Jet aircraft facts for kids
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by jet engines (jet propulsion).
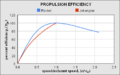
Whereas the engines in propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much lower speeds and altitudes, jet engines and aircraft achieve maximum efficiency (see specific impulse) at speeds close to or even well above the speed of sound. Jet aircraft generally cruise at faster than about Mach 0.8 (609 mph, 981 km/h or 273 m/s) at altitudes around 10,000–15,000 metres (33,000–49,000 ft) or more.
Frank Whittle, an English inventor and RAF officer, developed the concept of the jet engine in 1928, and Hans von Ohain in Germany developed the concept independently in the early 1930s. He wrote in February 1936 to Ernst Heinkel, who led the construction of the world's first turbojet aircraft and jet plane Heinkel He 178.
Rocket-powered jet aircraft were pioneered in Germany. The first aircraft to fly under rocket power was the Lippisch Ente, in 1928. The Ente had previously been flown as a glider. The next year, in 1929, the Opel RAK.1 became the first purpose-built rocket plane to fly.
Images for kids
-
McDonnell Douglas DC-10 of Continental Airlines is an example of a Trijet configuration
-
The Concorde was the longest running commercial SST providing service from 1976 to 2003
-
The Sikorsky S-69 was a compound helicopter with auxiliary turbojets
-
The Lockheed SR-71 was one of the fastest jet flying at Mach 3.35 (3,661 km/h (2,275 mph)
See also
 In Spanish: Avión de reacción para niños
In Spanish: Avión de reacción para niños