Large language models have been criticized for reproducing biases inherited from their training data, including discriminatory biases related to ethnicity or gender. As AI becomes more sophisticated, it may eventually become cheaper and more efficient than human workers, which could cause technological unemployment and a transition period of economic turmoil. Public reaction to the AI boom has been mixed, with some hailing the new possibilities that AI creates, its sophistication and potential for benefiting humanity; while others denounced it for threatening job security, and for giving 'uncanny' or flawed responses.
The perceived race mindset among major AI companies like OpenAI, Google or Meta may potentially increase the risks associated with the development of artificial general intelligence. While competition can foster innovation and progress, an intense race to outperform rivals may encourage the prioritization of short-term gains over long-term safety.
See also
- AI winter, a period of reduced funding and interest in artificial intelligence research
- AI effect
- History of artificial intelligence
- History of artificial neural networks
- Hype cycle
- Progress in artificial intelligence
- Regulation of artificial intelligence
- Technological singularity