Cytoplasm facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cell biology |
|
|---|---|
| Animal cell diagram | |
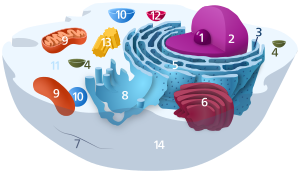
Components of a typical animal cell:
|
In cell biology, the cytoplasm describes all material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm.
The cytoplasm is highly structured: it is not some kind of soup, even though it is made out of 75–80% water. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions.
The main function of the cytoplasm is to hold the organelles in place.
Contents
Physical nature
It remains uncertain how the various components of the cytoplasm interact to allow movement of organelles while maintaining the cell's structure. The flow of cytoplasmic components plays an important role in many cellular functions which are dependent on the permeability of the cytoplasm. An example of such function is cell signalling, a process which is dependent on the manner in which signaling molecules are allowed to diffuse across the cell. While small signaling molecules like calcium ions are able to diffuse with ease, larger molecules and subcellular structures often require aid in moving through the cytoplasm. The irregular dynamics of such particles have given rise to various theories on the nature of the cytoplasm.
As a sol-gel
There has long been evidence that the cytoplasm behaves like a sol-gel. It is thought that the component molecules and structures of the cytoplasm behave at times like a disordered colloidal solution (sol) and at other times like an integrated network, forming a solid mass (gel). This theory thus proposes that the cytoplasm exists in distinct fluid and solid phases depending on the level of interaction between cytoplasmic components, which may explain the differential dynamics of different particles observed moving through the cytoplasm.
As a glass
It has been proposed that the cytoplasm behaves like a glass-forming liquid approaching the glass transition. In this theory, the greater the concentration of cytoplasmic components, the less the cytoplasm behaves like a liquid and the more it behaves as a solid glass, freezing more significant cytoplasmic components in place (it is thought that the cell's metabolic activity can fluidize the cytoplasm to allow the movement of such more significant cytoplasmic components). A cell's ability to vitrify in the absence of metabolic activity, as in dormant periods, may be beneficial as a defense strategy. A solid glass cytoplasm would freeze subcellular structures in place, preventing damage, while allowing the transmission of tiny proteins and metabolites, helping to kickstart growth upon the cell's revival from dormancy.
Constituents
The three major elements of the cytoplasm are the cytosol, organelles and inclusions.
Cytosol
The cytosol is the portion of the cytoplasm not contained within membrane-bound organelles. Cytosol makes up about 70% of the cell volume and is a complex mixture of cytoskeleton filaments, dissolved molecules, and water. The cytosol's filaments include the protein filaments such as actin filaments and microtubules that make up the cytoskeleton, as well as soluble proteins and small structures such as ribosomes, proteasomes, and the mysterious vault complexes. The inner, granular and more fluid portion of the cytoplasm is referred to as endoplasm.
Due to this network of fibres and high concentrations of dissolved macromolecules, such as proteins, an effect called macromolecular crowding occurs and the cytosol does not act as an ideal solution. This crowding effect alters how the components of the cytosol interact with each other.
Organelles
Organelles (literally "little organs") are usually membrane-bound structures inside the cell that have specific functions. Some major organelles that are suspended in the cytosol are the mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, vacuoles, lysosomes, and in plant cells, chloroplasts.
Cytoplasmic inclusions
The inclusions are small particles of insoluble substances suspended in the cytosol. A huge range of inclusions exist in different cell types, and range from crystals of calcium oxalate or silicon dioxide in plants, to granules of energy-storage materials such as starch, glycogen, or polyhydroxybutyrate. A particularly widespread example are lipid droplets, which are spherical droplets composed of lipids and proteins that are used in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes as a way of storing lipids such as fatty acids and sterols. Lipid droplets make up much of the volume of adipocytes, which are specialized lipid-storage cells, but they are also found in a range of other cell types.
Interesting factas about Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless.
- Rudolf von Kölliker was the first to introduce the term 'cytoplasm' in 1863, originally as a synonym for protoplasm, but later it has come to mean the cell substance and organelles outside the nucleus.
- Many cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, photosynthesis, and processes such as cell division.
See also
 In Spanish: Citoplasma para niños
In Spanish: Citoplasma para niños

