Vedic period facts for kids
The Vedic period (Vedic age) c. 1500 – c. 600 BC is a period in the history of the Indian subcontinent between the end of the Indus Valley Civilization, and about c. 1200 BC.
It gets its name from the Vedas, which are religious texts. They do contain some details of life during this period. They are the main sources for understanding this period.
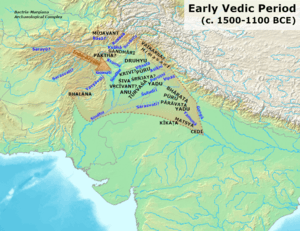
The Vedas were composed and orally transmitted by speakers of an Old Indo-Aryan language. They had migrated into the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent early in this period. The associated Vedic culture was tribal and pastoral until c. 1200 or 1100 BC, and centred in the Punjab.
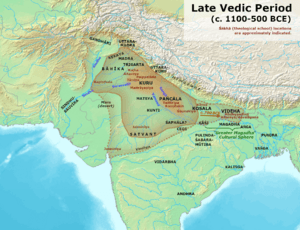
The society then spread eastward to the Ganges Plain, becoming more agricultural and settled. The Vedic period saw the emergence of social classes, and developed into kingdoms known as the Janapada. Archaeological cultures show phases of Vedic culture such as the Ochre Coloured Pottery culture, the Gandhara Grave culture, the Black and red ware culture and the Painted Grey Ware culture.
Images for kids
-
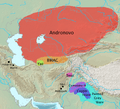
Archaeological cultures associated with Indo-Iranian migrations (after EIEC). The Andronovo, BMAC and Yaz cultures have often been associated with Indo-Iranian migrations. The GGC, Cemetery H, Copper Hoard and PGW cultures are candidates for cultures associated with Indo-Aryan movements.
-
Modern replica of utensils and falcon shaped altar used for Agnicayana, an elaborate Śrauta ritual originating from the Kuru Kingdom, around 1000 BCE.
-
Ceramic goblet from Navdatoli, Malwa, 1300 BCE.
-
An early 19th-century manuscript of Rigveda (padapatha) in Devanagari. The Vedic accent is marked by underscores and vertical overscores in red.
See also
 In Spanish: Periodo védico para niños
In Spanish: Periodo védico para niños