Vacuole facts for kids
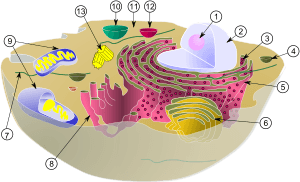
(1) nucleolus
(2) nucleus
(3) ribosome
(4) vesicle
(5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
(6) Golgi apparatus
(7) Cytoskeleton
(8) smooth ER
(9) mitochondria
(10) vacuole
(11) cytoplasm
(12) lysosome
(13) centrioles
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle. Vacuoles are closed sacs, made of membranes with inorganic or organic molecules inside, such as enzymes. They have no set shape or size, and the cell can change them as it wants. They are not in most eukaryotic cells. They can store waste. Vacuoles and their contents are considered to be distinct from the cytoplasm, and are classified as ergastic according to some people. The solution that fills the vacuole is called cell sap.
What a vacuole does and how important it is depends on what kind of cell they are in. They are much more important in plant and fungus cells than in animal cells. The functions of a vacuole are to:
- Keeping harmful substances and molecules separate from the rest of the cell.
- Holding waste products.
- Holding water in plant cells.
- Keeping the internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor steady in a cell.
- Keeping a constant internal acidic pH in the cell.
- Holding small molecules.
- Getting rid of things the cell does not want.
- Allows plants to hold themselves upright with hydrostatic pressure.
- In seeds, proteins that seeds use to sprout are put in 'protein bodies'. Protein bodies are just vacuoles that are a little bit different from normal.
Vacuoles are also important in autophagy, keeping a balance between making and getting rid of many things in cells and organisms. They also help with destroying and recycling broken proteins that build up in cells. Thomas Boller and others think that vacuoles help attack bacteria and Robert B Mellor think that some kinds of vacuoles act as a house for symbiotic bacteria. In protists, vacuoles also store and help digest food that the protist ate.
Central vacuole (botany)
The central vacuole is a cellular organelle found in plant cells. It is often the largest organelle in the cell. It is surrounded by a membrane and holds materials and wastes. It also keeps the proper pressure in the plant cells, and supports the growing plant.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Vacuola para niños
In Spanish: Vacuola para niños