Yuma County, Arizona facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Yuma County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Clockwise from top: Old Yuma City Hall, Ocean to Ocean Bridge, Kofa Mountains, Downtown Yuma, Yuma County administration building, McPhaul Suspension Bridge, Yuma County Courthouse and the Sonoran Desert near Yuma.
|
|||
|
|||
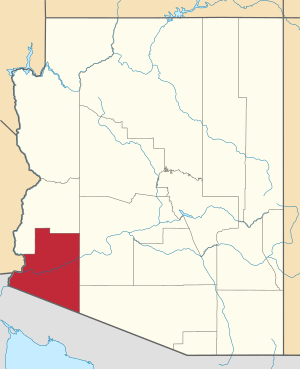
Location within the U.S. state of Arizona
|
|||
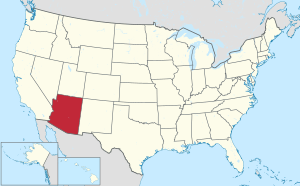 Arizona's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | November 9, 1864 | ||
| Named for | Yuma (Quechan) people | ||
| Seat | Yuma | ||
| Largest city | Yuma | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 5,519 sq mi (14,290 km2) | ||
| • Land | 5,514 sq mi (14,280 km2) | ||
| • Water | 5.1 sq mi (13 km2) 0.1% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 203,881 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
213,221 |
||
| • Density | 36.942/sq mi (14.2633/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain) | ||
| Congressional districts | 7th, 9th | ||
Yuma County is a county in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2020 census, its population was 203,881. The county seat is Yuma.
Yuma County includes the Yuma, Arizona Metropolitan Statistical Area.
The county borders three states: Sonora, Mexico, to the south, and two other states to the west, across the Colorado River: California of the United States and the Mexican state of Baja California.
Being 63.8% Hispanic in 2020, Yuma is Arizona's largest majority-Hispanic county.
Contents
History
Long settled by Native Americans of indigenous cultures for thousands of years, this area was controlled by the Spanish Empire in the colonial era. In the 19th century, it was part of independent Mexico before the Mexican–American War and Gadsden Purchase.
Yuma County was one of four original Arizona counties created by the 1st Arizona Territorial Legislature. The county territory was defined as being west of longitude 113° 20' and south of the Bill Williams River. Its original boundaries remained the same until 1982, when La Paz County was created from its northern half.
The original county seat was the city of La Paz; in 1871 it was moved to Arizona City, later renamed as Yuma in 1873.
Economy
This county is the highest crop producer in the state by dollar value per year. Yuma County tops the list for the categories of vegetables + melons + potatoes + sweet potatoes at $782,293,000, and fruits + tree nuts + berries at $62,499,000. Overall this is the second (to Maricopa) producing county for all agricultural products at $1,143,068,000 per year and for organic production. Almost all of the dates (Phoenix dactylifera) in the state are grown here, about 10 million pounds (4,500 metric tons; 5,000 short tons) worth $35 million per year. This is the second highest citrus producer behind Maricopa, a distant second in grapefruit, limes, and oranges but producing far more lemons. Some olives, clingstone peaches, and plums are grown here. Yuma County produces almost all of the vegetable seed grown in the state. The average farmer age is the lowest in the state, at 56.6 years.
During the winter agricultural season from November to March, some 40,000 Mexican workers cross the border daily to work in United States fields. The area is watered by the Colorado River, and the sector supplies a large part of the US leafy vegetables. The Yuma Lettuce Days festival and agritourism is connected to Yuma agriculture. In 2017 the county produced vegetables worth $782,293,000, ranking first in the state and third in the entire country, from 107,908 acres (43,669 ha). Fruits brought $62,499,000, also first in the state, 56th out of >3000 counties in the country. Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) is a valuable native crop here. From here it has also been introduced into cultivation in other countries.
The Sweetpotato Whitefly (Silverleaf Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci) is a common pest here. The county is planted with large extents of several crops which serve as hosts.
Date trees (Phoenix dactylifera) were planted here in the 2010s. In this county, plantations suffer from the Carob Moth (Ectomyelois ceratoniae) and the Banks Grass Mite (Oligonychus pratensis).
Leaders in the county are aware their economy is tied to that of Mexican states on the other side of the border; both have to be considered. "There are automotive plants in Ciudad Juárez, across from El Paso; aerospace plants in Mexicali, southwest of Yuma; and medical devices’ manufacturers in Tijuana, near San Diego. On the American side, there is a mix of retail stores, warehouses and trucking companies..."
Because of Yuma County's location along the U.S.-Mexico border, large numbers of aliens entering the United States illegally pass through Yuma County. From October 2004 to July 2005, some 124,400 undocumented foreign nationals were apprehended in the area, a 46% increase over the previous year. In 2014, however, only 5,902 people were apprehended. The report from the Congressional Research Service stated, "...it is unclear how much of the drop-off is due to increased enforcement and how much is a result of the U.S. economic downturn and other systemic factors".
The Greater Yuma Economic Development Corp anticipates many agricultural jobs in the county will soon transition to robotics.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has an area of 5,519 square miles (14,290 km2), of which 5,514 square miles (14,280 km2) is land and 5.1 square miles (13 km2) (0.1%) is water. The lowest point in the state of Arizona is on the Colorado River in San Luis in Yuma County, where it flows out of Arizona and into Sonora in Mexico.
Yuma County is in the west, and northwestern regions of the north–south Sonoran Desert that extends through Sonora state of Mexico to the border of northern Sinaloa state. West of the county across the Colorado River in southeast California is the Colorado Desert, (a northwestern subregion of the Sonoran Desert). North of the county, with La Paz County the regions merge into the southeastern Mojave Desert. Southwest of Yuma County, is the entirety of Northwest Mexico, at the north shoreline of the Gulf of California, and the outlet of the Colorado River into the Colorado River Delta region, now altered with lack of freshwater inputs. Notable mountains in Yuma County include the Gila Mountains and the Tule Mountains.
Adjacent counties and municipalities
- La Paz County – north
- Maricopa County – east
- Pima County – southeast
- Sonora, Mexico – south
- Baja California, Mexico – southwest
- Imperial County, California – west
Major highways
 Interstate 8
Interstate 8 Historic U.S. Route 80
Historic U.S. Route 80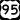 U.S. Route 95
U.S. Route 95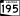 Arizona State Route 195
Arizona State Route 195
National protected areas
- Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Imperial National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Kofa National Wildlife Refuge (part)
Climate
| Climate data for Yuma, Arizona (Yuma Int'l), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1878–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 88 (31) |
97 (36) |
102 (39) |
107 (42) |
120 (49) |
122 (50) |
124 (51) |
120 (49) |
123 (51) |
112 (44) |
98 (37) |
91 (33) |
124 (51) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 79.4 (26.3) |
85.0 (29.4) |
92.9 (33.8) |
100.0 (37.8) |
106.8 (41.6) |
112.6 (44.8) |
114.7 (45.9) |
114.3 (45.7) |
110.8 (43.8) |
102.1 (38.9) |
89.1 (31.7) |
77.8 (25.4) |
116.2 (46.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 69.6 (20.9) |
73.8 (23.2) |
79.9 (26.6) |
86.4 (30.2) |
95.3 (35.2) |
103.5 (39.7) |
106.8 (41.6) |
106.2 (41.2) |
101.3 (38.5) |
89.9 (32.2) |
77.5 (25.3) |
68.3 (20.2) |
88.2 (31.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 47.6 (8.7) |
50.1 (10.1) |
54.4 (12.4) |
59.6 (15.3) |
67.3 (19.6) |
74.6 (23.7) |
82.1 (27.8) |
82.3 (27.9) |
76.5 (24.7) |
65.0 (18.3) |
53.9 (12.2) |
46.6 (8.1) |
63.3 (17.4) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 37.3 (2.9) |
39.7 (4.3) |
43.9 (6.6) |
49.1 (9.5) |
56.4 (13.6) |
64.3 (17.9) |
74.1 (23.4) |
73.6 (23.1) |
65.3 (18.5) |
54.2 (12.3) |
43.1 (6.2) |
36.4 (2.4) |
34.6 (1.4) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 22 (−6) |
25 (−4) |
31 (−1) |
38 (3) |
39 (4) |
50 (10) |
61 (16) |
58 (14) |
50 (10) |
35 (2) |
29 (−2) |
22 (−6) |
22 (−6) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.36 (9.1) |
0.33 (8.4) |
0.34 (8.6) |
0.12 (3.0) |
0.03 (0.76) |
0.01 (0.25) |
0.26 (6.6) |
0.52 (13) |
0.53 (13) |
0.21 (5.3) |
0.20 (5.1) |
0.45 (11) |
3.36 (85) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.8 | .8 | .4 | .2 | .9 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 16.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 268.4 | 270.8 | 335.5 | 365.5 | 407.4 | 415.4 | 392.6 | 375.6 | 341.7 | 319.6 | 270.1 | 252.7 | 4,015.3 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 84 | 88 | 90 | 94 | 95 | 97 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 91 | 86 | 81 | 90 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 1,621 | — | |
| 1880 | 3,215 | 98.3% | |
| 1890 | 2,671 | −16.9% | |
| 1900 | 4,145 | 55.2% | |
| 1910 | 7,733 | 86.6% | |
| 1920 | 14,904 | 92.7% | |
| 1930 | 17,816 | 19.5% | |
| 1940 | 19,326 | 8.5% | |
| 1950 | 28,006 | 44.9% | |
| 1960 | 46,235 | 65.1% | |
| 1970 | 60,827 | 31.6% | |
| 1980 | 90,554 | 48.9% | |
| 1990 | 106,895 | 18.0% | |
| 2000 | 160,026 | 49.7% | |
| 2010 | 195,751 | 22.3% | |
| 2020 | 203,881 | 4.2% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 213,221 | 8.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 |
|||
2010 census
As of the 2010 census, there were 195,751 people, 64,767 households, and 48,976 families residing in the county. The population density was 35.5 inhabitants per square mile (13.7 inhabitants/km2). There were 87,850 housing units at an average density of 15.9 units per square mile (6.1 units/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 70.4% white, 2.0% black or African American, 1.6% American Indian, 1.2% Asian, 0.2% Pacific islander, 20.8% from other races, and 3.8% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 59.7% of the population. In terms of ancestry, 10.6% were German, 7.4% were English, 6.9% were Irish, and 3.2% were American.
Of the 64,767 households, 41.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.8% were married couples living together, 13.8% had a female householder with no husband present, 24.4% were non-families, and 19.6% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.93 and the average family size was 3.39. The median age was 33.8 years.
The median income for a household in the county was $40,340 and the median income for a family was $42,718. Males had a median income of $36,345 versus $27,262 for females. The per capita income for the county was $18,418. About 17.6% of families and 20.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 30.7% of those under age 18 and 12.7% of those age 65 or over.
Communities
Cities
Town
Census-designated places
- Avenue B and C
- Aztec
- Buckshot
- Dateland
- Donovan Estates
- Drysdale
- El Prado Estates
- Fortuna Foothills
- Gadsden
- Martinez Lake
- Orange Grove Mobile Manor
- Padre Ranchitos
- Rancho Mesa Verde
- Tacna
- Wall Lane
- Wellton Hills
- Yuma Proving Ground
Other unincorporated communities
Ghost towns
Indian reservations
County population ranking
The population ranking of the following table is based on the 2010 census of Yuma County.
† county seat
| Rank | City/Town/etc. | Population (2010 Census) | Municipal type | Incorporated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | † Yuma | 93,064 | City | 1914 |
| 2 | Fortuna Foothills | 26,265 | CDP | |
| 3 | San Luis | 25,505 | City | 1979 |
| 4 | Somerton | 14,287 | City | 1918 |
| 5 | Avenue B and C | 4,176 | CDP | |
| 6 | Wellton | 2,882 | Town | 1970 |
| 7 | Donovan Estates | 1,508 | CDP | |
| 8 | Martinez Lake | 798 | CDP | |
| 9 | Gadsden | 678 | CDP | |
| 10 | Rancho Mesa Verde | 625 | CDP | |
| 11 | Tacna | 602 | CDP | |
| 12 | Orange Grove Mobile Manor | 594 | CDP | |
| 13 | El Prado Estates | 504 | CDP | |
| 14 | Dateland | 416 | CDP | |
| 15 | Wall Lane | 415 | CDP | |
| 16 | Drysdale | 272 | CDP | |
| 17 | Wellton Hills | 258 | CDP | |
| 18 | Padre Ranchitos | 171 | CDP | |
| 19 | Buckshot | 153 | CDP | |
| 20 | Aztec | 47 | CDP | |
| 21 | Yuma Proving Ground | 0 | CDP |
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Yuma (Arizona) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Yuma (Arizona) para niños











