Tweed New Haven Airport facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Tweed-New Haven Regional Airport
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Owner | City of New Haven | ||||||||||
| Operator | Tweed-New Haven Regional Airport Authority | ||||||||||
| Serves | New Haven, Connecticut | ||||||||||
| Location | New Haven County | ||||||||||
| Opened | August 29, 1931 | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 12 ft / 4 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°15′50″N 072°53′12″W / 41.26389°N 72.88667°W | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
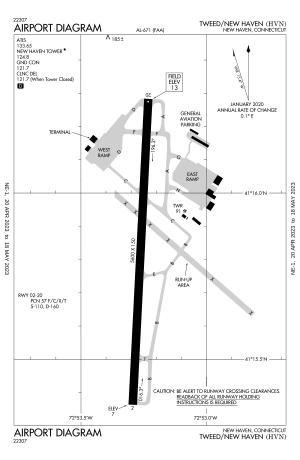 FAA airport diagram |
|||||||||||
| Runway | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Statistics (12 months ending August 2022 except where noted) | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
Sources: FAA, BTS
|
|||||||||||
Tweed-New Haven Regional Airport (IATA: HVN, ICAO: KHVN, FAA LID: HVN) is a public airport located three miles southeast of downtown New Haven, in New Haven County, Connecticut, United States. The airport is partly located in the City of New Haven, which owns the airport, and partly in the town of East Haven.
Tweed is one of two airports with regularly scheduled commercial service in Connecticut, the other being Bradley International Airport in Windsor Locks.
It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a non-hub primary commercial service facility.
Contents
History
Historical airline service
Ground-breaking ceremonies for the new airport occurred on November 11, 1929. The facility was later dedicated and opened for traffic on August 29, 1931, as the New Haven Municipal Airport. In 1961 it was renamed in honor of John H. "Jack" Tweed, its first airport manager. The first airline to serve New Haven was Li-Con Airways, Inc., (Long Island-Connecticut Airways) of Islip, Long Island, New York. That carrier commenced service on November 10, 1933, and provided passenger and airmail service until July 1934. In the fall of 1934, American Airlines began serving New Haven as a stop on flights between New York and Boston and continued service until 1960. The American service was then replaced by Allegheny Airlines and Allegheny Commuter (with the latter being operated by commuter air carriers Suburban Airlines and Pennsylvania Airlines). Allegheny operated British Aircraft Corporation BAC One-Eleven jets into Tweed in the mid-1970s. Eastern Airlines initiated service in 1948 and then left in 1970 due to legal challenges pertaining to a runway extension. Eastern returned briefly from 1972 to 1974 with Boeing 727 and McDonnell Douglas DC-9-30 "Whisperjet" service nonstop to Baltimore-Washington (BWI), Washington-National (DCA) and Boston. The carrier also offered one-stop service to Miami (MIA) and Atlanta (ATL).
1970s and 1980s
Fixed base operator (FBO) New Haven Airways started scheduled flights in 1978 and became New Haven's hometown airline, NewAir, in 1980. The airline operated flights to New York's JFK and LaGuardia Airports, Philadelphia, Baltimore/Washington International, and Washington National Airports, with de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter, Embraer EMB-110 Bandeirante and Short 360 commuter turboprop aircraft. NewAir ended all service in 1985.
Competing was Pilgrim Airlines based at Groton–New London, to New York–JFK and LaGuardia, Boston, Washington (DCA) on de Havilland Canada Twin Otters and Fokker F27 turbprops. By the mid-1980s the two airlines merged and were then purchased by Hartford-based Business Express Airlines, which initially flew only from Brainard Airport to Boston and Philadelphia. Business Express established a code-sharing relationship with Delta Air Lines and became a Delta Connection feeder airline in 1985.
In 1987 Hyannis-based Provincetown-Boston Airlines (PBA), a commuter airline for PeoplExpress Airlines (which was subsequently merged into Continental Airlines), began flights to New Haven. PBA operating as Continental Express flew Embraer EMB-110s from Tweed to Continental's hub at Newark and also to Hyannis and Nantucket, Massachusetts.
USAir Express (operated by commuter air carriers PSA, Piedmont, Allegheny) flew to Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, and Washington, DC area airports, utilizing Shorts 360, Dash-8 100/300, Dornier 328 and Beechcraft 1900 turboprop aircraft.
Jet flights from New Haven to Chicago O'Hare Airport started in 1985–86, initially on Air Wisconsin's BAe-146s operating code sharing service as "United Express” on behalf of United Airlines. From 1991 to 1996, United Airlines Boeing 737-300s and 737-500s flew non-stop to O'Hare. Tweed was also served by Atlantic Coast Airlines operating code sharing service as United Express flying Embraer EMB-120 Brasilia turboprops to Washington Dulles Airport.
Continental Express (flown by PBA) service continued with Beechcraft 1900 and ATR 42 turboprops, while Business Express flights were operated with Saab 340 and Beechcraft 1900 turboprops.
Other small air carriers serving New Haven over the years include Ocean Airlines, Astec Air East, East Hampton Aire, Trans International Express, TW Express operated by Pocono Airlines on behalf of Trans World Airlines (TWA), and Northwest Airlink operated by Precision Airlines and Northeast Express Regional Airlines on behalf of Northwest Airlines.
1990s
By the late 1990s service began to decline to the airport. Business Express service ended, as it put its Saab-340s out of service after its acquisition by AMR Corporation. Continental Express flights ended in 1994, returned in 1995, and then left again on December 17, 1997.
21st century
Comair (Delta Connection) began service to HVN in 2004 with three daily flights to Cincinnati-Northern Kentucky International Airport using CRJ-200 aircraft. The airline ceased operations at HVN in January 2006.
Pan Am Clipper Connection, operated by Boston-Maine Airways, began non-stop flights to Baltimore-Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Hanscom Field, and Pease International Airport on March 8, 2007 using 19-seat Jetstream 31 aircraft. Service ended on July 30, 2007.
This left US Airways Express (Piedmont) as the only airline at Tweed, which in 2015 became American Eagle.
American Eagle was the only airline serving New Haven year-round. As of November 29, 2017, PSA replaced Piedmont's Dash 8-100 turboprop service with three daily round trips to and from Philadelphia on Canadair CRJ-200, Canadair CRJ-700 and occasionally Canadair CRJ-900 regional jets. Weekly flights to Charlotte Douglas International Airport started on December 22, 2018. Service by Republic Airways to Philadelphia and flying the Embraer E-175 commenced on May 3, 2019. On September 9, 2020, all service was shifted to Charlotte then subsequently canceled one month later on October 7, 2020. American Eagle service resumed on January 5, 2021, after a renewal of the government-subsidized CARES Act created by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Service was shifted back to Philadelphia with one daily flight; however, all service ended once again on September 30, 2021.
United Airlines connects to New Haven's Union Station in downtown New Haven via Amtrak train to/from Newark Liberty International Airport (IATA: EWR); the airport code for New Haven, in this case, is (IATA: ZVE), but United does not fly to Tweed.
Today, the airport is operated by AFCO AvPorts of Dulles, Virginia, under contract with the Tweed-New Haven Regional Airport Authority.
Public transit to the airport is available on Connecticut Transit's 206 route.
On April 18, 2019, Shoreline Aviation announced a merger with Cape Air. This popular New Haven-based seaplane service is expected to continue connecting HVN with the 23rd Street Seaplane Base in New York City. The merger could also provide future connection opportunities within Cape Air/Nantucket Airline's New England service area.
On June 14, 2019, Southern Airways Express, a Florida-based-Part 135 commuter carrier, began seasonal nonstop service between Tweed and Nantucket, Massachusetts.
On May 6, 2021, Houston-based low-cost startup Avelo Airlines announced that it would be opening its first East Coast base at New Haven Tweed. The airline operates a fleet of Boeing 737-700 aircraft and initial routes from Tweed would be to Fort Lauderdale, Fort Myers, Orlando, and Tampa beginning on November 3, 2021. Before service even started, two more routes were announced to Sarasota and West Palm Beach. Service began as planned on November 3 with the first flight departing New Haven to Orlando. By the start of 2023, service had been expanded to 14 cities.
Facilities and aircraft
Tweed-New Haven Airport covers 394 acres (159 ha) at an elevation of 12 feet (4 m) above mean sea level. It has one asphalt runway: 2/20 is 5,600 by 150 feet (1,707 x 46 m). The airport previously had a crosswind runway, 14/32, which was decommissioned in 2015.
For the 12-month period ending May 31, 2021, the airport served 36,029 aircraft operations, averaging 99 per day: 92% general aviation, 6% air taxi, 1% scheduled commercial, and <1% military. In November 2022, 63 aircraft were then based at this airport: 46 single-engine, 4 multi-engine, and 13 jet.
General aviation operations at the airport are handled by the Fixed-Base Operator, Robinson Aviation, Inc, which has been providing FBO services at the airport since 1989. Services offered include on-site maintenance, flight training and aircraft rental via New Haven Aviation Center, in addition to normal ground handling, fueling, and concierge services. General aviation accounts for the majority of traffic at the airport, catering to corporate, charter, and private-use aircraft of all sizes.
The Connecticut Wing Civil Air Patrol 73rd Minuteman Squadron (NER-CT-073) operates out of the airport.
Planned expansion and opposition
The future of the airport has been the subject of disagreement between the City of New Haven and the Town of East Haven. New Haven has advocated airport runway expansion, which would be required to attract more commercial air service and larger planes. Some groups of local residents have historically been opposed, saying that expansion would negatively affect the local environment and health of New Haven and East Haven residents.
In 2002, the FAA and the State of Connecticut had approved the airport's layout plan which specified the installation of safety overruns and extending the length of Tweed's main runway 02–20. In 2007, the FAA and the State of Connecticut approved the addition of safety overruns to Tweed's main runway. The City of New Haven issued the wetlands and building permits for the project, but officials in East Haven voted to reject the upgrade proposal and deny permits for work on the East Haven (North) side; the Airport Authority and the City of New Haven filed a lawsuit against the Town of East Haven to allow work on the north overrun, and won.
Since the lawsuit, the Airport Authority has completed the work for the $25 million safety overruns on the New Haven (south) side of the airport, as well as the East Haven (north) side.
On March 16, 2009, New Haven and East Haven announced that an agreement had been reached, keeping the main runway at 5,600 feet (1,700 m), with all obstructions in the approach zones to be removed. Departures are to be capped at 30 per day, with a passenger cap of 180,000 boardings per year.
In July 2014, the Tweed New Haven Airport Authority and the City of New Haven sought federal grant money as a part of the Small Community Air Service Development Program. Language within this air service proposal described the airport's hope to lengthen the main runway past 5,600 feet (1,700 m). In the same month, the airport also sought an increase in annually-appropriated State of Connecticut funds, specifically to pave the runway safety areas in order to expand the length of the runway. This legislation was not enacted and federal money for air service development was not granted. In 2015, Mayor Toni Harp of New Haven and Rep. Rosa DeLauro wrote a joint letter to residents pledging their support for runway expansion.
Opposition to the airport runway expansion is strong among some local residents, resulting in a small grassroots campaign. Tensions flared up at May 20, 2015 and May 21, 2015 community meetings. East Haven voters and Mayor Joseph Maturo still oppose Tweed expansion proposals.
In November 2015, the Airport Authority's board of directors voted to sue the State of Connecticut in Federal court.
Tim Larson, former Executive Director and State Senator for East Hartford, described Tweed as "an airport at a critical juncture. Commercial carriers are interested in servicing the Southern Connecticut market but will not consider coming to Tweed until the runway is lengthened." He added that "American (formerly US Airways), may discontinue our existing service when in the next few years they replace the current Dash-8 aircraft with planes that require a longer runway." Activist residents responded with a new effort against the expansion and a reporting app for noise, health, and quality of life complaints. East Haven Mayor Maturo described the lawsuit as "foolish".
In July 2019, the 2nd Circuit Court of Appeals ruled in favor of Tweed New Haven Airport. In a unanimous opinion, the court ruled that the state statute limiting the length of the runway is preempted by federal law, and is therefore invalid.
In December 2019, Connecticut Attorney General William Tong submitted an appeal to the Supreme Court of the United States seeking a challenge to the runway expansion.
On March 23, 2020, the Supreme Court of the United States declined to hear the State of Connecticut's appeal to the proposed runway expansion. Having exhausted all legal options, the state can no longer prevent the airport from expanding its runway and adding additional services.
On May 6, 2021, Avelo Airlines announced that their new East Coast hub would be located at Tweed and would hire 100 new employees to be based in New Haven. Avelo Airlines announced that flights would begin in the third quarter of 2021. It was also announced that Avports would build a new terminal on the East Haven side of the airport in addition to expanding the length of the runway. Service began with flights to four destinations in Florida, but it quickly expanded to 14 destinations in eight states. During Avelo's first full year of service, over 340,000 enplanements were recorded, an all-time record for the airport.
Airline and destinations
| Airlines | Destinations | Refs |
|---|---|---|
| Avelo Airlines | Baltimore, Charleston (SC), Daytona Beach, Fort Lauderdale, Fort Myers, Greenville/Spartanburg, Melbourne/Orlando, Myrtle Beach, Nashville, Orlando, Raleigh/Durham, San Juan (begins November 15, 2023), Sarasota, Savannah, Tampa, West Palm Beach, Wilmington (NC) Seasonal: Chicago–Midway |
Statistics
Enplanements
| Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 | 44,883 | 2000 | 38,159 | 2001 | 38,766 | 2002 | 21,904 |
| 2003 | 15,446 | 2004 | 39,739 | 2005 | 65,142 | 2006 | 38,144 |
| 2007 | 36,637 | 2008 | 33,988 | 2009 | 33,000 | 2010 | 35,854 |
| 2011 | 40,074 | 2012 | 36,975 | 2013 | 37,434 | 2014 | 33,625 |
| 2015 | 30,955 | 2016 | 27,911 | 2017 | 28,662 | 2018 | 39,030 |
| 2019 | 50,355 | 2020 | 11,370 | 2021 | 29,560 | 2022 | 372,000 |
Top destinations
| Rank | Airport | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94,000 | Avelo | |
| 2 | 48,000 | Avelo | |
| 3 | 45,000 | Avelo | |
| 4 | 43,000 | Avelo | |
| 5 | 43,000 | Avelo | |
| 6 | 29,000 | Avelo | |
| 7 | 22,000 | Avelo | |
| 8 | 20,000 | Avelo | |
| 9 | 20,000 | Avelo | |
| 10 | 14,000 | Avelo |
Accidents and incidents
- On March 1, 1958, an American Airlines Convair CV-240-O with eight passengers destined for Bridgeport Airport crashed on the runway after the landing gear was retracted before the aircraft had lifted off. The plane landed on its belly and a small engine fire occurred. There were no injuries.
- On June 7, 1971, an Allegheny Airlines Convair 580 with 30 passengers arriving from Groton-New London Airport crashed, striking cottages 4,890 feet (1,490 m) from the runway. 28 occupants died. It was blamed on pilot error.
- On January 7, 2011, a Bombardier Dash 8-100, operating as Piedmont Airlines flight 4507 from Philadelphia International Airport to New Haven was struck by lightning over the Long Island Sound. The captain reported electrical problems and diverted safely to Long Island Macarthur Airport due to better weather. The flight carried 33 passengers who were bused to New Haven.
- On August 9, 2013, a Rockwell International Turbo Commander 690B from Teterboro Airport in New Jersey crashed into two houses in an East Haven residential neighborhood while on approach to this airport. The impact and the resulting fires destroyed both houses. The incident resulted in the deaths of both people on the plane (the 54-year-old pilot Bill Henningsgaard and his 17-year-old son Maxwell) and two children in one of the homes (13-year-old Sade Brantley and her 1-year-old sister Madisyn Mitchell).
- On February 22, 2017, a single-engine Piper PA-38-112, which was operated by the Connecticut Flight Academy, crashed southeast of Runway 2 in a swamp. This is the second deadliest crash for the flight academy. The student pilot was killed on impact, the flight instructor was listed in critical condition. Eyewitnesses reported seeing the plane nosedive prior to crashing. The NTSB wrapped up its investigation and published a final report on the accident on February 12, 2018. A plastic valve inside the fuel selector was found to have failed in such a position as to restrict fuel flow to the engine, resulting in a total loss of engine power due to fuel starvation. Final blame was shared between the flight school, whom the NTSB said failed to properly address progressive wear and binding of the part, as well as the flight instructor's exceeding the critical angle of attack for the plane while attempting an emergency return to the airport, resulting in an aerodynamic stall/spin.
- On May 3, 2020, at about 3:30 pm, a large brush fire broke out on airport property between Dean Street and Runway 02/20. The fire was extinguished in a few hours by New Haven Fire Department. No injuries were reported and no aircraft or buildings were reported damaged. The incident was not linked to any aircraft operations.
- On June 30, 2022, at about 5:20 pm, a single-engine prop plane headed from Florida to Massachusetts crashed into the Quinnipiac River after the plane began to experience some engine troubles over New Haven. The two people on board radioed into Tweed New Haven Airport alerting them to the engine troubles. Tweed Airport personnel advised the pilot to attempt to make it to the airport to land the plane. The pilot stated that he would not make it and would ditch into the river. Both persons and a dog were rescued thanks to nearby boaters and bystanders at the Quinnipiac Marina. Fire crews along with other partners were able to safely pull the plane out of the water. The incident is being investigated by the NTSB and FAA.
See also
 In Spanish: Aeropuerto Regional Tweed-New Haven para niños
In Spanish: Aeropuerto Regional Tweed-New Haven para niños
- Hartford–Brainard Airport (HFD)
- List of airports in Connecticut
- Westover Metropolitan Airport (CEF) – previously marketed by Skybus Airlines as "Hartford (Chicopee, MA)"; however, due to the collapse of Skybus Airlines in April 2008, the passenger terminal is currently empty.




